




An Overview of Class 11 Chemistry Determination Of Boiling Point Experiment
The boiling point is a physical change in the state of any compound. For example: When we boil water, it changes into water vapours, i.e., steam. The boiling point is a specific temperature at which that liquid converts into a gaseous state. Water boils at 100℃; it converts into gaseous form at 1 atmospheric pressure. It has many uses in our daily life.
A pressure cooker works on the principle of boiling point. In a pressure cooker, food cooks faster due to the increase in the pressure; the boiling point of water also increases around 121oC.
Another example is antifreeze in car radiators. In car radiators, the hot weather combines with a hot engine and elevates the temperature of the water in the radiator, which can damage the engine. Antifreeze has a high boiling point, which protects the engine from overheating.
Table of Content
Aim
Apparatus Required
Theory
Procedure
Determination of Boiling point of Organic Compounds
Observation
Result
Precautions
Aim
Determination of the boiling points of the organic compounds (Benzene, Benzaldehyde, Butane, Diethyl ether, Butanol, n-pentane, neopentane, Pentene, Heptene and Octene) through experiment.
Apparatus Required
A Glass beaker
A test tube
A thermometer
A tripod stand
A burner
A capillary tube
An iron stand with a clamp
A wire gauze
Liquid paraffin
Con. H2SO4
Liquid/ Solid compound
Theory
The boiling point theory says the boiling point is the temperature at which a liquid converts into vapours at a pressure equal to atmospheric pressure.
The boiling point of organic compounds gives essential information about compounds, like their physical properties and structural characteristics.
It is an indicator of the compound's volatility; the compound has a higher boiling point and a lesser rate of volatility.
The boiling point of a liquid depends upon
The strength of the intermolecular force.
Carbon-carbon chain
Branching
The strength of intermolecular forces: The compounds that have no functional group have less dipole-dipole interaction and have low boiling points than the compound having a functional group.
Carbon-Carbon Chain effect on boiling Point: As the length of the carbon chain increases, the compound's boiling point also increases.
Effect of Branching on Boiling Point: Branching in the compound decreases the boiling points as the surface area of the compound increases, and the Vander Waal dispersion also decreases. Vander Waal interaction is directly proportional to the surface area of the compound.
The order of boiling points in the organic compound is like this;
(The intermolecular forces in ionic bond> hydrogen Bonding> Dipole-dipole interaction> Vander-Waals forces)
Procedure
Here is the procedure for the boiling point determination experiment for organic compounds like benzaldehyde and other compounds.
First, set up the boiling point apparatus like a tripod stand, burner, and clamp stand.
Fill the given liquid in the test tube to ⅔ whose boiling has to find.
Fix the test tube with a thermometer with the help of a rubber band.
Now attach the test tube with the clamp of the stand in such a way that the test tube with a thermometer is dipped in the liquid paraffin bath.
Now take a capillary of about 5-6 cm sealed from one end, and then place it in the test tube containing liquid.
Start the burner, heat the paraffin bath, and stir it slowly.
Keep an eye on the thermometer to check the temperature.
The liquid starts boiling, and bubbles are seen escaping liquid from the capillary dipping.
Now note the temperature at which the liquid starts boiling and steam comes out.
Then remove the flame and note the temperature.
Find the mean of the two temperatures, which will be the boiling point of that liquid.
Note: If we are measuring the solid boiling point, we will use con.H2SO4 instead of liquid paraffin.
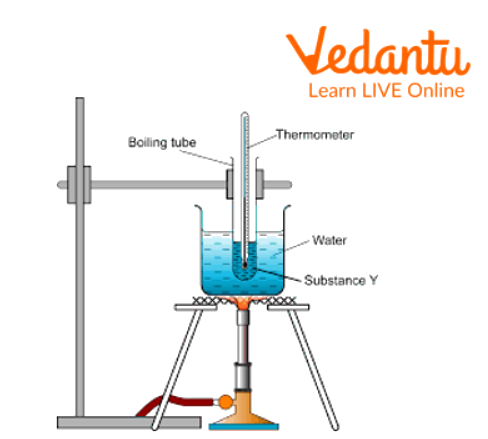
Boiling Point Apparatus Diagram
Determination of Boiling Point of Organic Compounds
First, set up the boiling point apparatus.
