
With a neat, labeled diagram, describe the parts of a typical angiosperm ovule.
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: In angiosperm, there is a presence of the embryo sac and also after the fusion of the male gametes, it may result in an endosperm that ultimately nourishes the offspring.
Complete answer:
Angiosperms of the group of flowering plants have their ovules covered. There is an attachment to the placenta of the overview which is done through this stock which is also called the funicle or funiculus. The hilum is the point of attachment of the funiculus to the structure of the ovule. There is a presence of the outer and inner into comment along with an embryo sac that is covered inside it. The nucellus is the portion outside the embryo sac and inner to the outer and inner integument. The integument is covering the entire nucleus except some of the upper portions which are known to be as the micropyle. The junction of the improvements and the nucellus is known to be as the chalaza and that particular end is known to be as a Chalazal end.
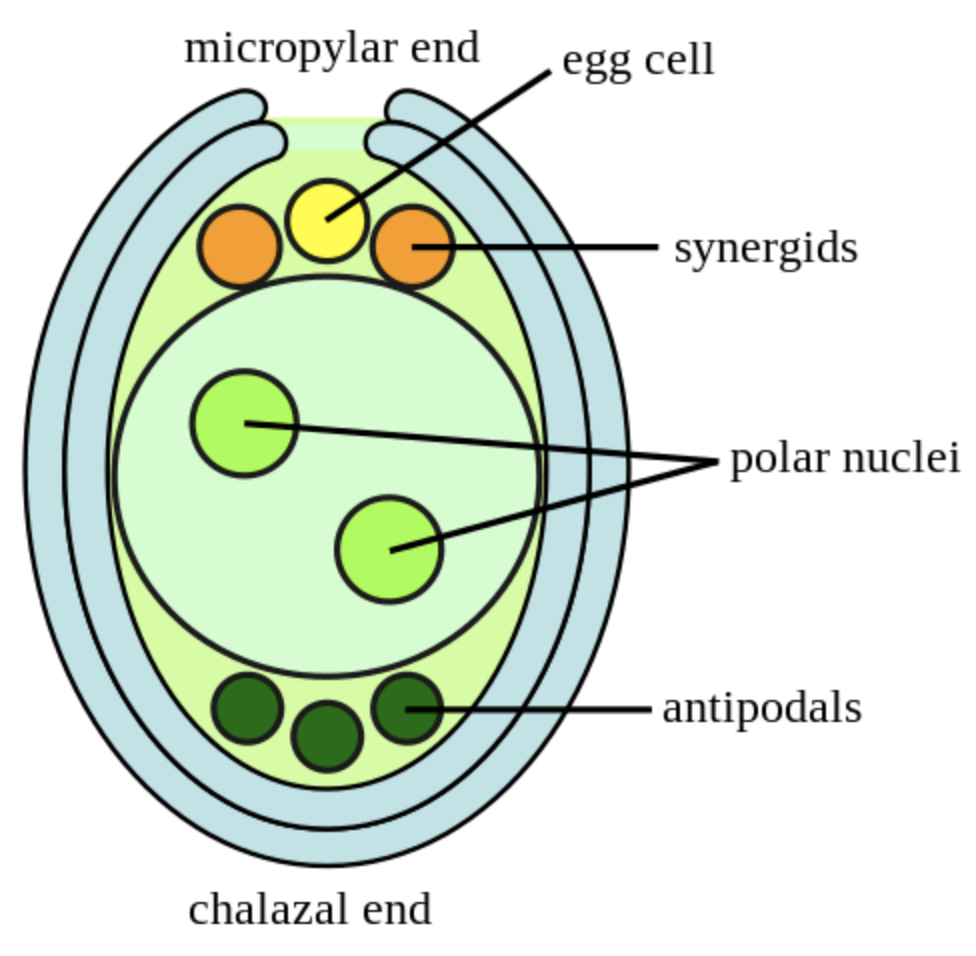
- The male gametes after its fusion with the excels produce zygote and the fusion with the polar nuclei results in the formation of the endosperm which poses as food for the new offspring.
- Inside the ovule in the nucellus there is also a presence of an oval cell at the end of the micropyle which is called the embryo sac or the female gametophyte which ultimately develops after fertilization into the megaspore.
- The inverted ovules are the most common type of ovules that are found in the angiosperms although there is the presence of many types of ovules based upon their position of the attachment to the stalk or the funiculus.
Note:
- The endosperm which is produced is triploid which is the result of the fusion of the sperms with the polar nuclei.
- The ovule where it is attached with the funiculus or the stock, till some distance, forms a structure which is ridge-like in shape and is called the raphe.
Complete answer:
Angiosperms of the group of flowering plants have their ovules covered. There is an attachment to the placenta of the overview which is done through this stock which is also called the funicle or funiculus. The hilum is the point of attachment of the funiculus to the structure of the ovule. There is a presence of the outer and inner into comment along with an embryo sac that is covered inside it. The nucellus is the portion outside the embryo sac and inner to the outer and inner integument. The integument is covering the entire nucleus except some of the upper portions which are known to be as the micropyle. The junction of the improvements and the nucellus is known to be as the chalaza and that particular end is known to be as a Chalazal end.

- The male gametes after its fusion with the excels produce zygote and the fusion with the polar nuclei results in the formation of the endosperm which poses as food for the new offspring.
- Inside the ovule in the nucellus there is also a presence of an oval cell at the end of the micropyle which is called the embryo sac or the female gametophyte which ultimately develops after fertilization into the megaspore.
- The inverted ovules are the most common type of ovules that are found in the angiosperms although there is the presence of many types of ovules based upon their position of the attachment to the stalk or the funiculus.
Note:
- The endosperm which is produced is triploid which is the result of the fusion of the sperms with the polar nuclei.
- The ovule where it is attached with the funiculus or the stock, till some distance, forms a structure which is ridge-like in shape and is called the raphe.
Watch videos on
With a neat, labeled diagram, describe the parts of a typical angiosperm ovule.

Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Class12 NCERT EXERCISE1.4| Class 12 Chapter 1| Kanika Sharma
Subscribe
 Share
Share likes
64 Views
2 years ago
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE



 Watch Video
Watch Video
