
Which class of lever always has \[M.A.>1\] and why?
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: A lever is a simple machine consisting of a bar that rotates around a fixed point called the fulcrum. \[M.A.\] of a lever is the mechanical advantage of a lever which is given as by dividing the distance from the fulcrum to the applied force by the distance from the fulcrum to the resistance force.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all, we must know that there are three basic classes of lever, called first-class, second-class, and third-class. A lever consists of a bar that rotates around a fulcrum. The mechanical advantage of a system is given by,
\[M.A.=\dfrac{{{f}_{input}}}{{{f}_{output}}}\]
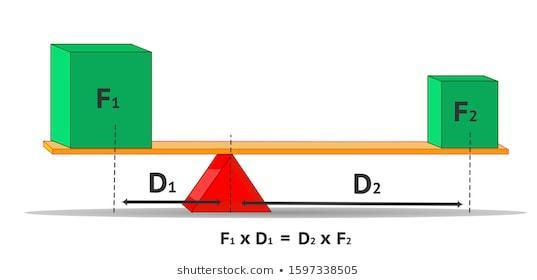
Then, in this case, \[M.A.=\dfrac{{{F}_{e}}}{{{F}_{r}}}\].
Now, let us compare all three classes of levers by analyzing the given figure,
In the first-class levers, the input force and output forces are on opposite sides of the fulcrum, the lever changes the direction of applied force. As both forces are the same distance from the fulcrum, the input distance equals to the output distance. So, the mechanical advantage will be equal to 1. i.e. \[M.A.=1\].
For both second and third class levers, the input and output forces are on the same side of the fulcrum, so the direction of applied force doesn’t change. In second-class levers, the input force applied is always farther from the fulcrum, I.e. the input distance is greater than the output distance, so the mechanical advantage will be always greater than 1. i.e. \[M.A.>1\].
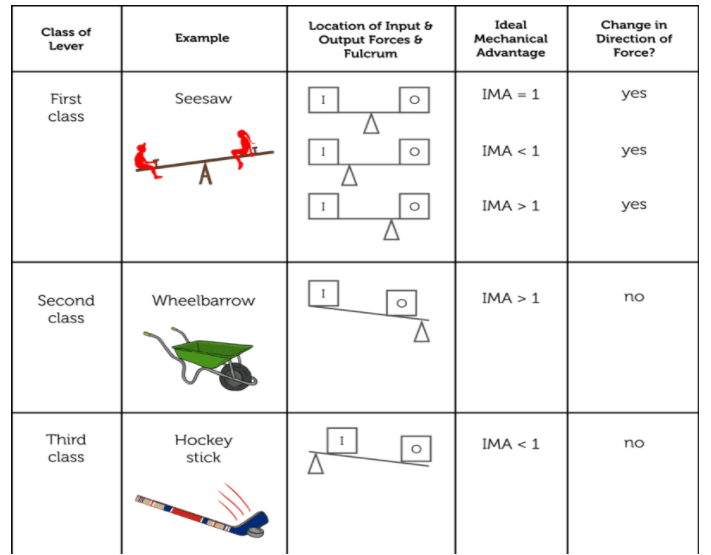
In the case of third-class levers, the input force applied is closer, so the input distance is less than the output distance. So the mechanical advantage will always be less than 1. i.e. \[M.A.<1\].
So, we can conclude that second-class levers will always have the mechanical advantage greater than 1.
Note:
In the case of levers, only a first-class lever changes the direction of the force. Even the \[M.A.<1\] for the third-class lever, there is an advantage of using them that the output force is applied over a greater distance than input force which means that the output end of the lever moves faster than the input end.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all, we must know that there are three basic classes of lever, called first-class, second-class, and third-class. A lever consists of a bar that rotates around a fulcrum. The mechanical advantage of a system is given by,
\[M.A.=\dfrac{{{f}_{input}}}{{{f}_{output}}}\]

Then, in this case, \[M.A.=\dfrac{{{F}_{e}}}{{{F}_{r}}}\].
Now, let us compare all three classes of levers by analyzing the given figure,
In the first-class levers, the input force and output forces are on opposite sides of the fulcrum, the lever changes the direction of applied force. As both forces are the same distance from the fulcrum, the input distance equals to the output distance. So, the mechanical advantage will be equal to 1. i.e. \[M.A.=1\].
For both second and third class levers, the input and output forces are on the same side of the fulcrum, so the direction of applied force doesn’t change. In second-class levers, the input force applied is always farther from the fulcrum, I.e. the input distance is greater than the output distance, so the mechanical advantage will be always greater than 1. i.e. \[M.A.>1\].

In the case of third-class levers, the input force applied is closer, so the input distance is less than the output distance. So the mechanical advantage will always be less than 1. i.e. \[M.A.<1\].
So, we can conclude that second-class levers will always have the mechanical advantage greater than 1.
Note:
In the case of levers, only a first-class lever changes the direction of the force. Even the \[M.A.<1\] for the third-class lever, there is an advantage of using them that the output force is applied over a greater distance than input force which means that the output end of the lever moves faster than the input end.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