Then, take a test tube and fill ⅔ of the benzene in the test tube.
Then tie the test tube with a thermometer and pour them into the beaker containing liquid paraffin, as shown in the boiling point apparatus diagram.
Start heating the beaker, note the temperatures t1 and t2 for benzene, and calculate the mean temperature.
Now, take another test tube and, fill that with benzaldehyde, repeat the same process.
Note the temperatures when benzaldehyde starts boiling t1 and when the vapour comes out the t2, then calculate the mean temperature.
Mean Temperature= \[\dfrac{{{t_1} + {t_2}}}{2}\]
Observation
Here are the boiling point determination experiment readings.
Observation Table 1:
Result
The boiling point of benzene is 78oC and benzaldehyde is 178oC.
The boiling point of butane, di ethyl ether and butanol is -1oC, 36.4oC and 117.7oC.
The boiling point of pentene, heptene, and octene is 36oC, 98.4oC and 125.7oC.
The boiling point of n-pentane and neo-pentane is 36oC and 9.5oC.
Precautions
Perform experiments in presence of a teacher or lab assistant.
Keep the thermometer bulb and the test tube at the same level.
Be conscious while recording temperature to minimize the error and note the readings when the liquid starts bubbling from the lower end of the capillary.
Make sure one end of the capillary is sealed properly.
Keep stirring the paraffin liquid for uniform heating.
Handle the Bunsen burner carefully.
Add boiling chips to the solution to avoid bumping.
Lab Manual Questions
1. What will you learn from this experiment?
Ans. You learn to define the boiling point of different organic and inorganic compounds, and it helps you identify the physical and structural properties of compounds.
2. What are the precautions taken while experimenting to find the boiling point?
Ans. We have to make sure that one end of the capillary is sealed properly. Keep the level of the ignition tube and bulb of the thermometer at the same level. Keep stirring the liquid paraffin for uniform heating.
3. How do remove errors while calculating boiling point?
Ans. To remove errors in the value of the boiling point calculated, we must take a 3% correction in the observed value of the boiling point. Then add this correction to the observed temperature. This is necessary as the boiling point changes due to changes in atmospheric pressure.
(Actual Boiling Point = Observed Boiling Point + 3% of observed Boiling Point)
4. What can we add to a given solution to avoid the bumping of liquid?
Ans. We must add boiling chips to the liquid to avoid bumping the liquid.
Viva Questions
1. Explain the factors that affect the boiling point of an organic compound.
Ans. The boiling point of organic compounds is affected by atmospheric pressure, the strength of the intermolecular forces, branching in the organic compound, and the length of the carbon-carbon chain in hydrocarbons.
2. Define the boiling point theory.
Ans. The boiling point is the temperature at which the vapour pressure of the solution is equal to the vapour pressure of the surroundings.
3. Differentiate between boiling point and melting point.
Ans.
4. The boiling point of a compound indicates what?
Ans. The boiling point of a compound indicates its purity, stability, and volatility of a compound.
5. What is the effect of atmospheric pressure on the boiling point?
Ans. The boiling point of the liquid increases by increasing the atmospheric pressure. The boiling point is lower in mountains and higher on sea surfaces, so the boiling point is low on mountains and high on sea surfaces.
6. Why is the boiling point of water at the sea surface is 100oC more than it is at Mount Everest, 69oC?
Ans. When the atmospheric pressure is higher, the boiling point of the liquid increases, at the sea surface where atmospheric pressure is 1 atm and the atmospheric pressure in mountains is low so the boiling of water also decreases.
