
Which of the following acids does not exhibit optical isomerism?
A. Tartaric acid
B. Lactic acid
C. Maleic acid
D. $\alpha -$ amino acid
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: Optical isomers are molecules that differ from each other in their behavior towards plane polarized light. Optical isomers have different three-dimensional arrangements of the same atoms / groups in a molecule.
Complete Solution :
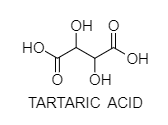
A. Tartaric Acid has two chiral centers yet two of the four potential stereo isomers of this compound are indistinguishable.
In this way there are three stereo-isomeric tartaric acids. Two of these stereo isomers are enantiomers and the third is an achiral diastereomers, called a meso compound.
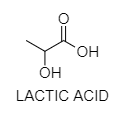
B. Optical activity of lactic acid. In lactic acid particles there is an asymmetrical chiral carbon molecule with four distinct groups which lead to two spatial setups (d-lactic acid l-lactic acid) which are super imposable mirror representations of one another.
- At the point when a plane polarized light is gone through a lactic acid arrangement the plane of polarized light gas rotates through a specific angle. This property of rotating the plane of polarized light towards right (clockwise) or towards (left)(anticlockwise) is called optical activity.
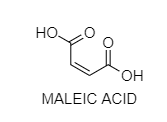
C. Maleic acid does not exhibit optical isomerism as it does not contain chiral C-atoms.
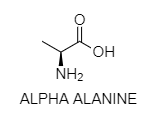
D. The carbon atom next to the carboxyl group (which is therefore numbered 2 in the carbon chain starting from that functional group) is called the -carbon. Amino acids containing an amino group bonded straightforwardly to the alpha carbon are known as alpha amino acids.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: The possibility of making a mistake is that you may confuse between chiral and achiral. The property of non-superimposability is called chirality and the property of superimposability is called achirality.
Complete Solution :
A. Tartaric Acid has two chiral centers yet two of the four potential stereo isomers of this compound are indistinguishable.
In this way there are three stereo-isomeric tartaric acids. Two of these stereo isomers are enantiomers and the third is an achiral diastereomers, called a meso compound.

B. Optical activity of lactic acid. In lactic acid particles there is an asymmetrical chiral carbon molecule with four distinct groups which lead to two spatial setups (d-lactic acid l-lactic acid) which are super imposable mirror representations of one another.
- At the point when a plane polarized light is gone through a lactic acid arrangement the plane of polarized light gas rotates through a specific angle. This property of rotating the plane of polarized light towards right (clockwise) or towards (left)(anticlockwise) is called optical activity.

C. Maleic acid does not exhibit optical isomerism as it does not contain chiral C-atoms.

D. The carbon atom next to the carboxyl group (which is therefore numbered 2 in the carbon chain starting from that functional group) is called the -carbon. Amino acids containing an amino group bonded straightforwardly to the alpha carbon are known as alpha amino acids.

So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: The possibility of making a mistake is that you may confuse between chiral and achiral. The property of non-superimposability is called chirality and the property of superimposability is called achirality.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




