
Which of the following pairs is correctly matched?
A) Amino Acid Alanine
B)
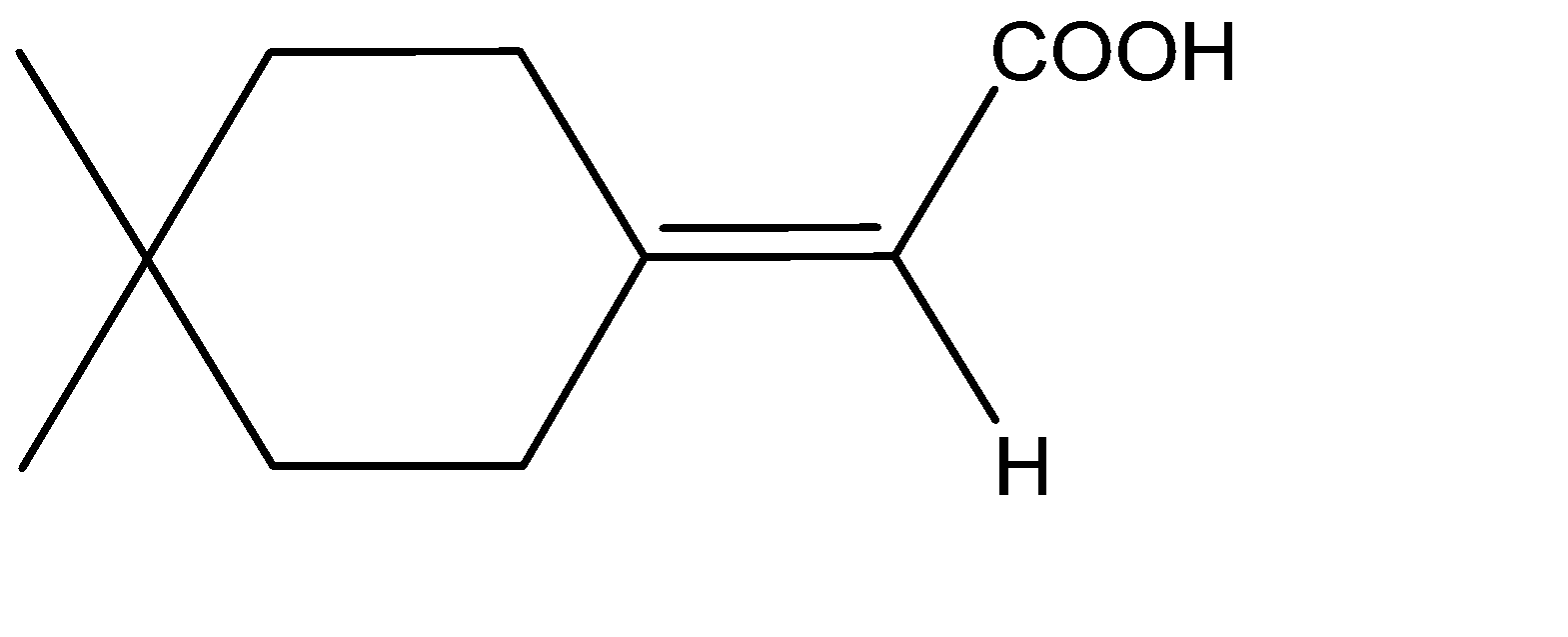
C)
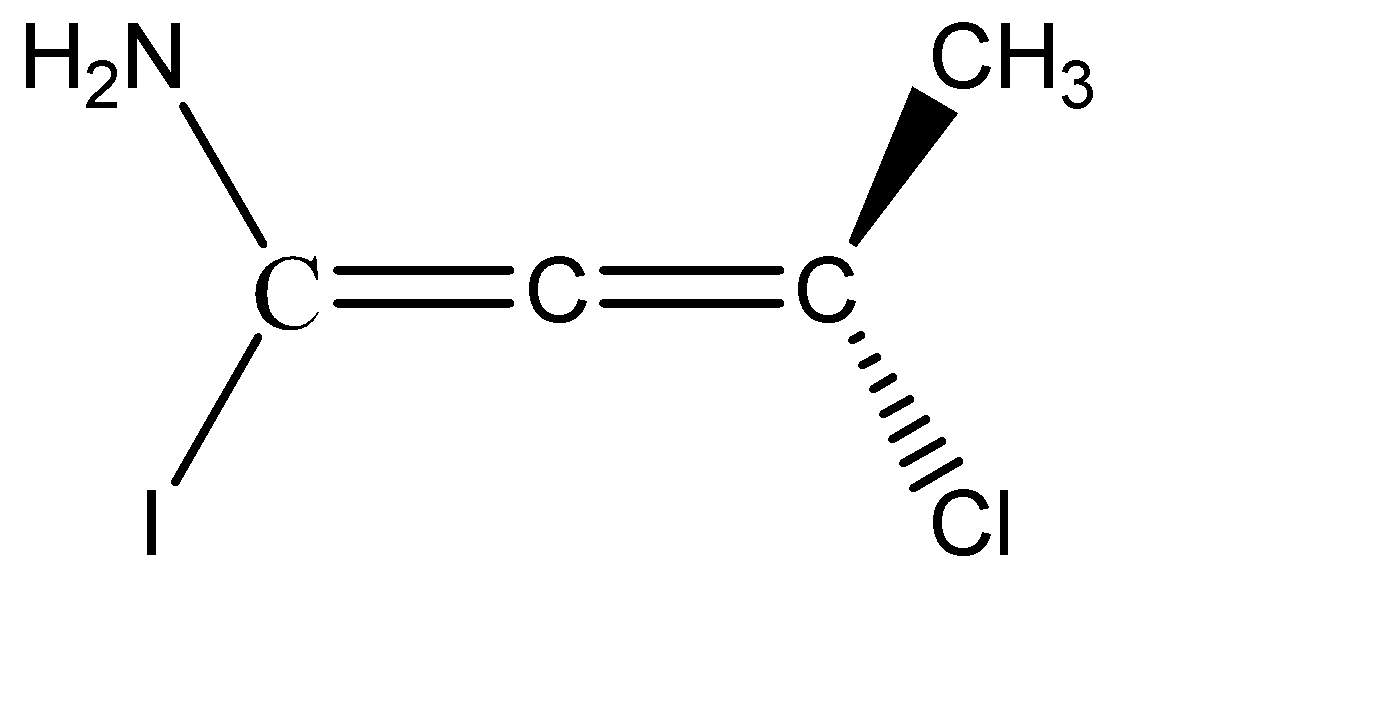
D)
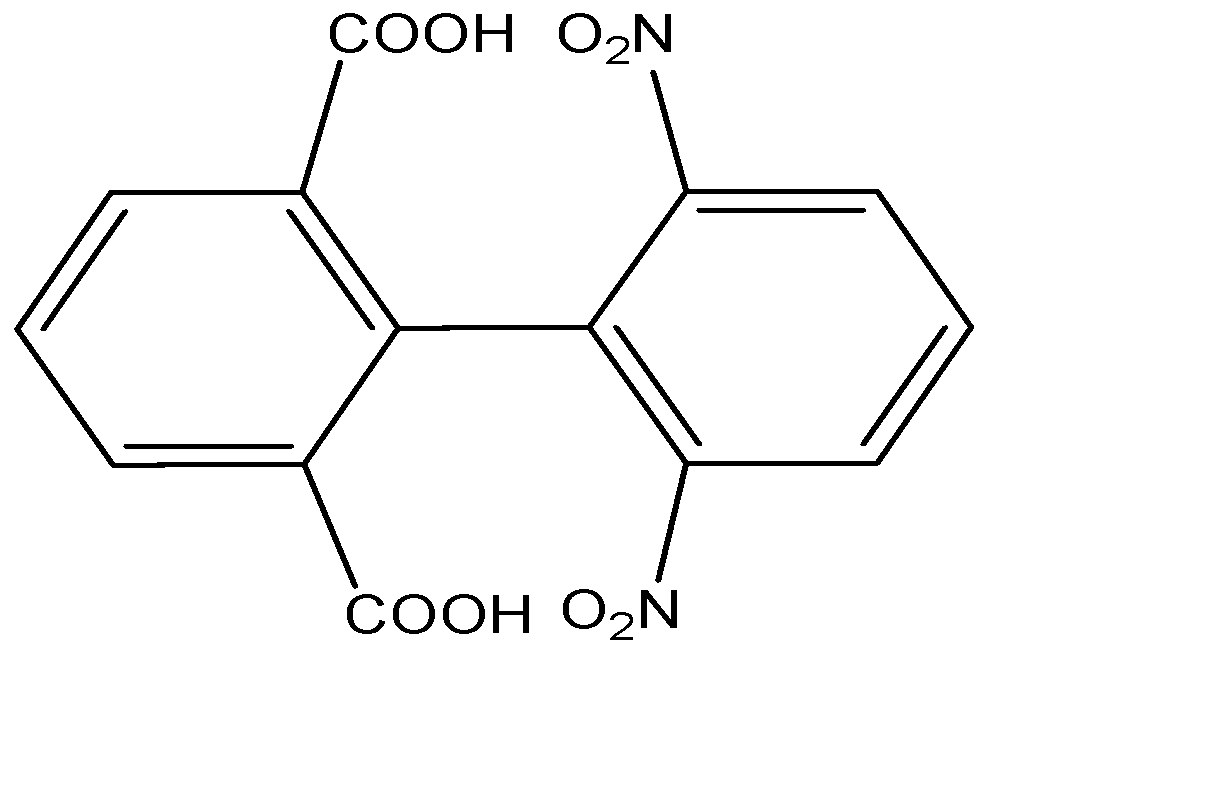



Answer
481.5k+ views
Hint: A molecule is said to be optically active, if the molecule is chiral and optically inactive if the molecule is achiral. A molecule is said to be chiral if it doesn’t possess a Plane of Symmetry and Centre of symmetry. In this question we will determine if the given molecules have a POS and COS.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
