
Which one of the following is a vinyl carbocation?
$\left( A \right)$ ${C_6}{H_5} - C{H_2}^ + $
$\left( B \right)$ $C{H_2} = CH - C{H_2}^ + $
$\left( C \right)\;\;C{H_2} = C{H^ + }$
$\left( D \right)\;$ All of the above
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: The vinyl carbocation is a carbocation with the charge on an alkene carbon. Vinylic cationic any disubstituted, trivalent carbon, where the carbon bearing the positive charge is a part of a double bond.
Complete answer:
Vinyl cation is one of the main types of reactive intermediates involving a non-tetrahedrally coordinated atom, and is important to refer to the broad class rather than the ${C^2}{H_3}^ + $ variant alone. The vinyl cation is one among the most sorts of reactive intermediates involving a non tetrahedrally coordinated atom, and is necessary to explain a wide variety of observed reactivity trends.
-Vinyl cations are observed as reactive intermediates in solvolysis, as well during electrophilic addition to alkynes. As expected from its ‘sp’ hybridization,
-Vinyl cation prefers a linear geometry
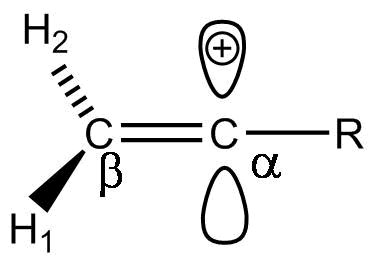
So, The correct answer is (C).
Additional Information: For vinyl cations, relative stabilities can be compared with respect to their neutral alkene analogs.
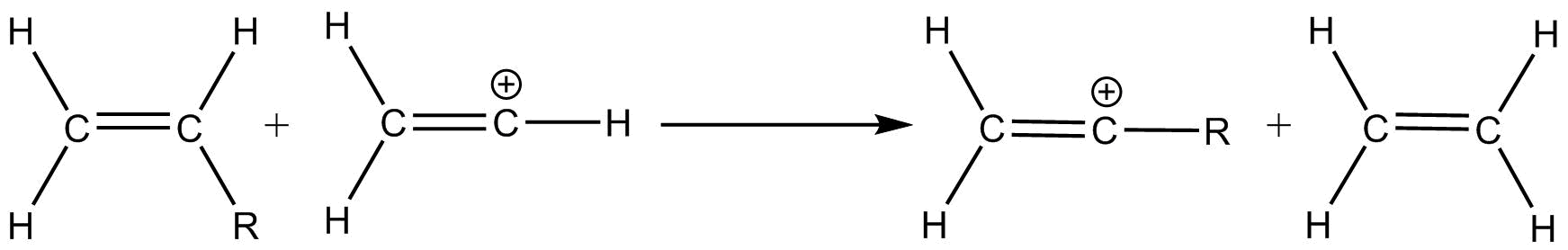
To obtain the stabilization properties of a substituent, the isodesmic reaction was used to calculate enthalpy difference between the substituted vinyl cation and its neutral alkenes precursor by getting its reaction enthalpy. This method is advantageous as it can be benchmarked against experimentally determined thermo chemical values.
Note:
Vinyl carbocations are the intermediate that are formed during reactions and can have a tendency to undergo rearrangements. These rearrangements into double bonds and rearrangements via the double bonds.
Complete answer:
Vinyl cation is one of the main types of reactive intermediates involving a non-tetrahedrally coordinated atom, and is important to refer to the broad class rather than the ${C^2}{H_3}^ + $ variant alone. The vinyl cation is one among the most sorts of reactive intermediates involving a non tetrahedrally coordinated atom, and is necessary to explain a wide variety of observed reactivity trends.
-Vinyl cations are observed as reactive intermediates in solvolysis, as well during electrophilic addition to alkynes. As expected from its ‘sp’ hybridization,
-Vinyl cation prefers a linear geometry

So, The correct answer is (C).
Additional Information: For vinyl cations, relative stabilities can be compared with respect to their neutral alkene analogs.

To obtain the stabilization properties of a substituent, the isodesmic reaction was used to calculate enthalpy difference between the substituted vinyl cation and its neutral alkenes precursor by getting its reaction enthalpy. This method is advantageous as it can be benchmarked against experimentally determined thermo chemical values.
Note:
Vinyl carbocations are the intermediate that are formed during reactions and can have a tendency to undergo rearrangements. These rearrangements into double bonds and rearrangements via the double bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




