
Write the mechanism of the following reaction:
\[nBuBr + KCN\xrightarrow{{EtOH - {H_2}O}}nBuCN\]
Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint: Nucleophile is a chemical species that donates its electron pair to form a bond with other atoms and thus, the nucleophile is also called an electron-rich species. When nucleophile undergoes substitution, based on the nature of reactant, it comes under two categories such as Unimolecular Nucleophilic substitution (\[{S_N}^1\]) and Bimolecular Nucleophilic substitution (\[{S_N}^2\]) reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
When n-butyl bromide is reacted to potassium cyanide in presence of ethanol in water, then n-butyl cyanide will be formed. The reaction can be written as,
\[nBuBr + KCN\xrightarrow{{EtOH - {H_2}O}}nBuCN\]
The above reaction is an example of an unimolecular Nucleophilic substitution reaction \[{S_N}^1\]. \[{S_N}^1\] is a two-step process and carbocation will be formed as an intermediate. The n-butyl group is bulky and therefore it won't undergo bimolecular Nucleophilic substitution reaction \[{S_N}^2\]. \[{S_N}^2\] is a single step process and it is affected by the steric effect. The steric effect is the crowding of atoms and it leads to creating disturbance for upcoming atoms.
The mechanism for \[{S_N}^1\] reaction of n-butyl cyanide formation can occur in two steps.
Step-1: Formation of carbocation
The n-butyl bromide will break into n-butyl carbocation and bromide ion. This step is a slow step process and thus, it is a rate-determining step. Here, bromide ion acts as the leaving group. The reaction can be written as,
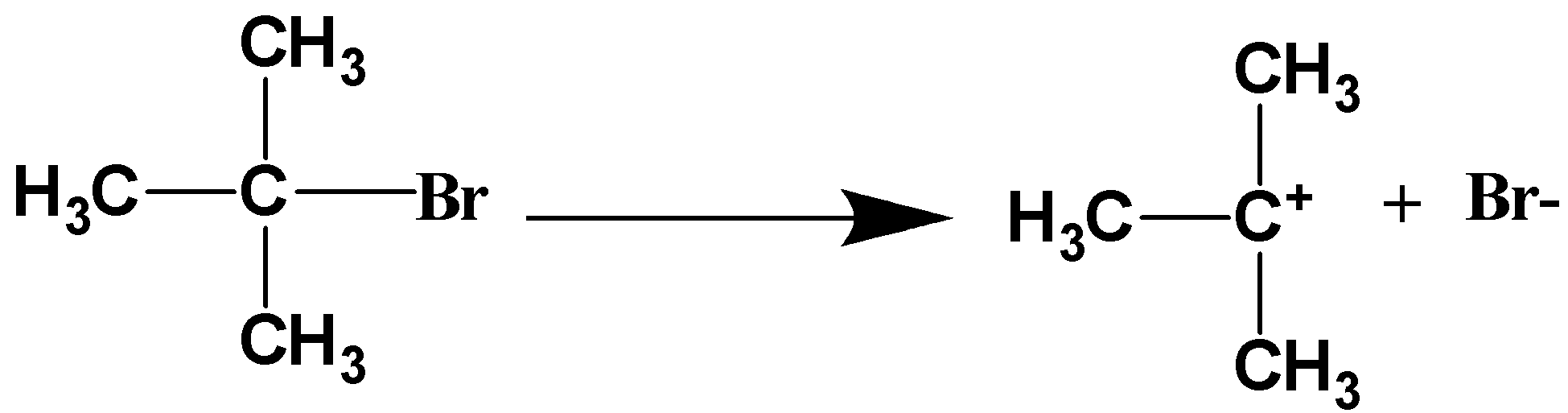
Step-2: Formation of n-butyl cyanide
Cyanide ion acts as a nucleophile. when cyanide ion approaches n-butyl carbocation, then cyanide ion gets substituted and it forms n-butyl cyanide. This step is the fast step process. The reaction can be written as follows,
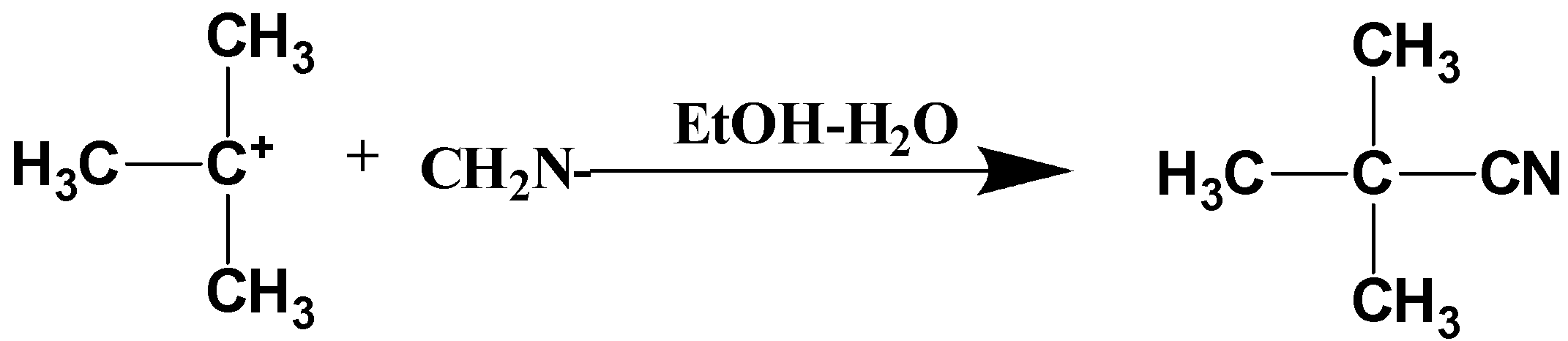
Thus, the above mechanism is the correct approach for the \[{S_N}^1\] reaction.
