
Write structure of D.D.T?
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint:DDT stands for dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane and it is a chemical compound with the formula \[{C_{14}}{H_9}C{l_5}\] . It is also called 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl) ethane, and is a synthetic insecticide which belongs to the family of organic halogen compounds.
Complete answer:
DDT is a colourless, tasteless (at standard conditions for temperature and pressure, STP) and almost odourless organochlorine. DDT is very popularly known for its insecticidal properties. It has been easily formulated in almost every form which includes solutions in petroleum distillates, emulsifiable concentrates, and smoke candles.
The structure of DDT is shown below:
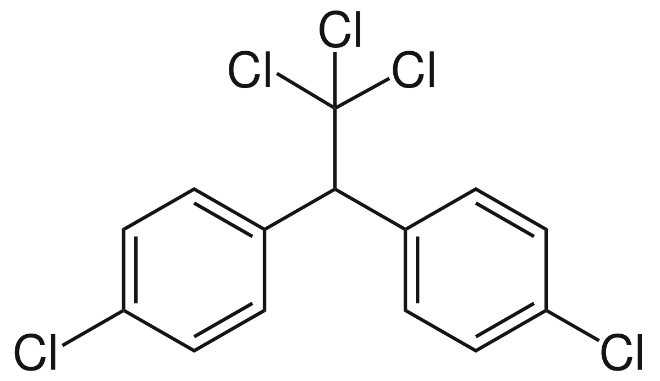
The molar mass of DDT corresponds to 354.48 grams per mole and under the standard conditions, the density of this compound is roughly equal to 1 gram per cubic centimetre. The melting point of this chemical compound is approximately equal to 108.5 degrees Celsius or 381.6 K and boiling point is approximately equal to 260 degrees Celsius or 533 K. DDT is very poorly soluble in water and for all practical purposes, this compound is insoluble in water. The solubility of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane in water corresponds to 25 micrograms per litre.
Note:
DDT is the first chlorinated organic insecticide which was prepared in 1873. The effectiveness of DDT as an insecticide was first discovered by Paul Muller of Geigy Pharmaceuticals in Switzerland. It was largely used after the Second World War to control diseases like malaria and typhus among the civilians and the troops and after the war, DDT was made available for agricultural uses and therefore when it comes to the use of DDT, it has immensely increased over time.
Complete answer:
DDT is a colourless, tasteless (at standard conditions for temperature and pressure, STP) and almost odourless organochlorine. DDT is very popularly known for its insecticidal properties. It has been easily formulated in almost every form which includes solutions in petroleum distillates, emulsifiable concentrates, and smoke candles.
The structure of DDT is shown below:

The molar mass of DDT corresponds to 354.48 grams per mole and under the standard conditions, the density of this compound is roughly equal to 1 gram per cubic centimetre. The melting point of this chemical compound is approximately equal to 108.5 degrees Celsius or 381.6 K and boiling point is approximately equal to 260 degrees Celsius or 533 K. DDT is very poorly soluble in water and for all practical purposes, this compound is insoluble in water. The solubility of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane in water corresponds to 25 micrograms per litre.
Note:
DDT is the first chlorinated organic insecticide which was prepared in 1873. The effectiveness of DDT as an insecticide was first discovered by Paul Muller of Geigy Pharmaceuticals in Switzerland. It was largely used after the Second World War to control diseases like malaria and typhus among the civilians and the troops and after the war, DDT was made available for agricultural uses and therefore when it comes to the use of DDT, it has immensely increased over time.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