We will analyse the given molecule
A) We are given the amino acid alanine. Let us know the structure of alanine. In Alanine the R group is methyl. The structure will be:
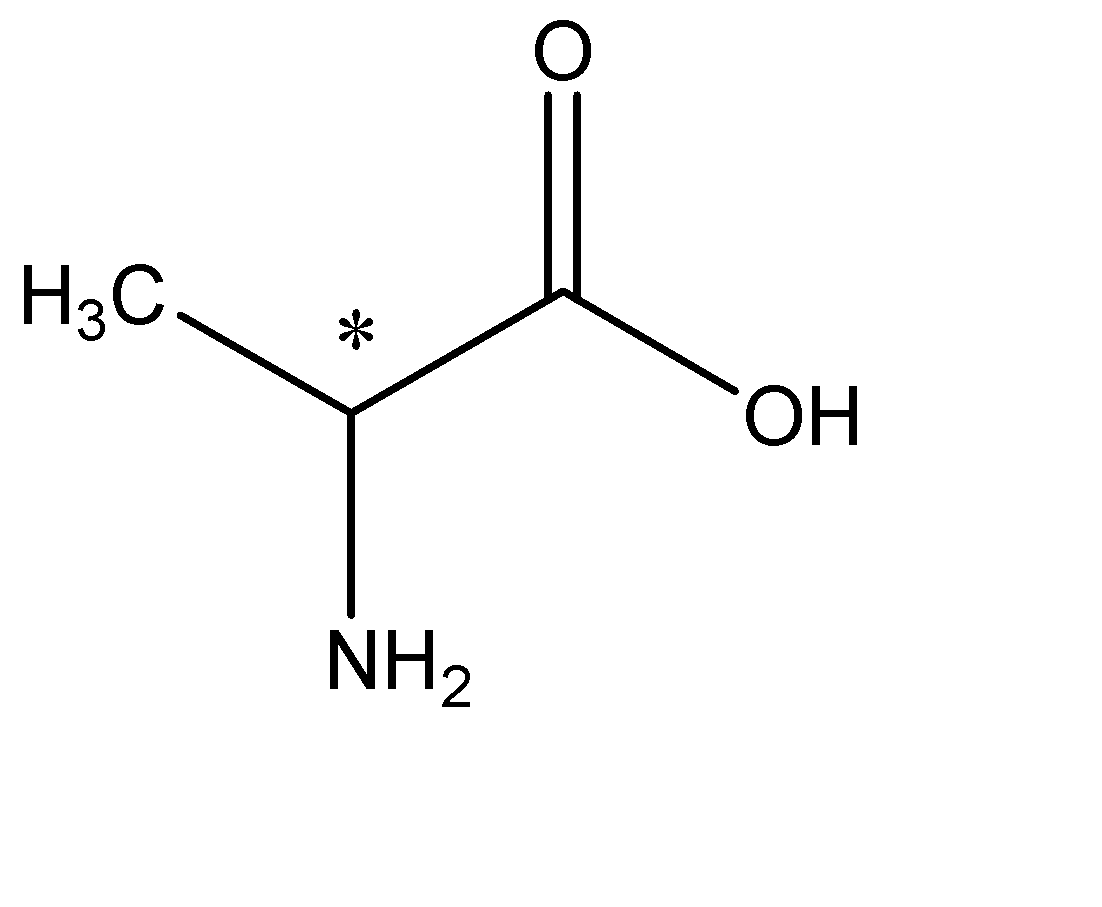
As we can see in the structure that the carbon with the asterisk (*) sign, is the chiral centre, meaning it is attached to four different substituents namely; Methyl, Amine, Hydrogen and Carboxyl group. Hence this molecule is Chiral and will be optically active. Option A is the correct answer