7. Which liquid bath is used when the temperature of the compound is more than 100oC?
Ans. The liquid paraffin for liquids and con. H2SO4 is used for a solid boiling point as a bath to find the boiling point.
8. Why is the boiling point of solids more than liquid compounds at room temperature?
Ans. There is no such rule that liquid boils at lower temperatures and solid boils at high temperatures. Solid Lead iodide melts at 402oC and then boils at 954oC. Water is a liquid that boils at 100oC, but some liquids like mercury boil at 357oC while mercury bromide boiling of solid is an example, as it boils at 236oC at room temperature.
9. What happens if a non-volatile liquid is added to the pure liquid?
Ans. The boiling point of the pure liquid increases upon adding a non-volatile liquid.
10. Why do carboxylic acids have a higher boiling point than hydrocarbons?
Ans. The carboxylic acids form intermolecular bonding that stabilizes the compound, while hydrocarbons do not form an intermolecular bond.
Practical Question
1. What is the boiling point of benzene?
78
80
100
None of the above.
Ans. The boiling point of benzene is 78oC.
2. What happens if we add sodium hydroxide to the water?
The boiling point of water increases.
The boiling point of water decreases.
The evaporation rate increases.
The evaporation rate decreases.
Ans. If we add sodium hydroxide to the water, the boiling point of the water increases.
3. While performing the boiling point determination experiment, the ignition tube and bulb of the thermometer were kept in a beaker at?
At the bottom of the beaker
Above the liquid paraffin
Properly dipped in liquid paraffin.
None of the above.
Ans. While performing the boiling point determination experiment, the ignition tube and bulb of the thermometer were kept in a beaker and properly dipped in liquid paraffin.
4. What happens when the atmospheric pressure decreases?
The boiling point of the liquid increases.
The boiling point of the liquid decreases.
The melting point decreases.
None of the above.
Ans. When the atmospheric pressure, decreases, the boiling point of liquid decreases.
5. Boiling of solid is an example of an ________________
Atmospheric pressure is equal to vapour pressure.
Atmospheric pressure is more than vapour pressure.
Atmospheric pressure is lower than vapour pressure.
None of the above.
Ans. The boiling of a solid is an example of atmospheric pressure being equal to vapour pressure.
6. Which compound has the highest boiling point?
Methane
Pentane
Heptane
None
Ans. Heptane is the compound that has the highest boiling point.
7. The boiling point of an impure liquid is higher or lower?
Remains the same as pure liquid.
Lower from the pure liquid.
Higher than pure liquid.
None of the above.
Ans. The boiling point of an impure liquid is higher than pure liquid.
8. The boiling point of a liquid depends upon the_________
The strength of the intermolecular force.
Carbon-hydrogen bond
Molecular Weight
All of the above.
Ans. The boiling point of a liquid depends upon the strength of the intermolecular force and molecular weight.
9. The methods of measuring boiling points?
Fractional method
Thiele Tube Method
Reflux Method
All of the above
Ans. The methods used to measure the boiling points are Thiele Tube Method and the Reflux Method.
10. The vapour pressure depends upon which factors?
Kinetic Energy
Structure of the molecule
Temperature.
Velocity, kinetic energy, and temperature.
Ans. The vapour pressure depends upon velocity, kinetic energy, and temperature.
Conclusion
From the above experiment, we have found the boiling point of benzene is less than benzaldehyde. The boiling point of pentene, heptene and octene increases by increasing the branching in the carbon-carbon chain. In the other group of compound butane, di ethyl ether and butanol the boiling point is increased in the derivative from the pure compound.
FAQs on Class 11 Chemistry Determination Of Boiling Point Experiment
1. What are the most important factors that affect the boiling point of a liquid for the CBSE Class 11 exam?
For the Class 11 Chemistry exam, the key factors influencing a liquid's boiling point are:
- Intermolecular Forces: Stronger forces (like hydrogen bonding) require more energy to overcome, resulting in a higher boiling point.
- Molecular Weight: For similar molecules, as the molecular weight increases, the boiling point generally increases due to stronger van der Waals forces.
