
Which of the following compounds will not show enolization?
A.
B.
C.
D.




Answer
513.3k+ views
Hint: We all know that Conversion of ketones or aldehyde into an enol is called enolization. This process is also known as keto-enol tautomerism. Also Enols also known by the name alkenes where alkenes represented two groups in it i.e. the word is made up of alkene and ol which represent there is one alkene group and alcoholic group is present in the enol rather than alcohol ketone is also there.
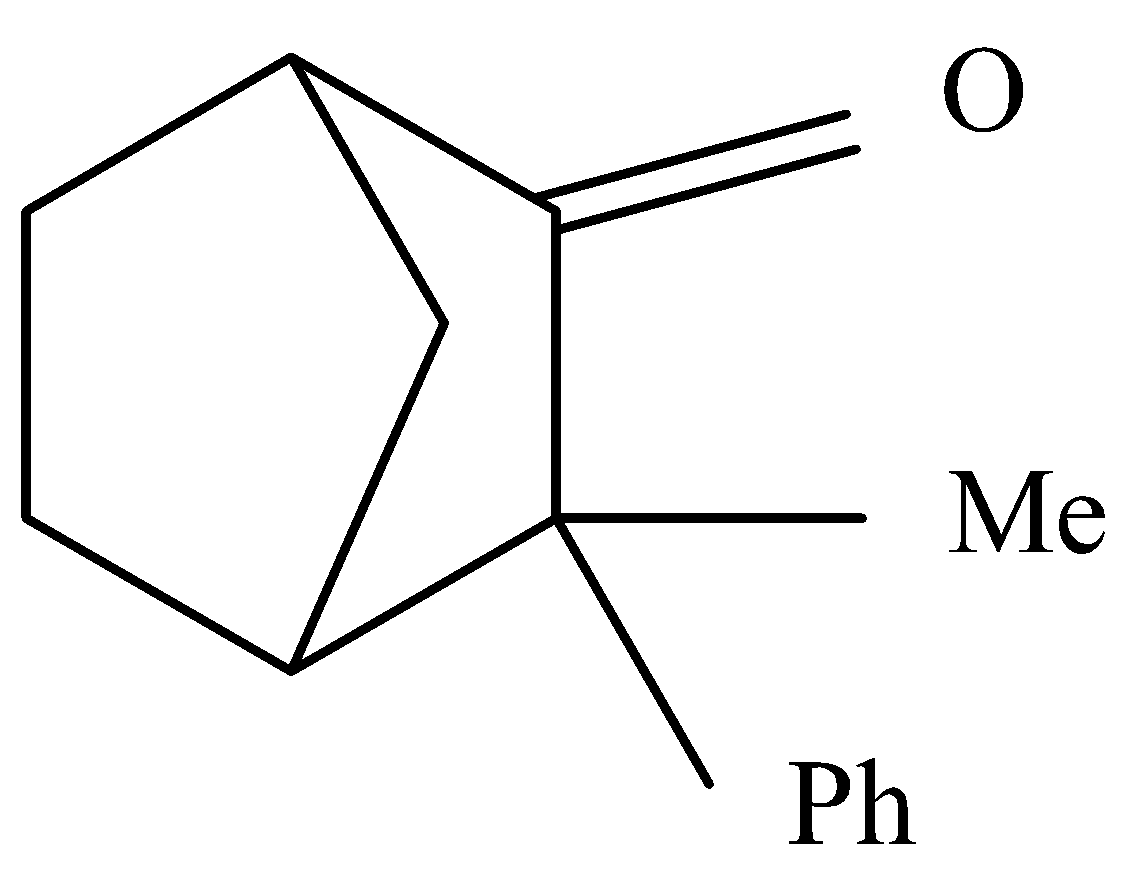
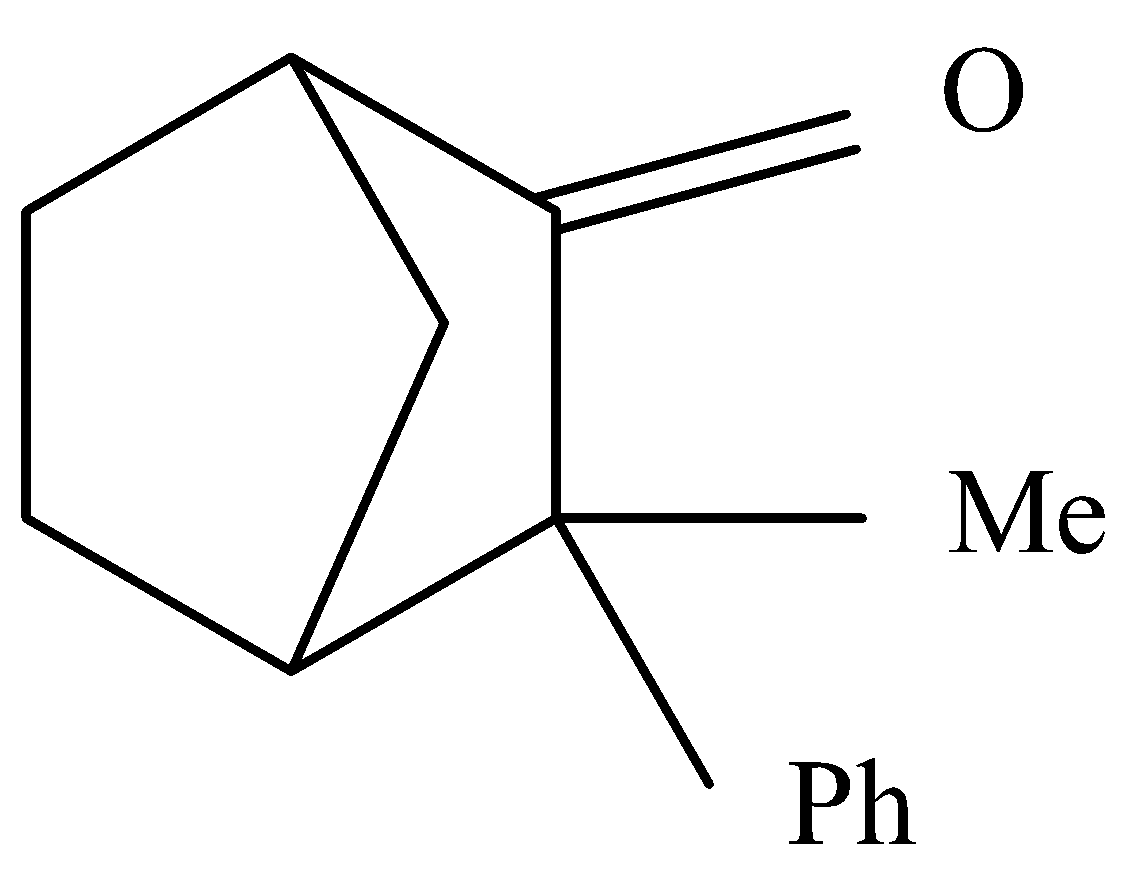
Complete answer: Enol are generally a type of reactive structure or intermediate in an organic chemistry where intermediate is that moiety which is produced from reactant and reacts further to produce product. This generally represented an alkene with hydroxyl group attached to one end of the alkene group. Here we know that the $\alpha $ hydrogen is required in a compound to undergo enolization. As seen in the below diagram there is an $\alpha $hydrogen present by , it cannot form a double bond because it is in the bridge head position , in this position the double bond is highly unstable.
