
Which of the following is a non-reducing sugar?
[A] Maltose
[B] Lactose
[C] Sucrose
[D] Glucose
[E] Fructose
Answer
588k+ views
HINT: A sugar which is not oxidised is a carbohydrate which is not oxidised by weak oxidising agents. Here, to find the correct answer, draw the structures of the sugars. If they have no free aldehyde or ketone groups, then it will be a non-reducing sugar.
COMPLETE STEP BY STEP SOLUTION: We know that sugars are basically a chain of carbohydrates and they are soluble in nature. Sugars are hydrocarbons i.e. they contain hydrogen, carbon along with oxygen.
Sugar can be oxidised by weak oxidising agents which after oxidation reduces other compounds and thus are called reducing sugars.
If a sugar is not oxidised, it will not be a reducing sugar and hence it will be a non-reducing sugar.
Generally, sugar which does not have a free aldehyde or ketone group are non-reducing sugars as they cannot be oxidised.
Let us draw the structures of the compounds mentioned and try to find out if they are reducing or non-reducing.
Firstly, we have maltose.
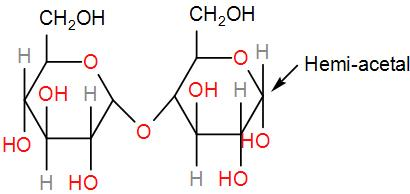
It contains a hemi-acetal group which can undergo oxidation and give an aldehyde. Therefore, it is reducing sugar.
Then, we have lactose.
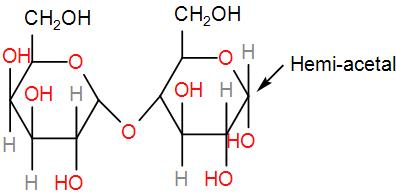
Like maltose it will also undergo oxidation and give us an aldehyde. Therefore, it is reducing sugar.
Then we have sucrose.
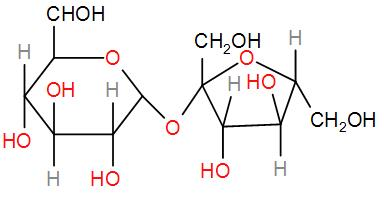
It lacks any hemi-acetal group that might undergo oxidation to give a reducing sugar. Therefore, this is a non-reducing sugar.
Then, we have glucose, which also is a reducing sugar due to the presence of the free aldehyde group.
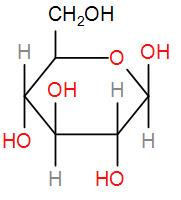
And lastly we have fructose
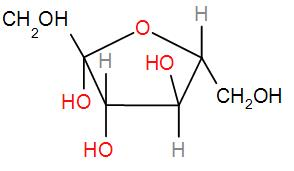
This also has a hemi-acetal part which can be oxidised.
We can see from the above discussion that sucrose is a non-reducing sugar.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [C] sucrose.
NOTE: There are certain tests for identification of reducing sugars. Benedict's test uses a reagent known as Benedict’s reagent and it contains copper (II) sulphate, sodium carbonate and sodium citrate. We take the sample and the reagent and mix them and place the test tube in a boiling water bath for 5 minutes. If there is no change in the colour of the solution i.e. it remains blue, it shows that no reducing sugar is present. If the colour change is to yellow then there is a small amount of reducing sugar present and if the solution is red, it indicates presence of reducing sugar in large amounts.
COMPLETE STEP BY STEP SOLUTION: We know that sugars are basically a chain of carbohydrates and they are soluble in nature. Sugars are hydrocarbons i.e. they contain hydrogen, carbon along with oxygen.
Sugar can be oxidised by weak oxidising agents which after oxidation reduces other compounds and thus are called reducing sugars.
If a sugar is not oxidised, it will not be a reducing sugar and hence it will be a non-reducing sugar.
Generally, sugar which does not have a free aldehyde or ketone group are non-reducing sugars as they cannot be oxidised.
Let us draw the structures of the compounds mentioned and try to find out if they are reducing or non-reducing.
Firstly, we have maltose.

It contains a hemi-acetal group which can undergo oxidation and give an aldehyde. Therefore, it is reducing sugar.
Then, we have lactose.

Like maltose it will also undergo oxidation and give us an aldehyde. Therefore, it is reducing sugar.
Then we have sucrose.

It lacks any hemi-acetal group that might undergo oxidation to give a reducing sugar. Therefore, this is a non-reducing sugar.
Then, we have glucose, which also is a reducing sugar due to the presence of the free aldehyde group.

And lastly we have fructose

This also has a hemi-acetal part which can be oxidised.
We can see from the above discussion that sucrose is a non-reducing sugar.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [C] sucrose.
NOTE: There are certain tests for identification of reducing sugars. Benedict's test uses a reagent known as Benedict’s reagent and it contains copper (II) sulphate, sodium carbonate and sodium citrate. We take the sample and the reagent and mix them and place the test tube in a boiling water bath for 5 minutes. If there is no change in the colour of the solution i.e. it remains blue, it shows that no reducing sugar is present. If the colour change is to yellow then there is a small amount of reducing sugar present and if the solution is red, it indicates presence of reducing sugar in large amounts.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