- Branching: In isomeric compounds, increased branching leads to a more compact, spherical shape, reducing the surface area and weakening intermolecular forces, which lowers the boiling point.
- External Pressure: The boiling point is the temperature at which vapour pressure equals the external atmospheric pressure. A lower external pressure (e.g., at high altitudes) results in a lower boiling point.
2. What are the key precautions a student must take when determining the boiling point in a chemistry practical?
To ensure accurate results and safety during the boiling point determination experiment, students must follow these precautions:
- Ensure the bulb of the thermometer and the fusion tube are at the same level to record the correct temperature.
- The apparatus should be clamped securely, and the thermometer should not touch the bottom or sides of the beaker.
- Add porcelain pieces or boiling chips to the liquid before heating to ensure smooth boiling and prevent bumping.
- Heat the liquid gently and stir the bath continuously for uniform temperature distribution.
- Keep your face away from the apparatus, as the fumes of some organic compounds can be toxic.
3. Why are porcelain pieces or boiling chips added to the liquid before heating? What happens if they are not used?
Porcelain pieces or boiling chips are added to a liquid before heating to ensure smooth and uniform boiling. Their porous surface provides nucleation sites where bubbles can form evenly. Without them, the liquid can become superheated (heated above its boiling point without boiling). This can lead to a sudden, violent boiling known as 'bumping', which can splash the hot liquid out of the container and cause inaccurate temperature readings.
4. How does the presence of a non-volatile impurity affect the boiling point of a pure liquid?
The presence of a non-volatile impurity in a pure liquid causes an elevation in its boiling point. This happens because the impurity particles occupy some of the liquid's surface area, which lowers the vapour pressure of the solvent at any given temperature. To make the vapour pressure equal to the atmospheric pressure, a higher temperature is required. This principle is a key concept in colligative properties and is crucial for understanding the purity of a substance.
5. For a 3-mark question, what are the essential components to label in the diagram of the apparatus for determining a liquid's boiling point?
For a diagram-based question in the exam, the following components are essential to label correctly:
- Beaker or Thiele's Tube: The container holding the heating bath.
- Liquid Bath: Usually paraffin oil or sulphuric acid for uniform heating.
- Thermometer: Positioned correctly with its bulb near the fusion tube.
- Fusion Tube: A small test tube containing the experimental liquid.
- Capillary Tube: Inverted inside the fusion tube with its sealed end up.
- Stirrer: To ensure even heat distribution in the bath.
- Tripod Stand and Wire Gauze: The support structure for heating.
6. Why is the boiling point of water lower in Shimla than in Mumbai?
This is a classic higher-order thinking question. The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which its vapour pressure equals the surrounding atmospheric pressure. Shimla is at a high altitude, where the atmospheric pressure is significantly lower than at sea level, where Mumbai is located. Because the external pressure is lower in Shimla, the water's vapour pressure needs to reach a lower value to start boiling. This occurs at a temperature below 100°C, which is the boiling point of water at standard sea-level pressure.
7. What is the specific function of the inverted capillary tube in this experiment?
The inverted capillary tube acts as an indicator for the boiling point. As the liquid is heated, air trapped inside the capillary tube expands and escapes as bubbles. When the liquid reaches its boiling point, its vapour fills the capillary tube, and a rapid, continuous stream of bubbles emerges from its lower end. This observation confirms that the vapour pressure of the liquid has become equal to the atmospheric pressure.
8. How can a student confirm that the recorded temperature is the true boiling point of the liquid during the experiment?
A student can confirm the true boiling point by carefully observing the capillary tube. The boiling point is not the temperature when the first bubble appears. The correct boiling point is the temperature recorded when a rapid and continuous stream of bubbles starts escaping from the lower end of the inverted capillary tube. At this moment, the vapour pressure of the liquid has become equal to the external atmospheric pressure, which is the precise definition of the boiling point.
