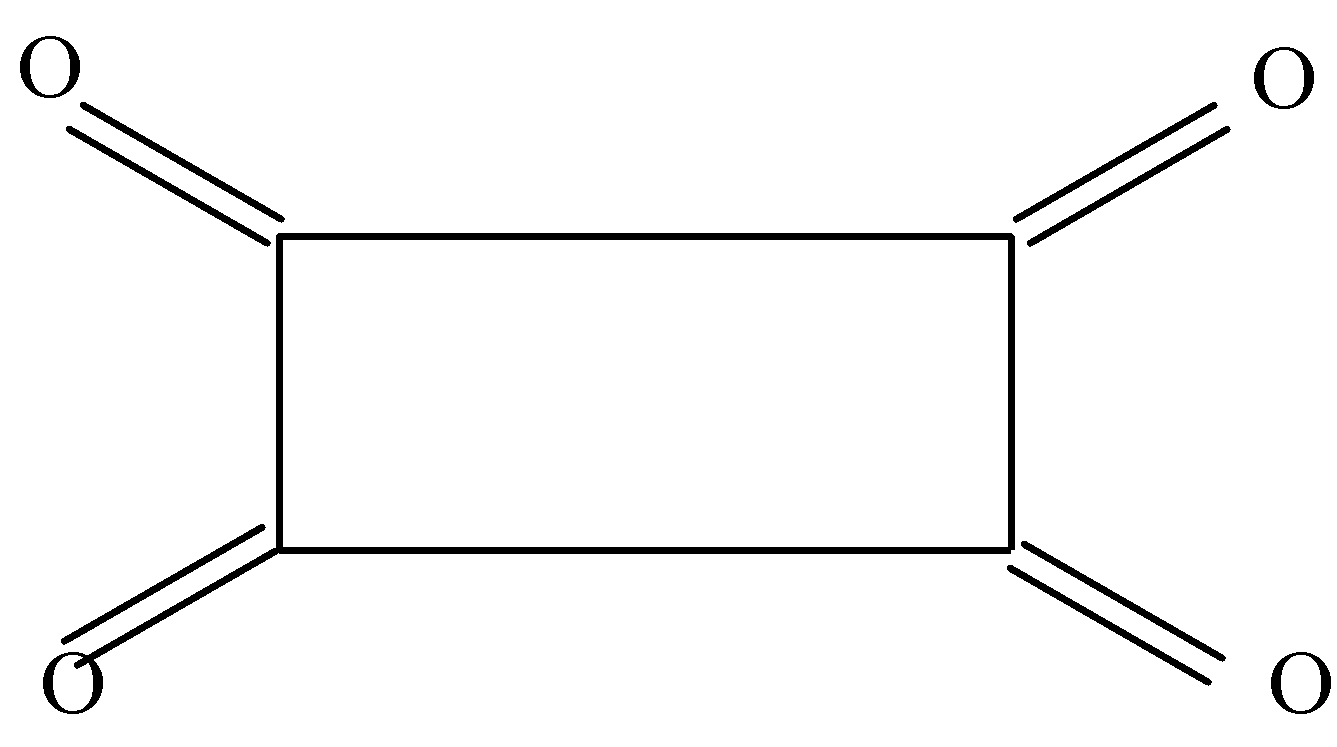
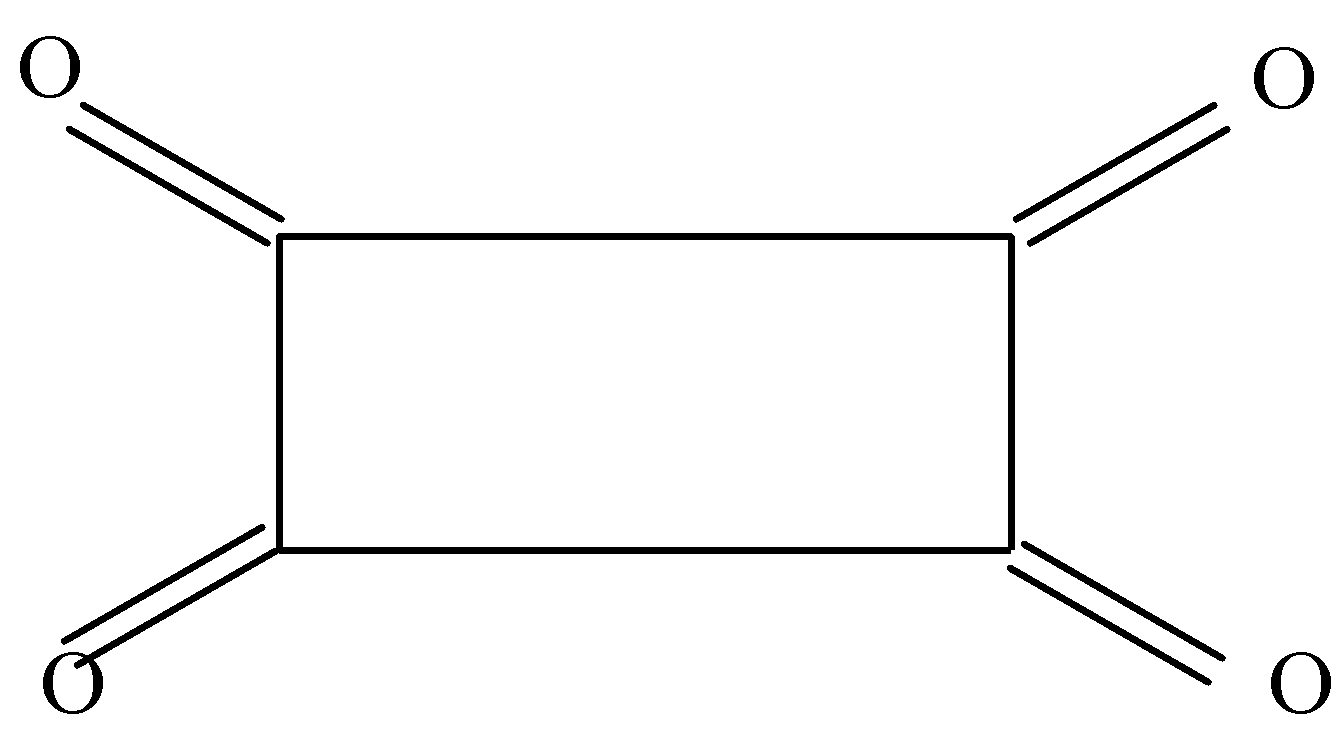
In the second option we can see that there are double