B) The molecule given to us consists of a cyclohexane ring. The ring can be considered as a double bond and the molecule will be similar to that of an allene. The structure will thus be:
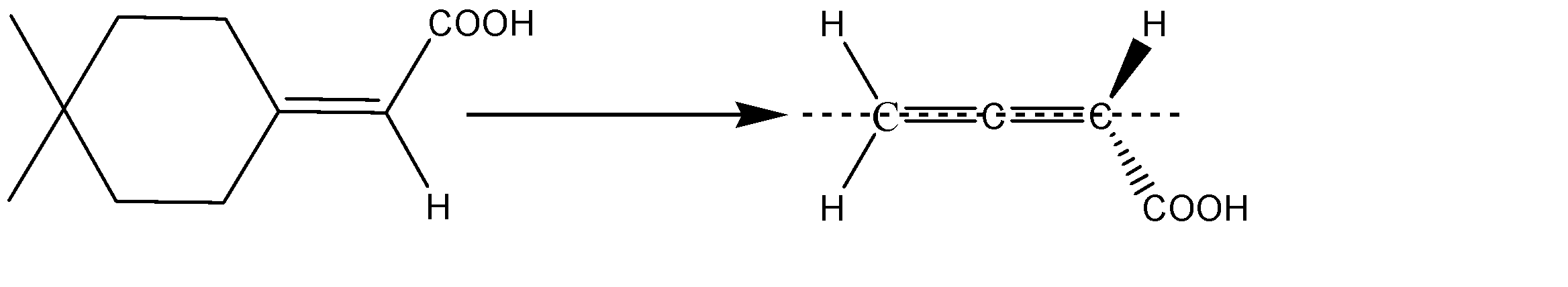
The two substituents hydrogen and carbonyl, being above and below the plane will be cut into equal halves, and the two hydrogens which are in plane, are cut into two halves. Hence, we can see that the two halves of the molecule are mirror images of each other, therefore, we can say that a given allene has a Plane Of Symmetry and therefore, it becomes achiral and is optically inactive. Option B is incorrect.
C) The third molecule given to us is an allene. From the structure of the allene it is clear that it is not a planar molecule. The two hydrogens on C-1 are planar, since they are denoted by solid single lines, and the two substituents on C-3 are one above the plane and one below the plane denoted by wedge and dash.
