
Write the mechanism of the reaction of $HI$ with methoxymethane.
Answer
598.8k+ views
Hint : The given reaction is cleavage of ethers by halogen acids. Here methoxymethane is a symmetric ether. We take equal amounts of hydrogen iodide and methoxymethane to for the production of the methyl alcohol and methyl iodide. In the case of mixed ether means two different alkyl groups react with hydrogen iodide then the formation of alcohol and alkyl iodide depends on the nature of the alkyl group.
Complete step by step solution:
The mechanism of the reaction of hydrogen iodide with methoxymethane involves the following steps.
Step $1$ - Protonation of methoxymethane: We know that methoxymethane is a Lewis base, so when it undergoes protonation it gives oxonium salts.
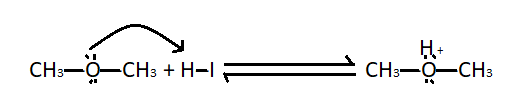
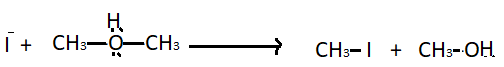
Step $2$ - Nucleophilic attack of iodide ions : The protonated ether undergoes nucleophilic attack of hydrogen iodide. It produces a molecule of methyl iodide and methyl alcohol.
Step $3$- When there is excess of hydrogen iodide in the reaction then reaction is carried out at a high temperature. The methanol formed in the second step starts reacting with another hydrogen iodide molecule and converted into methyl iodide.
First two steps are important. The last step is the informative step of this reaction.
Note: Hence we have learnt about the mechanism of reaction when methoxy methane reacts with hydrogen iodide. methoxymethane is a colourless gaseous ether which possesses medicine like odour. It is used as an aerosol propellant, as a blowing agent for production of some foams. It is fairly soluble in water. The product methyl alcohol is a very essential organic compound of chemistry. It is used in automotive antifreezes, in rocket fuels and cleaning of burning fuels.
Complete step by step solution:
The mechanism of the reaction of hydrogen iodide with methoxymethane involves the following steps.
Step $1$ - Protonation of methoxymethane: We know that methoxymethane is a Lewis base, so when it undergoes protonation it gives oxonium salts.
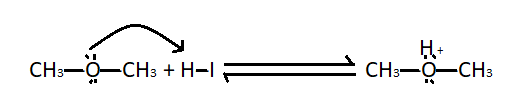
Step $2$ - Nucleophilic attack of iodide ions : The protonated ether undergoes nucleophilic attack of hydrogen iodide. It produces a molecule of methyl iodide and methyl alcohol.

Step $3$- When there is excess of hydrogen iodide in the reaction then reaction is carried out at a high temperature. The methanol formed in the second step starts reacting with another hydrogen iodide molecule and converted into methyl iodide.
First two steps are important. The last step is the informative step of this reaction.
Note: Hence we have learnt about the mechanism of reaction when methoxy methane reacts with hydrogen iodide. methoxymethane is a colourless gaseous ether which possesses medicine like odour. It is used as an aerosol propellant, as a blowing agent for production of some foams. It is fairly soluble in water. The product methyl alcohol is a very essential organic compound of chemistry. It is used in automotive antifreezes, in rocket fuels and cleaning of burning fuels.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