Note: Carbocation is affected by electronic factors. Since the rate-determining step is carbocation formation, then the electronic factor is one of the important factors in \[{S_N}^1\] reaction. Thus, tertiary alkyl favours \[{S_N}^1\] reaction than secondary alkyl groups.
The order of reactivity for \[{S_N}^1\] reaction can be written as,
Tertiary alkyl> Secondary alkyl> Primary alkyl
Complete step by step answer:
When n-butyl bromide is reacted to potassium cyanide in presence of ethanol in water, then n-butyl cyanide will be formed. The reaction can be written as,
\[nBuBr + KCN\xrightarrow{{EtOH - {H_2}O}}nBuCN\]
The above reaction is an example of an unimolecular Nucleophilic substitution reaction \[{S_N}^1\]. \[{S_N}^1\] is a two-step process and carbocation will be formed as an intermediate. The n-butyl group is bulky and therefore it won't undergo bimolecular Nucleophilic substitution reaction \[{S_N}^2\]. \[{S_N}^2\] is a single step process and it is affected by the steric effect. The steric effect is the crowding of atoms and it leads to creating disturbance for upcoming atoms.
The mechanism for \[{S_N}^1\] reaction of n-butyl cyanide formation can occur in two steps.
Step-1: Formation of carbocation
The n-butyl bromide will break into n-butyl carbocation and bromide ion. This step is a slow step process and thus, it is a rate-determining step. Here, bromide ion acts as the leaving group. The reaction can be written as,

Step-2: Formation of n-butyl cyanide
Cyanide ion acts as a nucleophile. when cyanide ion approaches n-butyl carbocation, then cyanide ion gets substituted and it forms n-butyl cyanide. This step is the fast step process. The reaction can be written as follows,
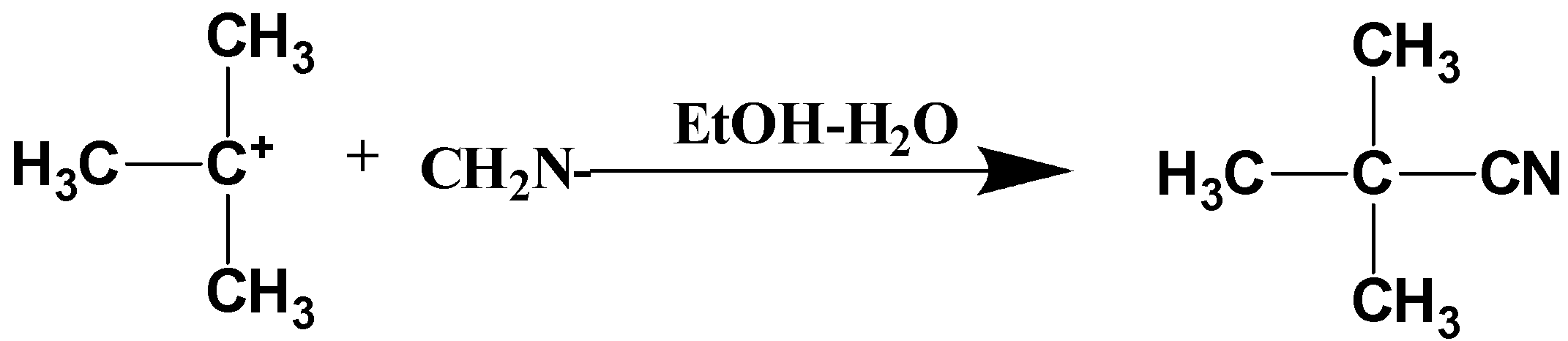
Thus, the above mechanism is the correct approach for the \[{S_N}^1\] reaction.
Note: Carbocation is affected by electronic factors. Since the rate-determining step is carbocation formation, then the electronic factor is one of the important factors in \[{S_N}^1\] reaction. Thus, tertiary alkyl favours \[{S_N}^1\] reaction than secondary alkyl groups.
The order of reactivity for \[{S_N}^1\] reaction can be written as,
Tertiary alkyl> Secondary alkyl> Primary alkyl
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




