
Which of the following will have metal deficiency defects?
(A) $NaCl$
(B) $FeO$
(C) $KCl$
(D) $ZnO$
Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: This type of defect occurs in compounds where the metal can exhibit variable valency or variable oxidation state. e.g., Transition metal compounds. Out of given options in the question $Zn$ and $Fe$ are transition elements. But $Fe$ can show variable oxidation state.
Complete step by step answer:
In a metal deficiency defect, from its lattice site the cation is missing. Metal deficiency defect is may be due to missing of a cation of lower valency and presence of a cation of higher valency. The nearest metal ion acquires an extra positive charge for maintaining electrical neutrality. In the given options, the only metal that exhibits a variable valency is $Fe$. $Fe$ can exhibit +2 oxidation state as well as +3 oxidation state.
When the conversion of ferrous to ferric ion takes place, charge gets compensated.
$F{e^{2 + }} + 2{e^ - } \to Fe$
For every vacancy of iron cation, two ferrous ions are converted into ferric ions by providing the two-electrons required by excess of oxygen.
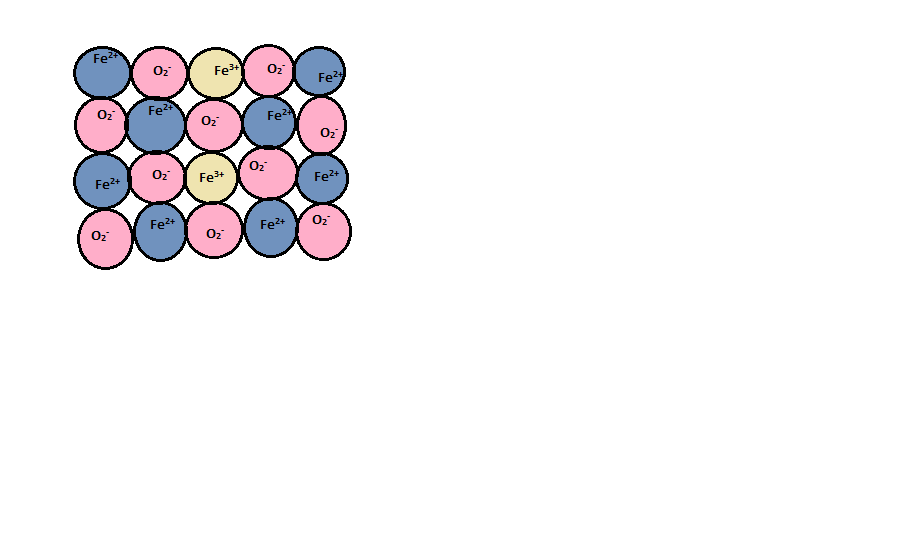
So, $FeO$ is the correct answer.
Thus, option (D) is the correct answer.
Note:
There are two types of non-stoichiometric defect, one is metal excess defect and another one is metal deficiency defect. In a metal deficiency defects, density of solids decreases while in metal excess defects, density of solids increases.
Complete step by step answer:
In a metal deficiency defect, from its lattice site the cation is missing. Metal deficiency defect is may be due to missing of a cation of lower valency and presence of a cation of higher valency. The nearest metal ion acquires an extra positive charge for maintaining electrical neutrality. In the given options, the only metal that exhibits a variable valency is $Fe$. $Fe$ can exhibit +2 oxidation state as well as +3 oxidation state.
When the conversion of ferrous to ferric ion takes place, charge gets compensated.
$F{e^{2 + }} + 2{e^ - } \to Fe$
For every vacancy of iron cation, two ferrous ions are converted into ferric ions by providing the two-electrons required by excess of oxygen.

So, $FeO$ is the correct answer.
Thus, option (D) is the correct answer.
Note:
There are two types of non-stoichiometric defect, one is metal excess defect and another one is metal deficiency defect. In a metal deficiency defects, density of solids decreases while in metal excess defects, density of solids increases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