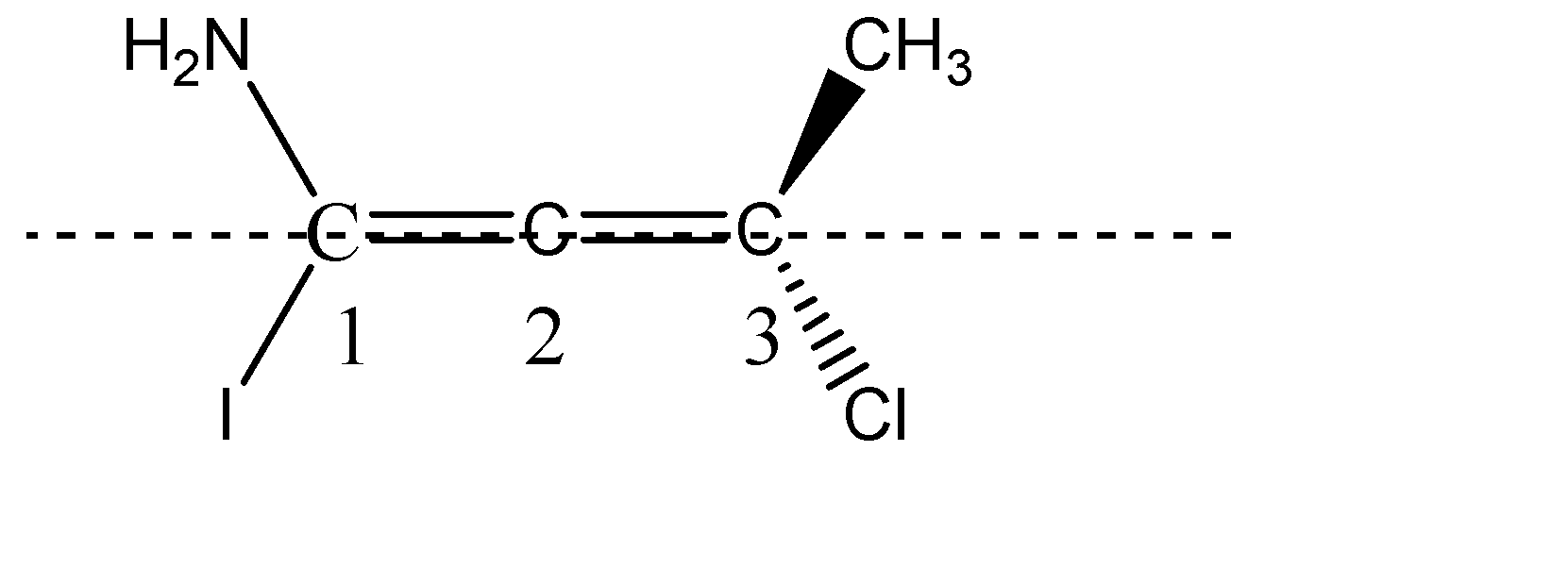
The two substituents chlorine and methyl, being above and below the plane will be cut into equal halves, and the two amine and Iodine which are in plane, are cut into two halves. Hence, we can see that the two halves of the molecule are not mirror images of each other, therefore, we can say that given allene do not have a Plane Of Symmetry and therefore, it becomes chiral and is optically active. Option C is correct.
D) The given compound is a biphenyl. The two biphenyl rings are perpendicular to each other to prevent the steric hindrance. The substituents attached to the biphenyls are bulky, and will restrict the rotation along the single bond.
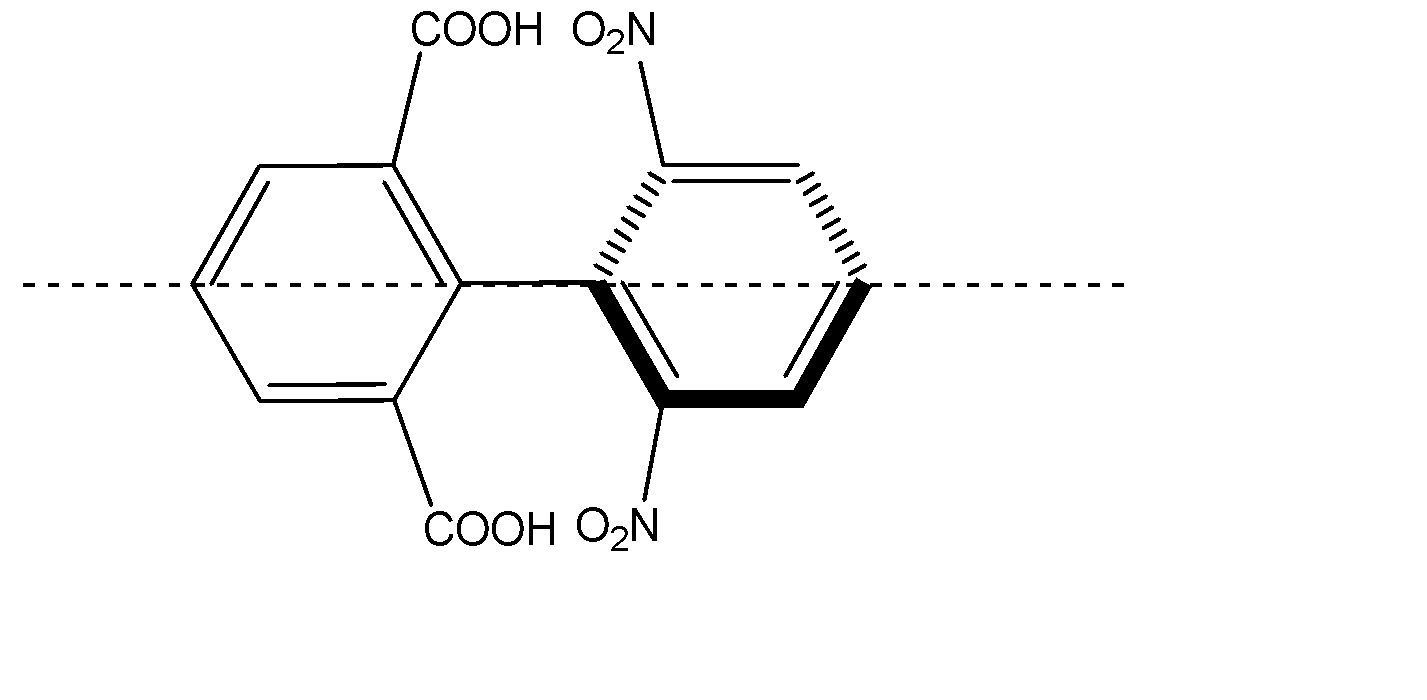
The plane passing through the middle of the biphenyl linkage will cut the molecule into two same halves which will be mirror images of each other, hence it will be achiral and the molecule is said to be optically inactive. Hence Option D is also correct.
Option A, B and D are correctly matched.
Note:
A shortcut to determine the chirality in allenes is that if either of the two ends of the allene are attached to identical substituents, it will be achiral (since it will have POS) and if neither of the two ends have identical substituents it will be chiral. Similarly in biphenyls, if different bully substituents are present in one ring, then it will become chiral.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
We will analyse the given molecule
A) We are given the amino acid alanine. Let us know the structure of alanine. In Alanine the R group is methyl. The structure will be:

As we can see in the structure that the carbon with the asterisk (*) sign, is the chiral centre, meaning it is attached to four different substituents namely; Methyl, Amine, Hydrogen and Carboxyl group. Hence this molecule is Chiral and will be optically active. Option A is the correct answer
B) The molecule given to us consists of a cyclohexane ring. The ring can be considered as a double bond and the molecule will be similar to that of an allene. The structure will thus be:

