
Which of the following has regular tetrahedral shape?
a.) $I_{3}^{-}$
b.) $S{{F}_{4}}$
c.) ${{[B{{F}_{4}}]}^{-}}$
d.) $Xe{{F}_{4}}$
Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint: We can get the shape of any compound with the help of hybridization. The shape of the compound depends primarily on the no. of bond pairs and lone pairs, but every unique pair of bonds and lone there is specific value hybridization.
Complete step by step solution:
$H=\dfrac{(V+M-C+A)}{2}$
H= hybridization
V= valance on the central atom
M= monovalent group
C = charge on cation
A= charge on anion
We can predict the shape of any molecule or compound by its hybridization. After hybridization by this table we can find the shape of the compound.
The table is given below: -
Here l.p refers to Lone pair electrons and b.p refers to bond pair electrons.
Now we can solve the shapes of compounds by this above table.
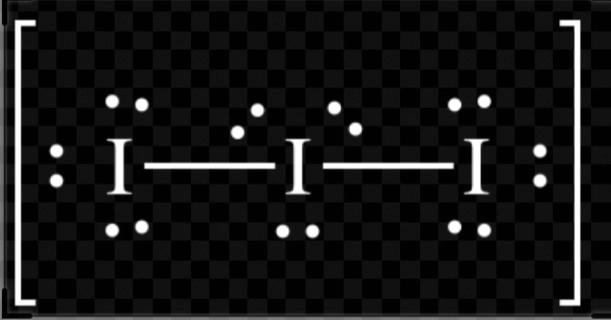
A. $I_{3}^{-}$
$H=\dfrac{(V+M-C+A)}{2}$
$H=\dfrac{(7+2-0+1)}{2}$
$H=\dfrac{10}{2}$= 5
So, hybridization of $I_{3}^{-}$= $s{{p}^{3}}d$
Shape= linear
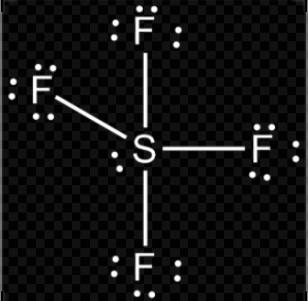
B. $S{{F}_{4}}$
$H=\dfrac{(V+M-C+A)}{2}$
$H=\dfrac{(6+4-0+0)}{2}$
$H=\dfrac{10}{2}$
So, hybridization of $S{{F}_{4}}$ = $s{{p}^{3}}d$
Shape = trigonal bipyramidal
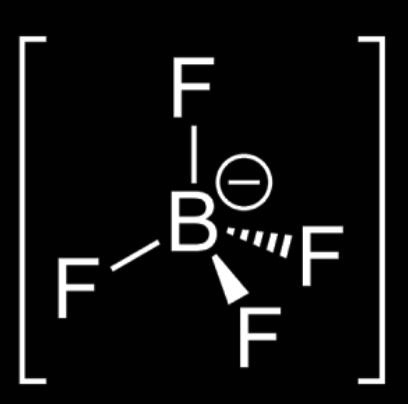
C. ${{[B{{F}_{4}}]}^{-}}$
$H=\dfrac{(V+M-C+A)}{2}$
$H=\dfrac{(3+4-2+1)}{2}$$H=\dfrac{(5+4-0+1)}{2}H=\dfrac{10}{2}$
$H=\dfrac{6}{2}$= 3
So, the Hybridization of molecule ${{[B{{F}_{4}}]}^{-}}$= $s{{p}^{2}}$
Shape = tetrahedral
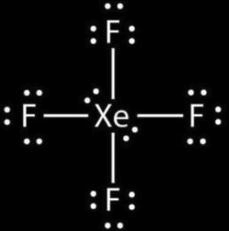
D. $Xe{{F}_{4}}$
$H=\dfrac{(V+M-C+A)}{2}$
$H=\dfrac{(5+4-0+1)}{2}$
$H=\dfrac{10}{2}$= 5
So, the hybridization of molecule $Xe{{F}_{4}}$= $s{{p}^{3}}d$
And shape = trigonal bipyramidal
Therefore, boron tetrafluoride has the regular shape of tetrahedral.
Note:
-Check the valence electron properly while calculation of hybridisation
-Check the charge of cation and anions on the molecule. It should also be taken into account
-Check the hybridization properly for concluding the final geometry of the molecule.
Complete step by step solution:
$H=\dfrac{(V+M-C+A)}{2}$
H= hybridization
V= valance on the central atom
M= monovalent group
C = charge on cation
A= charge on anion
We can predict the shape of any molecule or compound by its hybridization. After hybridization by this table we can find the shape of the compound.
The table is given below: -
| H= l.p.+ b.p. | Hybridization state | Shapes |
| 2 | $sp$ | Linear |
| 3 | $s{{p}^{2}}$ | Trigonal planar |
| 4 | $s{{p}^{3}}$ | Tetrahedral or pyramidal or v- shaped |
| 5 | $s{{p}^{3}}d$ | Trigonal bipyramidal or T- shaped or linear |
| 6 | $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ | Octahedral or square pyramid or planner |
| 7 | $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{3}}$ | Pentagonal bipyramidal or distorted or distorted pentagonal bipyramid |
Here l.p refers to Lone pair electrons and b.p refers to bond pair electrons.
Now we can solve the shapes of compounds by this above table.
A. $I_{3}^{-}$
$H=\dfrac{(V+M-C+A)}{2}$
$H=\dfrac{(7+2-0+1)}{2}$
$H=\dfrac{10}{2}$= 5
So, hybridization of $I_{3}^{-}$= $s{{p}^{3}}d$
Shape= linear

B. $S{{F}_{4}}$
$H=\dfrac{(V+M-C+A)}{2}$
$H=\dfrac{(6+4-0+0)}{2}$
$H=\dfrac{10}{2}$
So, hybridization of $S{{F}_{4}}$ = $s{{p}^{3}}d$
Shape = trigonal bipyramidal

C. ${{[B{{F}_{4}}]}^{-}}$
$H=\dfrac{(V+M-C+A)}{2}$
$H=\dfrac{(3+4-2+1)}{2}$$H=\dfrac{(5+4-0+1)}{2}H=\dfrac{10}{2}$
$H=\dfrac{6}{2}$= 3
So, the Hybridization of molecule ${{[B{{F}_{4}}]}^{-}}$= $s{{p}^{2}}$
Shape = tetrahedral

D. $Xe{{F}_{4}}$
$H=\dfrac{(V+M-C+A)}{2}$
$H=\dfrac{(5+4-0+1)}{2}$
$H=\dfrac{10}{2}$= 5
So, the hybridization of molecule $Xe{{F}_{4}}$= $s{{p}^{3}}d$
And shape = trigonal bipyramidal

Therefore, boron tetrafluoride has the regular shape of tetrahedral.
Note:
-Check the valence electron properly while calculation of hybridisation
-Check the charge of cation and anions on the molecule. It should also be taken into account
-Check the hybridization properly for concluding the final geometry of the molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




