
Which of the following will show tautomerism: -
A.
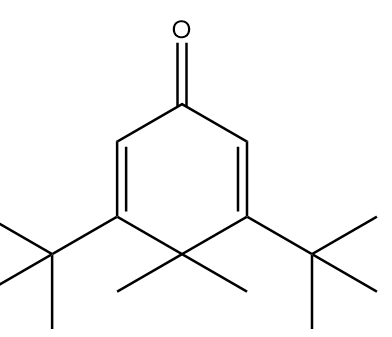
B.
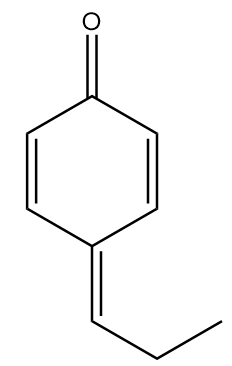
C.

D.
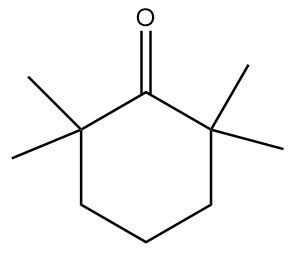




Answer
509.4k+ views
Hint: A phenomenon in which a single organic compound has a tendency to exist in more than one structures which differ by the relative position of only one proton, is known as tautomerism. The interconvertible structures which are formed by tautomerism are known as tautomers. These structures always exist in dynamic equilibrium.
Complete answer:
The basic structural requirements for a compound to show tautomerism are as follows:
1.The compound must contain polar molecules and weakly acidic functional groups.
2.There must be at least one alpha hydrogen present in the compound.
3.It can occur in both, planar as well as non-planar molecules.
4.The carbonyl group i.e., a compound containing $C = O$ group must be connected to a $s{p^3}$ hybridized carbon.
Now, to check the tautomerism, we must check the basic requirement i.e., count of alpha hydrogen atoms for each molecule which are as follows:
In molecule A:
The structure is given as follows:

In the figure, the carbonyl group is connected to $s{p^2}$ hybridized carbon atoms and the carbon atoms red in colour represent alpha positions. So, the number of alpha hydrogens in the compound $ = 0$. Hence, the given compound will not show tautomerism.
In molecule B:
The structure is given as follows:
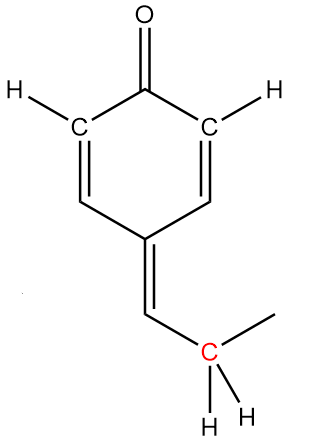
In the figure, the carbonyl group is connected to $s{p^2}$ hybridized carbon atoms and the carbon atoms red in colour represent alpha positions. So, the number of alpha hydrogens in the compound $ = 2$. Hence, the given compound has the tendency to show tautomerism.
In molecule C:
The structure is given as follows:
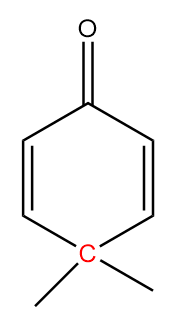
In the figure, the carbonyl group is connected to $s{p^2}$ hybridized carbon atoms and the carbon atoms red in colour represent alpha positions. So, the number of alpha hydrogens in the compound $ = 0$. Hence, the given compound will not show tautomerism.
In molecule D:
The structure is given as follows:

In the figure, the carbonyl group is connected to $s{p^3}$ hybridized carbon atoms but the carbon atoms which are red in colour and represent alpha positions have no alpha hydrogens. Hence, the given compound will not show tautomerism.
Thus, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to note that tautomerism always occurs in the presence of a catalyst. In the presence of acidic catalyst, protonation of the compound occurs and the cation is delocalized followed by the deprotonation of the compound whereas in the presence of base catalyst, deprotonation occurs first and anion is delocalized followed by the protonation of the compound.
Complete answer:
The basic structural requirements for a compound to show tautomerism are as follows:
1.The compound must contain polar molecules and weakly acidic functional groups.
2.There must be at least one alpha hydrogen present in the compound.
3.It can occur in both, planar as well as non-planar molecules.
4.The carbonyl group i.e., a compound containing $C = O$ group must be connected to a $s{p^3}$ hybridized carbon.
Now, to check the tautomerism, we must check the basic requirement i.e., count of alpha hydrogen atoms for each molecule which are as follows:
In molecule A:
The structure is given as follows:

In the figure, the carbonyl group is connected to $s{p^2}$ hybridized carbon atoms and the carbon atoms red in colour represent alpha positions. So, the number of alpha hydrogens in the compound $ = 0$. Hence, the given compound will not show tautomerism.
In molecule B:
The structure is given as follows:

In the figure, the carbonyl group is connected to $s{p^2}$ hybridized carbon atoms and the carbon atoms red in colour represent alpha positions. So, the number of alpha hydrogens in the compound $ = 2$. Hence, the given compound has the tendency to show tautomerism.
In molecule C:
The structure is given as follows:

In the figure, the carbonyl group is connected to $s{p^2}$ hybridized carbon atoms and the carbon atoms red in colour represent alpha positions. So, the number of alpha hydrogens in the compound $ = 0$. Hence, the given compound will not show tautomerism.
In molecule D:
The structure is given as follows:

In the figure, the carbonyl group is connected to $s{p^3}$ hybridized carbon atoms but the carbon atoms which are red in colour and represent alpha positions have no alpha hydrogens. Hence, the given compound will not show tautomerism.
Thus, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to note that tautomerism always occurs in the presence of a catalyst. In the presence of acidic catalyst, protonation of the compound occurs and the cation is delocalized followed by the deprotonation of the compound whereas in the presence of base catalyst, deprotonation occurs first and anion is delocalized followed by the protonation of the compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




