
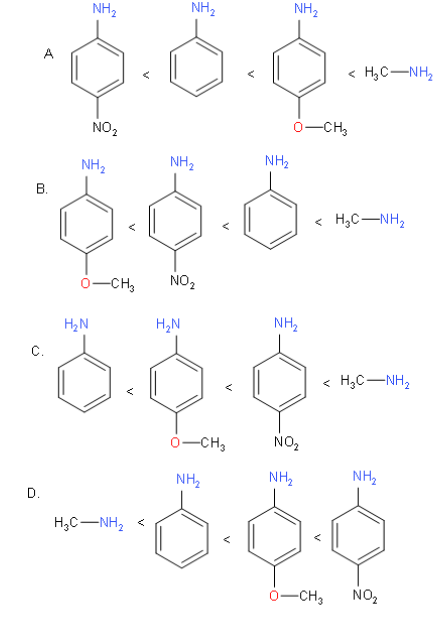
Which of the following is the correct order of amines?

Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: Amine is a functional group in organic chemistry. It consists of a basic nitrogen group and a lone pair of electrons. The amines are formed from the ammonia when one or 2 hydrogen atoms are replaced by the other molecules.
Complete Answer:
-To write the correct order of the basicity of amines we have to study all the given structures of amine.
-In the first structure i.e. of methylamine, the methyl group has +I effect due to which it can easily donate the electrons $\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{2}}$
-Also, the lone pair of electrons is present on the methylamine which does not participate in the resonance.
-Due to which the electron density increases on the nitrogen atom and the basicity decreases.
-So, it is the most basic amine from the given figures.
-Now, in the second structure i.e. p-nitroaniline the electron-withdrawing group is present i.e.$\text{N}{{\text{O}}_{2}}$.
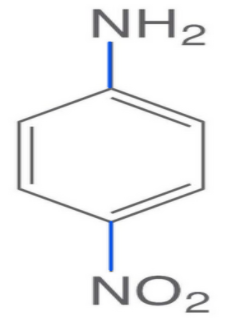
-Electron withdrawing groups are those atoms which accept or draw the electron density from the adjacent atom via resonance or inductive effect.
-So, it will decrease the electron density and it will become difficult for the nitrogen to donate electron pairs. So, it will be the least basic due to the presence of the electron-withdrawing group.
-Now, in the third structure i.e. p-methoxy aniline it is more basic than the aniline i.e. ${{\text{C}}_{6}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{2}}$because of the presence of methoxy group $\left( \text{OC}{{\text{H}}_{3}} \right)$.
-The electron-withdrawing group will increase the chances of nitrogen to donate the lone pair of electron and makes it more basic whereas aniline lacks electron-donating groups.
-So, aniline will be less basic than p-methoxy aniline but more basic than p-nitroaniline.
Therefore, the correct order of amines is given in option A.
Note:
Electron withdrawing group are those elements which tend to withdraw the electron density from the neighbour atom. For example, $\text{N}{{\text{O}}_{2}}\text{, CN}$, etc. Whereas electron-donating groups are those elements which tend to donate the electron density to the neighbour atom. For example, alkyl groups.
Complete Answer:
-To write the correct order of the basicity of amines we have to study all the given structures of amine.
-In the first structure i.e. of methylamine, the methyl group has +I effect due to which it can easily donate the electrons $\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{2}}$
-Also, the lone pair of electrons is present on the methylamine which does not participate in the resonance.
-Due to which the electron density increases on the nitrogen atom and the basicity decreases.
-So, it is the most basic amine from the given figures.
-Now, in the second structure i.e. p-nitroaniline the electron-withdrawing group is present i.e.$\text{N}{{\text{O}}_{2}}$.

-Electron withdrawing groups are those atoms which accept or draw the electron density from the adjacent atom via resonance or inductive effect.
-So, it will decrease the electron density and it will become difficult for the nitrogen to donate electron pairs. So, it will be the least basic due to the presence of the electron-withdrawing group.
-Now, in the third structure i.e. p-methoxy aniline it is more basic than the aniline i.e. ${{\text{C}}_{6}}{{\text{H}}_{5}}\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{2}}$because of the presence of methoxy group $\left( \text{OC}{{\text{H}}_{3}} \right)$.
-The electron-withdrawing group will increase the chances of nitrogen to donate the lone pair of electron and makes it more basic whereas aniline lacks electron-donating groups.
-So, aniline will be less basic than p-methoxy aniline but more basic than p-nitroaniline.
Therefore, the correct order of amines is given in option A.
Note:
Electron withdrawing group are those elements which tend to withdraw the electron density from the neighbour atom. For example, $\text{N}{{\text{O}}_{2}}\text{, CN}$, etc. Whereas electron-donating groups are those elements which tend to donate the electron density to the neighbour atom. For example, alkyl groups.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




