
Which of the following is the most stable diazonium salt?
A. \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{N}_{\text{2}}^{\text{+}}{{\text{X}}^{\text{-}}}\]
B. \[\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{N}_{_{\text{2}}}^{\text{+}}{{\text{X}}^{\text{-}}}\]
C. \[\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{N}_{\text{2}}^{\text{+}}{{\text{X}}^{\text{-}}}\]
D. \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}\text{N}_{\text{2}}^{\text{+}}{{\text{X}}^{\text{-}}}\]
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: When we talk about the stability of diazonium salts,one important factor that is considered is the stabilisation of aromatic compounds by resonance.So,we should try drawing the resonance stabilized structure and check for the most stable diazonium salt.
Complete step by step solution: Now in the following question,let’s check whether the compounds are aliphatic or aromatic:
- We should first try eliminating the options B and C ,as aliphatic amines do not give any diazonium compounds under normal conditions,as they form highly unstable alkyl diazonium salts.
- So,now let's check for the aryl diazonium salts,so here resonance comes into play,as there is a dispersal of positive charge on the benzene ring,due to which the ring acquires partial double bond character,and thus is more stable, but less reactive whereas the aliphatic ones are more reactive and less stable.
- Let's see the resonance stabilised structure of benzene diazonium salt.
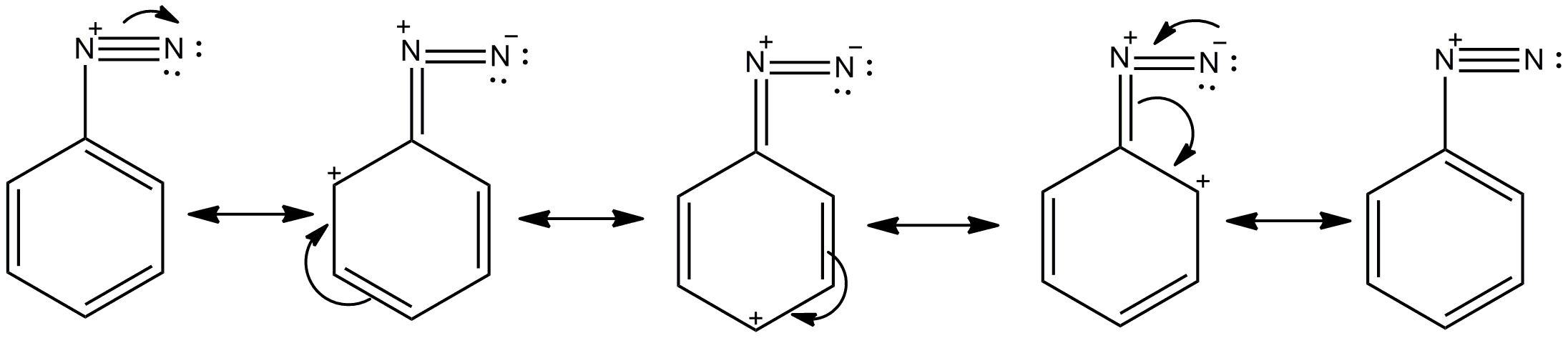
- So here we can see through the diagram the stability achieved by the resonance structures of option D,which is the benzene diazonium salt,which allows the distribution of charge in the whole ring.
-So option D is the correct answer.
Note: In case of aromatic diazonium salts ,we must remember that the positive charge on nitrogen stays in conjugation with the benzene ring,and hence stabilises the carbons of the ring,which the aliphatic diazonium fails to do and they simply liberate nitrogen gas, and form Alcohols,thus accounting for low stability.
Complete step by step solution: Now in the following question,let’s check whether the compounds are aliphatic or aromatic:
- We should first try eliminating the options B and C ,as aliphatic amines do not give any diazonium compounds under normal conditions,as they form highly unstable alkyl diazonium salts.
- So,now let's check for the aryl diazonium salts,so here resonance comes into play,as there is a dispersal of positive charge on the benzene ring,due to which the ring acquires partial double bond character,and thus is more stable, but less reactive whereas the aliphatic ones are more reactive and less stable.
- Let's see the resonance stabilised structure of benzene diazonium salt.

- So here we can see through the diagram the stability achieved by the resonance structures of option D,which is the benzene diazonium salt,which allows the distribution of charge in the whole ring.
-So option D is the correct answer.
Note: In case of aromatic diazonium salts ,we must remember that the positive charge on nitrogen stays in conjugation with the benzene ring,and hence stabilises the carbons of the ring,which the aliphatic diazonium fails to do and they simply liberate nitrogen gas, and form Alcohols,thus accounting for low stability.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




