




An Overview of Class 11 Chemistry Determine The Ph Of Solutions Of Some Salts Using A Paper Or Universal Indicator Experiment
Soren Peder Lauritz Sorensen, a Danish chemist, was first introduced to pH. Based on the concentration of hydrogen ions, the pH value varies. The solution where hydrogen ions are rich is the acidic solution while basic solutions are poor in hydrogen ions. The substance that generates hydrogen ions when dissolved in water is known as acids. Bases generate hydroxyl ions when dissolved in water.
Table of Content
Aim
Apparatus Required
Theory
Procedure
Observation
Result
Precautions
Lab Manual Questions
Viva Questions
Practical Based Questions
Aim
To determine the pH of solutions of some salts using pH paper or a universal indicator.
Apparatus Required
Test tubes
Measuring Cylinder
Glass rod
pH paper
Universal indicator solution
0.1 M and 0.01 M solutions of CH3COONa, Na2CO3 , FeCl3 , BaCl2, NH4Cl, NaCl, salts.
Theory
In the pH paper method, the pH paper is dipped in a specific solution, and the change of colour is observed.
Then the change of colour is compared to the colour chart and determines the pH of the solution.
A universal indicator is a mixture of various indicators and shows a range of colours depending on the pH of the solution.
It comes in a liquid solution of ethanol. A universal indicator is constituted of a solution of several compounds.
Thymol blue, methyl red, bromothymol blue, phenolphthalein etc. are the components of universal indicators.
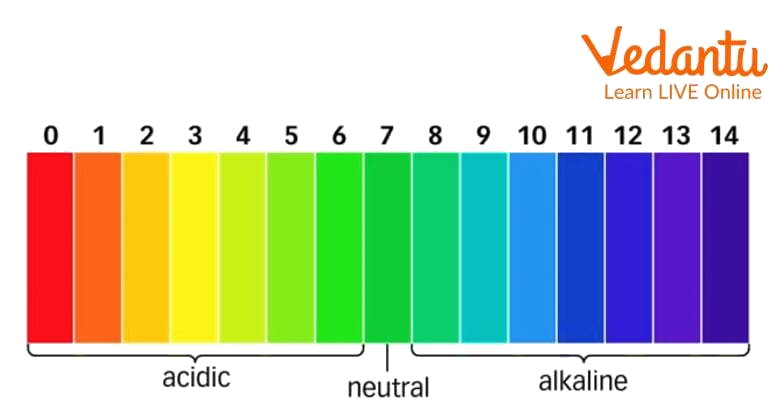
pH scale
Procedure
Using pH Paper:
Take a strip of pH paper.
Next, put 1-2 drops of CH3COONa (0.1M) salt solution on it with the help of a glass rod.
Observe the colour of the pH paper.
Now compare the colour of the pH paper strip to the standard pH chart.
Note down the value of the pH of the tested samples.
Repeat the process with different salt solutions and record the observations.
Using a Universal pH Indicator
Take some clean and dry test tubes.
Make sure that 5 ml of each salt solution should be transferred to the clean test tubes with the help of a measuring cylinder.
Add 3-4 drops of a universal indicator in each solution with a dropper and mix it thoroughly.
Observe the colour of each solution and compare it with the chart that presents in the bottle.
Note down the value of the tested samples.
Observation
Results
The solutions of CH3COONa, FeCl3 and NH4Cl have values less than 7 and hence, they are acidic in nature.
The solutions of Na2CO3 have pH value of 11.8, hence, it is basic in nature.
The pH of common salt and BaCl2 are 7.
Precautions
Test tubes should be properly cleaned and dry.
Avoid using the same dropper for the transfer of salt solutions.
The universal indicator should be equal in quantity for all the samples.
pH paper should be clean and away from fumes.
Observe the colour of the solution that appears with the standard pH chart.
Lab Manual Questions
1. What are strong acids?
Ans: The acids that dissociate completely and produce H+ ions are known as strong acids. For example, HCl, HNO3 and H2SO4.
2. How is pH paper made?
Ans: A blotting paper is dipped in a universal indicator. When the paper absorbs the indicators, it is allowed to dry.
3. What is the pH scale?
Ans: The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14 and is used to measure the strength of acids and bases.
4. How to measure pH?
Ans: The pH of a solution can be determined using an instrument like a pH metre or various indicators which change their colour accordingly depending upon the nature of the test solution.