bonds present on all sides of the rectangle and hence there is no $\alpha $ hydrogen to form enol.
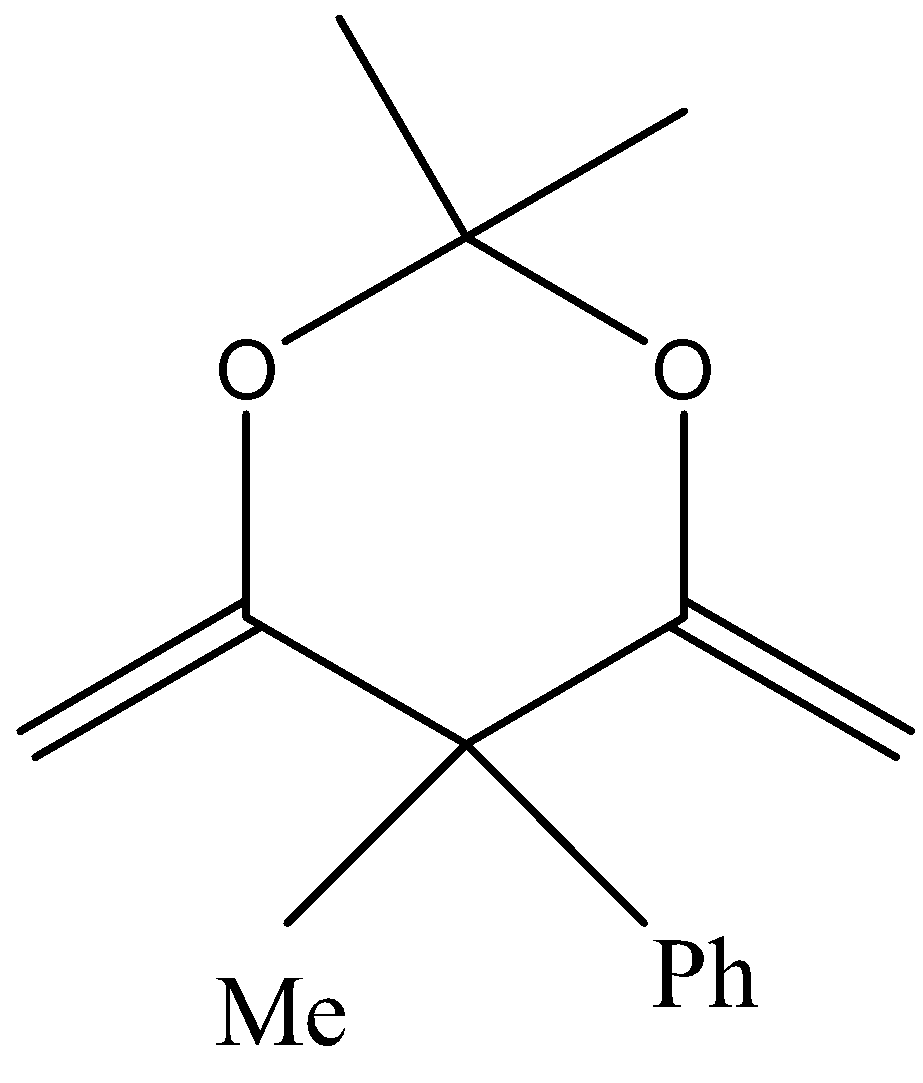