The two substituents hydrogen and carbonyl, being above and below the plane will be cut into equal halves, and the two hydrogens which are in plane, are cut into two halves. Hence, we can see that the two halves of the molecule are mirror images of each other, therefore, we can say that a given allene has a Plane Of Symmetry and therefore, it becomes achiral and is optically inactive. Option B is incorrect.
C) The third molecule given to us is an allene. From the structure of the allene it is clear that it is not a planar molecule. The two hydrogens on C-1 are planar, since they are denoted by solid single lines, and the two substituents on C-3 are one above the plane and one below the plane denoted by wedge and dash.

The two substituents chlorine and methyl, being above and below the plane will be cut into equal halves, and the two amine and Iodine which are in plane, are cut into two halves. Hence, we can see that the two halves of the molecule are not mirror images of each other, therefore, we can say that given allene do not have a Plane Of Symmetry and therefore, it becomes chiral and is optically active. Option C is correct.
D) The given compound is a biphenyl. The two biphenyl rings are perpendicular to each other to prevent the steric hindrance. The substituents attached to the biphenyls are bulky, and will restrict the rotation along the single bond.

The plane passing through the middle of the biphenyl linkage will cut the molecule into two same halves which will be mirror images of each other, hence it will be achiral and the molecule is said to be optically inactive. Hence Option D is also correct.
Option A, B and D are correctly matched.
Note:
A shortcut to determine the chirality in allenes is that if either of the two ends of the allene are attached to identical substituents, it will be achiral (since it will have POS) and if neither of the two ends have identical substituents it will be chiral. Similarly in biphenyls, if different bully substituents are present in one ring, then it will become chiral.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