Viva Questions
1. Name the scientist who has introduced pH.
Ans: Soren Peder Lauritz Sorensen, a Danish chemist, first introduced the concept of pH.
2. What do you understand the pH of a solution means?
Ans: pH of the solution means the amount of H+ ions present in a given solution.
3. What will be the colour of the pH paper if the pH value is 7?
Ans: The colour of the pH paper will be green if the pH value is 7.
4. What is an indicator?
Ans: It is a chemical that changes its colour when it comes in contact with an acid or base.
5. Which method of measuring pH is more accurate?
Ans: In comparison to others, the pH metre gives accurate results.
6. What will be the colour of the pH paper when a common salt solution is added to it?
Ans: When common salt dissolves in water, it gives a neutral solution and, as a result, the colour of the pH paper remains green.
7. What will be the colour of the pH paper when the NH4Cl solution is added to it?
Ans: As the NH4Cl solution is acidic, it turns the pH paper to orange colour.
8. What will be the colour of pH paper if the solution is weak alkaline?
Ans: The colour of the pH paper turns blue if the solution is weak alkaline.
9. What is the common name for sodium chloride?
Ans: Sodium chloride is commonly known as common salt or table salt.
10. Give examples of strong bases.
Ans: Strong bases are NaOH, KOH, CsOH etc.
Practical Based Questions (MCQs)
Which of the following is a component of a universal indicator?
Methyl red
Safranin
Thymol blue
Both A & C
Ans: Both A & C
Which of the following turns the pH paper green?
Milk of magnesia
Baking soda
Oxalic acid solution
NaCl solution
Ans: NaCl solution
Which one of the following is not required to find the pH of a solution?
pH paper
NaCl
Universal indicator
Standard pH value chart
Ans: NaCl
If the pH of the solution changes from 6 to 4, the solution becomes
Less basic
Less acidic
More acidic
Neutral
Ans: More acidic
If the pH paper colour is obtained orange on putting a drop of solution, the solution is
Acidic
Highly acidic
Basic
Highly basic
Ans: Acidic
The two colours seen on the extreme ends of the pH chart are
Red and blue
Red and green
Green and blue
Orange and green.
Ans: Red and blue
The colours obtained on a pH paper for highly acidic, basic and neutral solutions, respectively, are
Blue, orange, green
Yellow, blue, green
Red, blue, green
Red, green and blue
Ans: Red, blue, and green
Which one of the following solutions is used to test the pH of a sample?
Blue litmus solution
Red litmus solution
Universal indicator solution
A mixture of red and blue litmus solution
Ans: Universal indicator solution
H2SO4 is a____acid and weak____
Strong, base
Alkaline, base
Weak, alkaline
Strong, acidic
Ans: Strong, base
HCl donates_____H+ ions and Sulphuric acids donates_____H+ ions.
1, 2
2,1
1,1
2,2
Ans: 1,2
Conclusion
From the above experiment, we conclude that pH helps us understand the acidity or basicity of a solution. Understanding and knowing the pH of any chemical is of paramount importance, as pH is an important parameter for various life processes occurring in organisms. When the pH of a solution is below 7, then such solutions are acidic and show colours such as red, yellow, orange etc. If the pH of a solution is above 7, then such solutions are basic and show blue, dark blue and violet colourations. If the pH is 7 and the colour of the solution/pH paper is green, then it is a neutral solution.
FAQs on Class 11 Chemistry Determine The Ph Of Solutions Of Some Salts Using A Paper Or Universal Indicator Experiment
1. Why is the pH of 0.1M NaCl solution neutral?
Sodium chloride is a salt formed due to the reaction of strong base NaOH and strong acid HCl. The NaOH and HCl react with each other as a result, a neutral salt is produced.
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
Since NaCl is neutral, it does not affect the [H+] and [OH–]in water and its concentration does not change the pH of its solution. So, pH of NaCl is 7 and remains neutral.
2. What is phenolphthalein?
Phenolphthalein, an organic compound with the chemical formula C20H14O4, is a weak acid which can be used as an indicator for acid-base titrations. In acidic solutions, the compound is colourless. It is pinkish in simple solutions (with the transition occurring around pH 9).
3. What is BaCl2?
Barium Chloride is an inorganic salt. It is made up of barium cations and chloride anions. The BaCl2 is used in the purification of brine solutions that are used in caustic chlorine plants.
























