
Which of the following has the lowest $ p{K_a} $ value? Why?
A. $ C{H_3}COOH $
B. $ ClC{H_2}COOH $
C. $ C{l_2}CHCOOH $
D. $ C{l_3}CCOOH $
Answer
491.1k+ views
Hint: The carboxylic acids are acidic in nature however they are very weak acids. They slow acidity lower than mineral acids. Dissociation constant $ \left( {K_a} \right) $ is used to express the strength of carboxylic acid. Dissociation constant provides the quantitative acidic strength of various acids including carboxylic acids.
Complete answer:
The mathematical expression to evaluate strength of carboxylic acid is expressed as:
$ RCOOH + {H_2}O \rightleftharpoons RCO{O^ - } + {H_3}{O^ + } $
Dissociation constant for the above equation is:
$ K_a = \dfrac{{\left[ {RCO{O^ - }} \right]\left[ {{H_3}{O^ + }} \right]}}{{\left[ {RCOOH} \right]}} $
Dissociation constant is also expressed in terms of $ p{K_a} $ as:
$ p{K_a} $ $ = - \log K_a $
It means that as the acidity of the carboxylic acid increases, the value of $ \left( {K_a} \right) $ increases but the value of $ p{K_a} $ decreases.
Acidity of the carboxylic acid depends upon the nature of substituents. Presence of electron withdrawing groups like $ \left( {Cl,N{O_2},CN} \right) $ generally increases the acidic strength of the carboxylic acid.
Electron withdrawing group $ \left( { - I} \right) $ increases the acidity by various ways including:
These groups tend to delocalize the negative charge on oxygen atoms and therefore, increases the stability of carboxylate ions. As the stability of carboxylate ions increases, forward reaction is favored which further promotes dissociation of acid to release hydronium ions and that is how the acidity of compound increases.
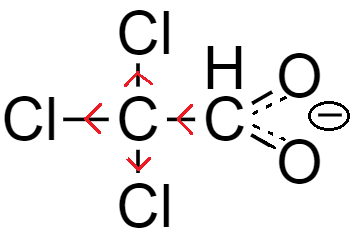
Another way to increase the acidity of carboxylic acid is by attracting the electron of the bond formed between oxygen and hydrogen atom of hydroxide functional group. As the electrons shift towards the oxygen atom due to pull exerted by the electron withdrawing group, hydrogen atom easily releases from the molecule and therefore, acidity of the carboxylic acid increases.
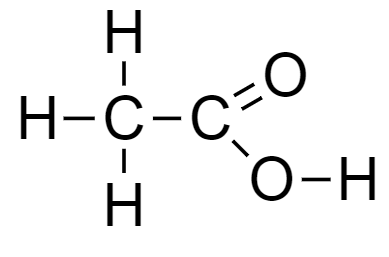
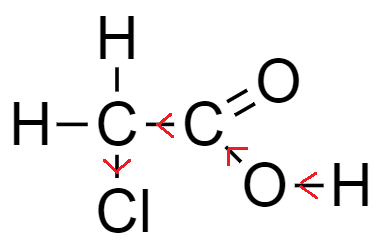
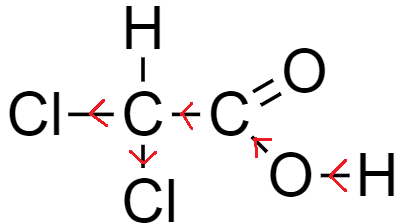
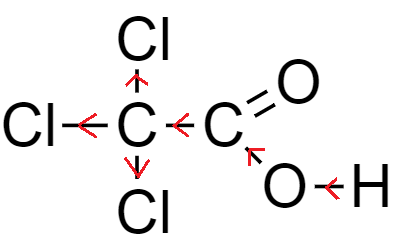
From the above-mentioned example, the number of chlorine atoms increases while the basic nucleus carboxylic acid remains the same, which is acetic acid.
We already see that with increase in electron withdrawing group in the molecule, acidic strength of the carboxylic acid increases. With increase in the number of chlorine atoms in the molecule $ \left( { - I} \right) $ effect of chlorine atoms increases and acidity increases.
Therefore, acidity of $ C{l_3}CCOOH $ is maximum because it contains the maximum number of chlorine atoms. Hence, the value of $ \left( {K_a} \right) $ is highest for $ C{l_3}CCOOH $ but the value of $ p{K_a} $ is minimum.
$ \Rightarrow $ Therefore, $ p{K_a} $ value of $ C{l_3}CCOOH $ is lowest due to presence of maximum inductive effect of chlorine atom.
Hence, option $ \left( D \right) $ is the correct option.
Note:
General rule for acidity of carboxylic acid is that higher the value of $ p{K_a} $ , the weaker the acid. Presence of electron donating group like $ \left( {C{H_3},C{H_3}OC{H_3}} \right) $ in the molecule decreases the charge delocalization and destabilize the molecule and hence, acidity of carboxylic acid decreases.
Complete answer:
The mathematical expression to evaluate strength of carboxylic acid is expressed as:
$ RCOOH + {H_2}O \rightleftharpoons RCO{O^ - } + {H_3}{O^ + } $
Dissociation constant for the above equation is:
$ K_a = \dfrac{{\left[ {RCO{O^ - }} \right]\left[ {{H_3}{O^ + }} \right]}}{{\left[ {RCOOH} \right]}} $
Dissociation constant is also expressed in terms of $ p{K_a} $ as:
$ p{K_a} $ $ = - \log K_a $
It means that as the acidity of the carboxylic acid increases, the value of $ \left( {K_a} \right) $ increases but the value of $ p{K_a} $ decreases.
Acidity of the carboxylic acid depends upon the nature of substituents. Presence of electron withdrawing groups like $ \left( {Cl,N{O_2},CN} \right) $ generally increases the acidic strength of the carboxylic acid.
Electron withdrawing group $ \left( { - I} \right) $ increases the acidity by various ways including:
These groups tend to delocalize the negative charge on oxygen atoms and therefore, increases the stability of carboxylate ions. As the stability of carboxylate ions increases, forward reaction is favored which further promotes dissociation of acid to release hydronium ions and that is how the acidity of compound increases.

Another way to increase the acidity of carboxylic acid is by attracting the electron of the bond formed between oxygen and hydrogen atom of hydroxide functional group. As the electrons shift towards the oxygen atom due to pull exerted by the electron withdrawing group, hydrogen atom easily releases from the molecule and therefore, acidity of the carboxylic acid increases.




From the above-mentioned example, the number of chlorine atoms increases while the basic nucleus carboxylic acid remains the same, which is acetic acid.
We already see that with increase in electron withdrawing group in the molecule, acidic strength of the carboxylic acid increases. With increase in the number of chlorine atoms in the molecule $ \left( { - I} \right) $ effect of chlorine atoms increases and acidity increases.
Therefore, acidity of $ C{l_3}CCOOH $ is maximum because it contains the maximum number of chlorine atoms. Hence, the value of $ \left( {K_a} \right) $ is highest for $ C{l_3}CCOOH $ but the value of $ p{K_a} $ is minimum.
$ \Rightarrow $ Therefore, $ p{K_a} $ value of $ C{l_3}CCOOH $ is lowest due to presence of maximum inductive effect of chlorine atom.
Hence, option $ \left( D \right) $ is the correct option.
Note:
General rule for acidity of carboxylic acid is that higher the value of $ p{K_a} $ , the weaker the acid. Presence of electron donating group like $ \left( {C{H_3},C{H_3}OC{H_3}} \right) $ in the molecule decreases the charge delocalization and destabilize the molecule and hence, acidity of carboxylic acid decreases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




