
Write the mechanism of Amination.
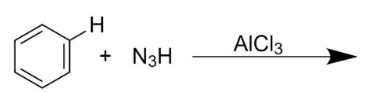
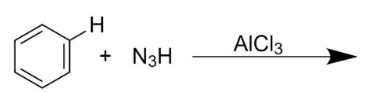
Answer
538.2k+ views
Hint: The process by which an amine group is added to an organic molecule is known as amination. Enzymes that are used as catalysts in the amination reaction are known as aminase. There are different methods of amination like reductive amination, acid-catalyzed hydroamination, Mannich reaction, Ritter reaction, electrophilic amination, hydroamination, etc.
Complete step by step solution:
One of the methods of animation is electrophilic amination reaction. In electrophilic amination reaction, the formation of a C-N bond takes place by reaction between a nucleophilic carbanion and electrophilic nitrogen source.
There are various types of electrophiles that can be used like chloramines, hydrazines, hydroxylamines or oxaziridines. Some reactions may also use imines, azides, azo, or oxime compounds, among others. These electrophiles are mostly amines which are substituted with groups which are electron-withdrawing in nature.
The above amination reaction is a type of an electrophilic amination reaction. It involves benzene $({{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}})$ as the nucleophilic carbon ion and hydrazoic acid $({{N}_{3}}H)$, an azide, as the electrophilic nitrogen source.
Direct electrophilic amination is one of the most promising methods for production of aromatic amines as it is rapid as well as cost-effective. It is also a one-step reaction route for the production of aromatic amines.
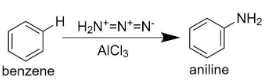
This is the proposed single step reaction mechanism for direction amination of benzene.
Note: It must be noted that the electrophilic nitrogen source used is an azide, hydrazoic acid $({{N}_{3}}H)$, and not ammonia $(N{{H}_{3}})$. Ammonia is used for amination of alcohols in the presence of solid acid catalysts to produce alkyl amines at an industrial level through acid-catalyzed hydroamination method.
Complete step by step solution:
One of the methods of animation is electrophilic amination reaction. In electrophilic amination reaction, the formation of a C-N bond takes place by reaction between a nucleophilic carbanion and electrophilic nitrogen source.
There are various types of electrophiles that can be used like chloramines, hydrazines, hydroxylamines or oxaziridines. Some reactions may also use imines, azides, azo, or oxime compounds, among others. These electrophiles are mostly amines which are substituted with groups which are electron-withdrawing in nature.
The above amination reaction is a type of an electrophilic amination reaction. It involves benzene $({{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}})$ as the nucleophilic carbon ion and hydrazoic acid $({{N}_{3}}H)$, an azide, as the electrophilic nitrogen source.
Direct electrophilic amination is one of the most promising methods for production of aromatic amines as it is rapid as well as cost-effective. It is also a one-step reaction route for the production of aromatic amines.

This is the proposed single step reaction mechanism for direction amination of benzene.
Note: It must be noted that the electrophilic nitrogen source used is an azide, hydrazoic acid $({{N}_{3}}H)$, and not ammonia $(N{{H}_{3}})$. Ammonia is used for amination of alcohols in the presence of solid acid catalysts to produce alkyl amines at an industrial level through acid-catalyzed hydroamination method.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