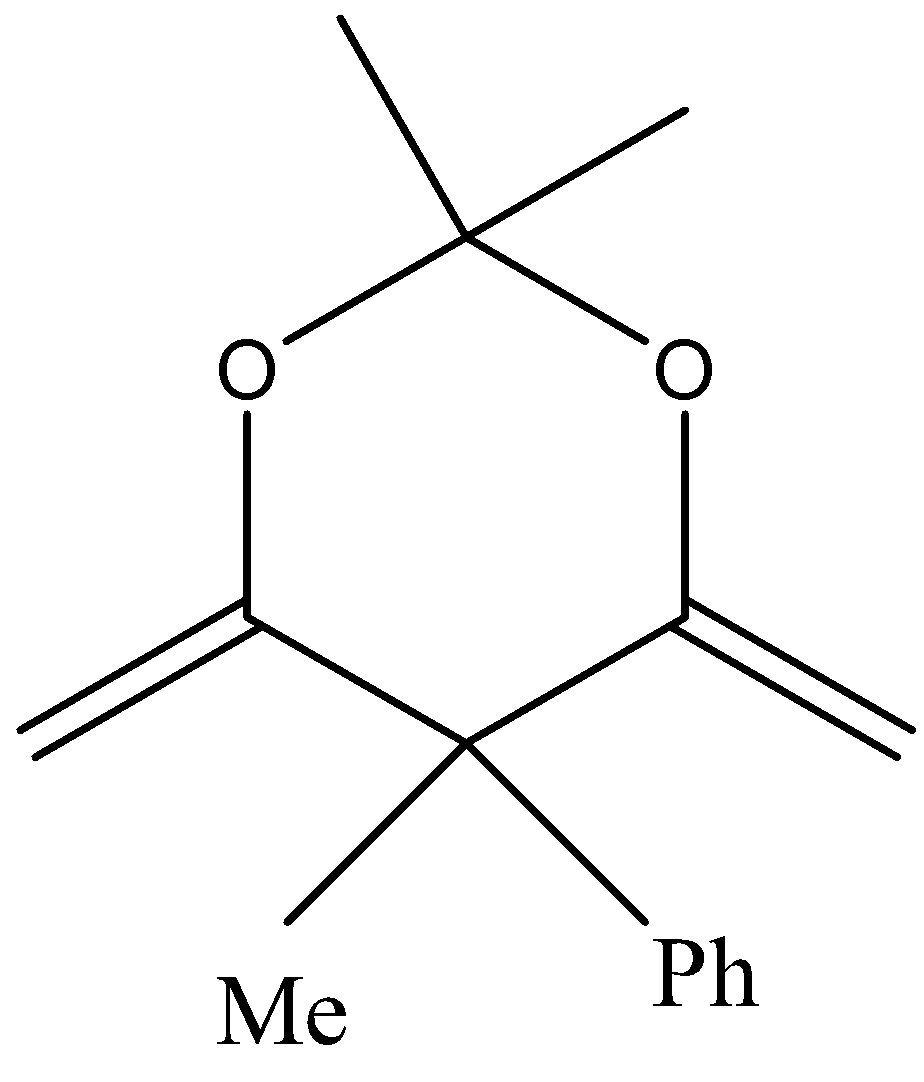
In the third option also we cannot see any $\alpha $hydrogen bond and hence no enol is formed.
