
Which of the following RNA’s should be most abundant in an animal cell?
(a) miRNA
(b) tRNA
(c) mRNA
(d) rRNA
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: This is a type of non- coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. This is a type of RNA which is a ribozyme and it carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
There are three main types of RNA, i.e. rRNA, RNA, and mRNA. rRNA is the most abundant form of RNA; because it is responsible for coding and protein synthesis in the cell and associated with ribosomes. mRNA provides the template for translation. tRNA brings amino acids and reads the genetic code.
Process of translation in protein synthesis:
- Decoding an mRNA message into a polypeptide substance is the method of translation in biology. A message written in the form of nucleotides is "translated" into the amino acids' chemical language. An mRNA prototype, amino acids, ribosomes, tRNAs, an energy source, and various additional accessory enzymes and small molecules are needed for translation.
- mRNA is transported to the cytoplasm, where it binds with ribosomes after mRNA is synthesized by the transcription process.
- Ribosomes are protein synthesis sites. There are three major binding sites for ribosomes, one for mRNA and two (A site and P site) for tRNA. The P site is occupied by the initial codon methionine and the A site is occupied by the second codon. A base pair with the mRNA in the A site forms the tRNA molecule whose anticodon is complementary to the mRNA.
- A peptide bond is formed between the amino acid attached to the A- site tRNA and the P- site methionine. The ribosome then slides down the mRNA in such a way that the tRNA moves to the P site from the A site, and the A site is filled by a new codon. Until one of the three stop codons occupies the A site, this process continues. The protein chain linked to the tRNA in the P site is released at that point and the translation is complete.
So, the correct answer is, ‘rRNA.’
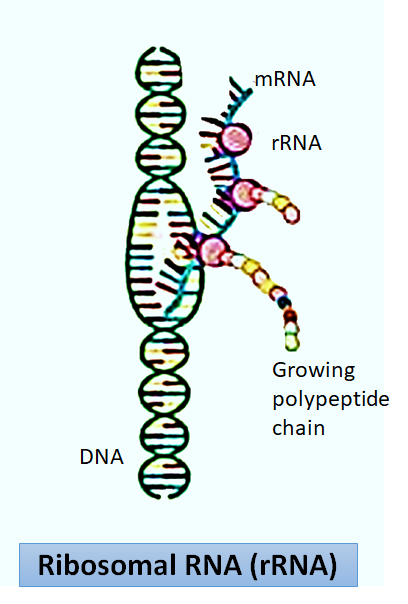
Note: Protein synthesis takes place primarily in two steps – transcription and translation. In eukaryotic cells, the first step i.e. transcription occurs in the nucleus, and in this step, DNA is used as a template to synthesize a molecule of mRNA. After formation, the mRNA leaves the nucleus and reaches the ribosomes present in the cytoplasm where the second step i.e. translation is completed. In this step, the genetic code present on the mRNA is read by the ribosomes, and a chain of amino acids is formed accordingly. A representative diagram of protein synthesis has been given below:
Complete Step by Step Answer:
There are three main types of RNA, i.e. rRNA, RNA, and mRNA. rRNA is the most abundant form of RNA; because it is responsible for coding and protein synthesis in the cell and associated with ribosomes. mRNA provides the template for translation. tRNA brings amino acids and reads the genetic code.
Process of translation in protein synthesis:
- Decoding an mRNA message into a polypeptide substance is the method of translation in biology. A message written in the form of nucleotides is "translated" into the amino acids' chemical language. An mRNA prototype, amino acids, ribosomes, tRNAs, an energy source, and various additional accessory enzymes and small molecules are needed for translation.
- mRNA is transported to the cytoplasm, where it binds with ribosomes after mRNA is synthesized by the transcription process.
- Ribosomes are protein synthesis sites. There are three major binding sites for ribosomes, one for mRNA and two (A site and P site) for tRNA. The P site is occupied by the initial codon methionine and the A site is occupied by the second codon. A base pair with the mRNA in the A site forms the tRNA molecule whose anticodon is complementary to the mRNA.
- A peptide bond is formed between the amino acid attached to the A- site tRNA and the P- site methionine. The ribosome then slides down the mRNA in such a way that the tRNA moves to the P site from the A site, and the A site is filled by a new codon. Until one of the three stop codons occupies the A site, this process continues. The protein chain linked to the tRNA in the P site is released at that point and the translation is complete.
So, the correct answer is, ‘rRNA.’
Note: Protein synthesis takes place primarily in two steps – transcription and translation. In eukaryotic cells, the first step i.e. transcription occurs in the nucleus, and in this step, DNA is used as a template to synthesize a molecule of mRNA. After formation, the mRNA leaves the nucleus and reaches the ribosomes present in the cytoplasm where the second step i.e. translation is completed. In this step, the genetic code present on the mRNA is read by the ribosomes, and a chain of amino acids is formed accordingly. A representative diagram of protein synthesis has been given below:

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




