
Which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on a concave mirror as shown in the figure?
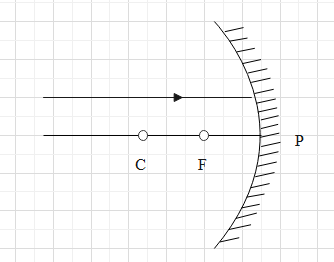
A.
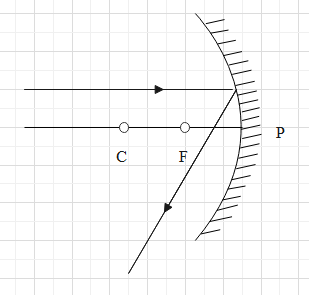
B.
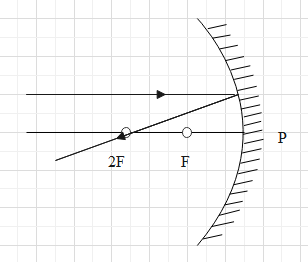
C.
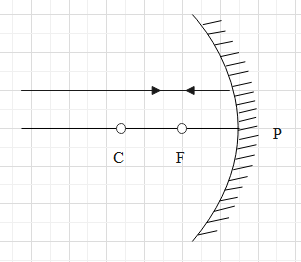
D.





Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: In the case of the concave mirror, the principal focus (also called the focal point) is a point at which the incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis converges after getting reflected from the mirror. Thus, the focal point and focal length are real.
Formula used:
\[\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}\]
Complete answer:
The Mirror formula is,
\[\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}\]
Where \[u\]is the object distance, \[v\]is the image distance and \[f\]is the focal length.
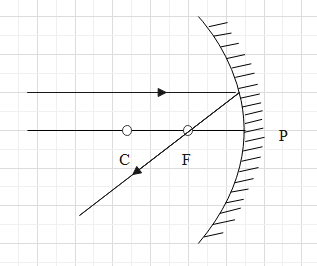
From the given figure it’s clear that the incident ray of light on the concave mirror is in parallel to the principal axis.
Therefore, the object distance is given by,
\[u=-\infty \]
As the ray of light is not coming from any point source, thus, assumed to be coming from the infinity.
Substitute the value of object distance in the Mirror formula.
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u} \\
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{-\infty } \\
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-0 \\
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v} \\
& f=v \\
\end{align}\]
From the above calculation, it’s clear that the focal length of the concave mirror is equal to the image distance. In other words, the image will form at the focus.
Therefore, the incident ray of light on the concave mirror must pass through the focus after reflecting from the mirror.
As the ray of light incident on a concave mirror after reflection passes through the focus of the concave mirror, option (D) is correct.
Note:
The things to be on your figure tips for further information on solving these types of problems are:
The concave mirror can produce both real and virtual images depending on the position of the object with respect to the mirror, whereas, the concave lens can only produce the virtual images.
Formula used:
\[\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}\]
Complete answer:
The Mirror formula is,
\[\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}\]
Where \[u\]is the object distance, \[v\]is the image distance and \[f\]is the focal length.
From the given figure it’s clear that the incident ray of light on the concave mirror is in parallel to the principal axis.
Therefore, the object distance is given by,
\[u=-\infty \]
As the ray of light is not coming from any point source, thus, assumed to be coming from the infinity.
Substitute the value of object distance in the Mirror formula.
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u} \\
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{-\infty } \\
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-0 \\
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v} \\
& f=v \\
\end{align}\]
From the above calculation, it’s clear that the focal length of the concave mirror is equal to the image distance. In other words, the image will form at the focus.
Therefore, the incident ray of light on the concave mirror must pass through the focus after reflecting from the mirror.
As the ray of light incident on a concave mirror after reflection passes through the focus of the concave mirror, option (D) is correct.
Note:
The things to be on your figure tips for further information on solving these types of problems are:
The concave mirror can produce both real and virtual images depending on the position of the object with respect to the mirror, whereas, the concave lens can only produce the virtual images.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