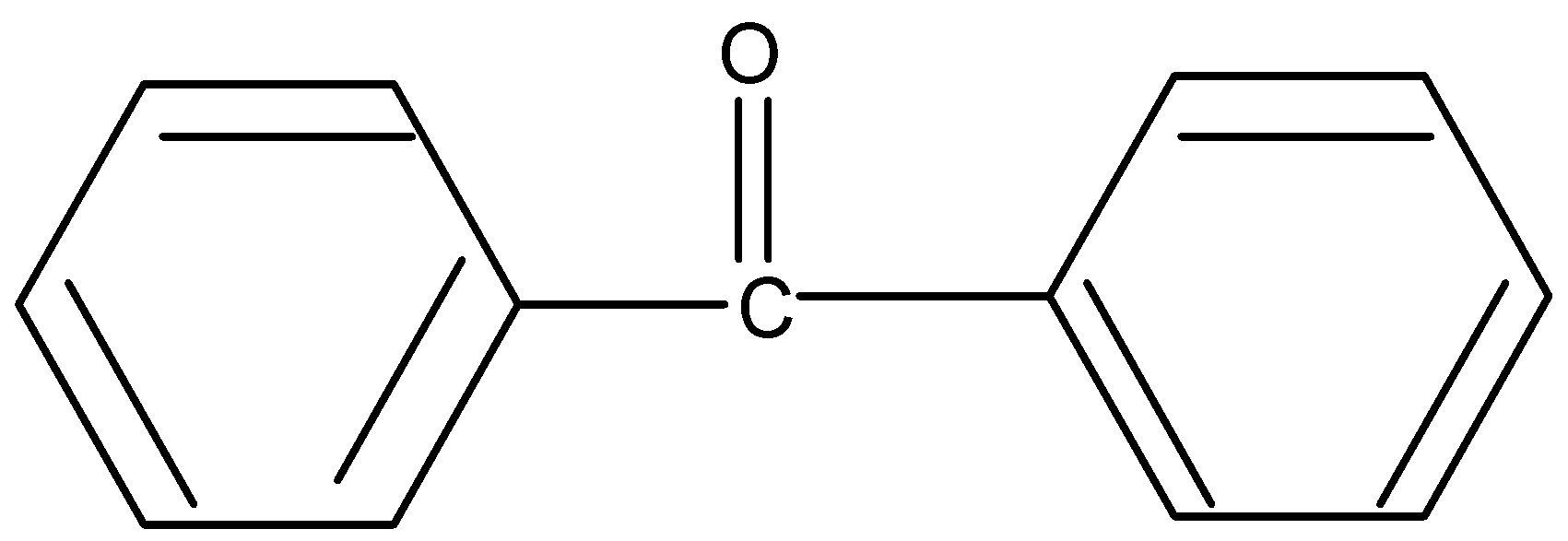
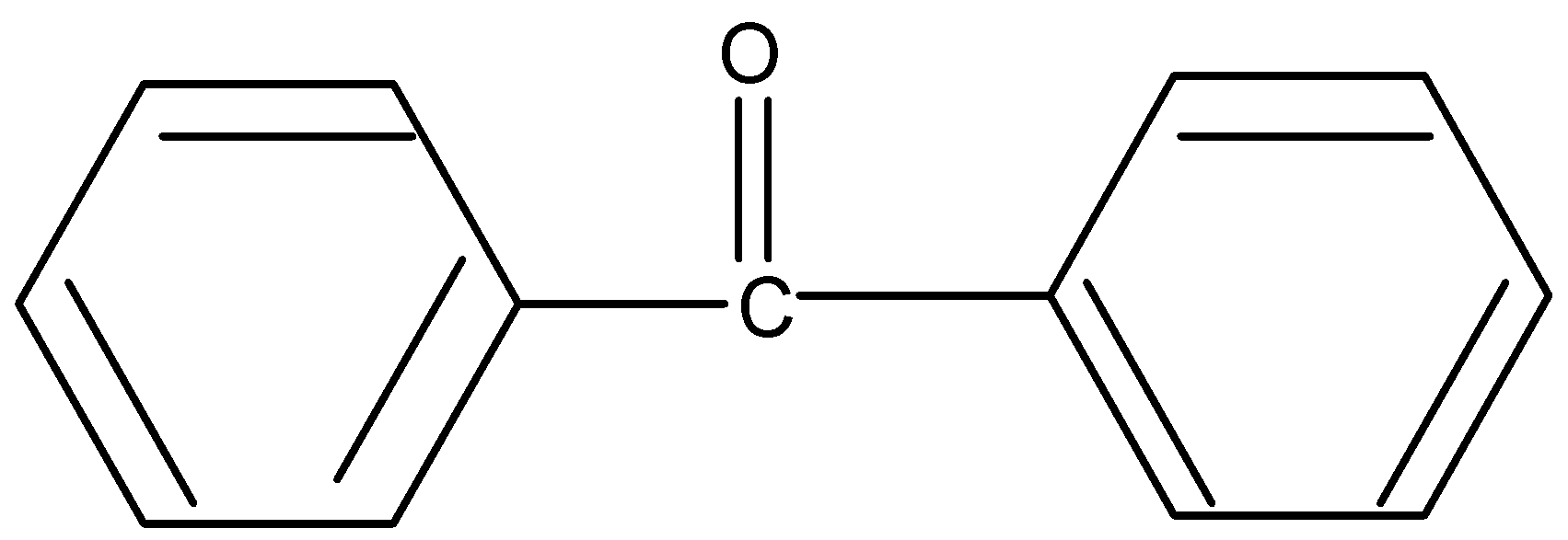
Similarly for option four lack of $\alpha $hydrogen resist enol formation.
Enolization occurs in both acid and base. But enolization in base is very common since it is a good catalyst.
Considering the above solution options A,B,C and D are all correct.
Note:
Remember that if the formation is in acidic form it is called enol. If the formation is in basic form it is called enolate. Enolisation also occurs in esters. Enols are basically the derivatives of vinyl alcohol. Deprotonation of enol gives enolate anions which are strong nucleophiles in nature. Enols have many applications in biochemistry, enzyme catalyzed reactions and in synthetic organic chemistry.
Complete answer: Enol are generally a type of reactive structure or intermediate in an organic chemistry where intermediate is that moiety which is produced from reactant and reacts further to produce product. This generally represented an alkene with hydroxyl group attached to one end of the alkene group. Here we know that the $\alpha $ hydrogen is required in a compound to undergo enolization. As seen in the below diagram there is an $\alpha $hydrogen present by , it cannot form a double bond because it is in the bridge head position , in this position the double bond is highly unstable.

In the second option we can see that there are double bonds present on all sides of the rectangle and hence there is no $\alpha $ hydrogen to form enol.

In the third option also we cannot see any $\alpha $hydrogen bond and hence no enol is formed.

Similarly for option four lack of $\alpha $hydrogen resist enol formation.

Enolization occurs in both acid and base. But enolization in base is very common since it is a good catalyst.
Considering the above solution options A,B,C and D are all correct.
Note:
Remember that if the formation is in acidic form it is called enol. If the formation is in basic form it is called enolate. Enolisation also occurs in esters. Enols are basically the derivatives of vinyl alcohol. Deprotonation of enol gives enolate anions which are strong nucleophiles in nature. Enols have many applications in biochemistry, enzyme catalyzed reactions and in synthetic organic chemistry.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




