
Which of the following is the best reagent to convert 1-methylcyclohexene into 2-methylcyclohexanol?
A. Dil. \[{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\]
B. $Hg{{(OAc)}_{2}}/NaB{{H}_{4}},{{H}_{2}}O$
C. ${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}/{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}},O{{H}^{-}}$
D. Conc.${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: To convert to convert 1-methylcyclohexene into 2-methylcyclohexanol, we need to add ${{H}_{2}}O$ on 1-methylcyclohexene according anti markovnikov law. That can be done by making it react with diborane, that will form a trialkyl borane with it and then oxidizing the trialkyl borane into the alcohol.
Complete step by step answer:
Diborane (${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$) is the dimer of \[B{{H}_{3}}\]. \[B{{H}_{3}}\]is a colorless gas. In this molecule Boron has an empty orbital and that’s why it forms dimer with another \[B{{H}_{3}}\] molecule via banana bonding to form its dimer.
Anti Markovnikov rule: According to this rule when electrophilic addition of a compound takes place on alkene then electrophile gets attached on the more substituted carbon atom.
Electronegativity of hydrogen is more than boron, that’s why when$B{{H}_{3}}$ reacts, it releases hydrogen as hydride ion. So on reacting with given cycloalkene, addition of hydride ion and boron will take place according to markovnikov rule and trialkyl borane forms.
Now when this trialkyl borane gets oxidized by ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ in alkaline medium, in place of each boron, one hydroxide ion forms a bond with carbon and a cycloalkane forms.
Overall addition of water is taking place on 1-methylcyclohexene where hydrogen is getting attached to more substituted carbon while hydroxide ion is getting attached on less substituted carbon.
Therefore overall it is similar to anti markovnikov addition.
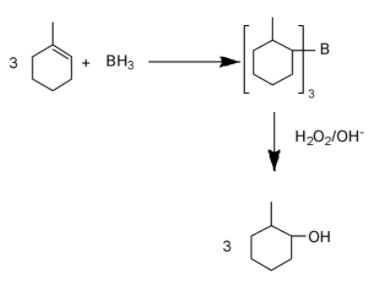
So, the answer is option C.
Additional information:
According to markovnikov rule when electrophile attacks on alkene, it gets attached to the less substituted carbon atom.
Note: 2-methylcyclohexanol is a colorless liquid with boiling point of $163-166{}^{0}C$. It is slightly soluble in water and has specific gravity equal to 0.930. 1-methylcyclohexene is a colorless clear liquid with boiling point of$110-111{}^{0}C$. It is soluble in benzene and ether and miscible with many hydrocarbons of similar structure.
Complete step by step answer:
Diborane (${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$) is the dimer of \[B{{H}_{3}}\]. \[B{{H}_{3}}\]is a colorless gas. In this molecule Boron has an empty orbital and that’s why it forms dimer with another \[B{{H}_{3}}\] molecule via banana bonding to form its dimer.
Anti Markovnikov rule: According to this rule when electrophilic addition of a compound takes place on alkene then electrophile gets attached on the more substituted carbon atom.
Electronegativity of hydrogen is more than boron, that’s why when$B{{H}_{3}}$ reacts, it releases hydrogen as hydride ion. So on reacting with given cycloalkene, addition of hydride ion and boron will take place according to markovnikov rule and trialkyl borane forms.
Now when this trialkyl borane gets oxidized by ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ in alkaline medium, in place of each boron, one hydroxide ion forms a bond with carbon and a cycloalkane forms.
Overall addition of water is taking place on 1-methylcyclohexene where hydrogen is getting attached to more substituted carbon while hydroxide ion is getting attached on less substituted carbon.
Therefore overall it is similar to anti markovnikov addition.

So, the answer is option C.
Additional information:
According to markovnikov rule when electrophile attacks on alkene, it gets attached to the less substituted carbon atom.
Note: 2-methylcyclohexanol is a colorless liquid with boiling point of $163-166{}^{0}C$. It is slightly soluble in water and has specific gravity equal to 0.930. 1-methylcyclohexene is a colorless clear liquid with boiling point of$110-111{}^{0}C$. It is soluble in benzene and ether and miscible with many hydrocarbons of similar structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




