
You are standing at a distance of 2 meters from a plane mirror.
A. What is the distance of your image from the mirror?
B. What is the distance between you and your image?
Answer
501.9k+ views
Hint: The laws of reflection state that,
(i) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection $\angle i = \angle r$
(ii) The incident ray, reflected ray and the normal ray lie in the same plane.
Image characteristics in a plane mirror are:
- The image formed is virtual.
- The image formed is of the same size.
- The image is laterally inverted.
- The image is formed at an equal distance from the mirror as of the object.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s visualize the situation
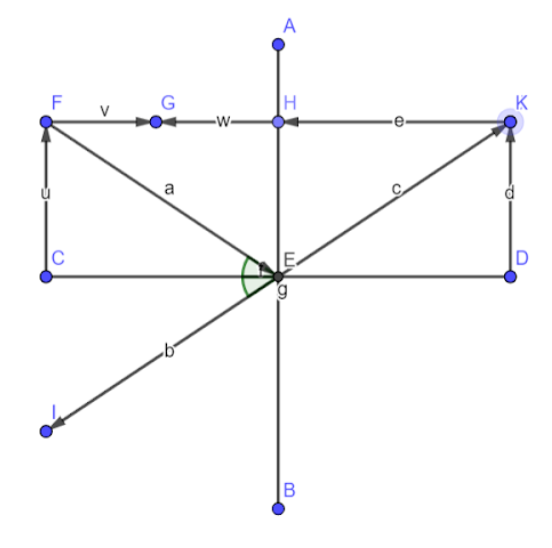
Here the line AB is the plane mirror and the line CD is the normal. When a ray FE is incident on the plane mirror it gets reflected along the path EI making equal angles of incidence and reflection as marked in green.
Consider yourself to be standing at point C where CF represents your height while CE is your distance from the mirror.
From the property of plane mirrors, we can say that CE=ED.
The distance of your image from the mirror is given by ED.
We have just now seen that ED=CE.
Hence
$ED = 2\,m$
So, the distance of your image from the mirror is $2\,m$
Now the distance between you and your image would be CE+ED
Since CE=ED the distance is 2ED
We know that $ED = 2\,m$ and so
The distance between you and your image is $2ED = 2 \times 2$ m
$ \Rightarrow 4\,m$
Note: In a plane mirror, though the image is laterally inverted, it is formed at the same distance as that of the object and has the same size. Any virtual image is formed by the backwards extrapolation of the incident and the reflected ray along the same angle. The angles are always measured from the normal and not from the baseline.
(i) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection $\angle i = \angle r$
(ii) The incident ray, reflected ray and the normal ray lie in the same plane.
Image characteristics in a plane mirror are:
- The image formed is virtual.
- The image formed is of the same size.
- The image is laterally inverted.
- The image is formed at an equal distance from the mirror as of the object.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s visualize the situation

Here the line AB is the plane mirror and the line CD is the normal. When a ray FE is incident on the plane mirror it gets reflected along the path EI making equal angles of incidence and reflection as marked in green.
Consider yourself to be standing at point C where CF represents your height while CE is your distance from the mirror.
From the property of plane mirrors, we can say that CE=ED.
The distance of your image from the mirror is given by ED.
We have just now seen that ED=CE.
Hence
$ED = 2\,m$
So, the distance of your image from the mirror is $2\,m$
Now the distance between you and your image would be CE+ED
Since CE=ED the distance is 2ED
We know that $ED = 2\,m$ and so
The distance between you and your image is $2ED = 2 \times 2$ m
$ \Rightarrow 4\,m$
Note: In a plane mirror, though the image is laterally inverted, it is formed at the same distance as that of the object and has the same size. Any virtual image is formed by the backwards extrapolation of the incident and the reflected ray along the same angle. The angles are always measured from the normal and not from the baseline.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




