
Which carbohydrate is used in silvering of mirrors?
A.Fructose
B.Glucose
C.Sucrose
D.Starch
Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint:Carbohydrates are defined as polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones and their derivatives. And are composed of carbon , hydrogen and oxygen. Carbohydrates have great importance in both the biological and commercial world, because they are used as a source of energy in all organisms and as structural materials in membrane cell walls.
Carbohydrates have general formula given by
${{\text{C}}_{\text{x}}}{\left( {{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}} \right)_{\text{y}}}$
Complete answer:
Carbohydrates are mainly classified into three types Monosaccharides, Oligosaccharides and Polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are simple sugars possessing a free aldehyde (-CHO) or ketone (C=O) group and two or more hydroxyl (-OH) groups. Simplest sugars which cannot be hydrolysed further into smaller units. Basically monosaccharides are reducing sugars.
Examples for monosaccharides:
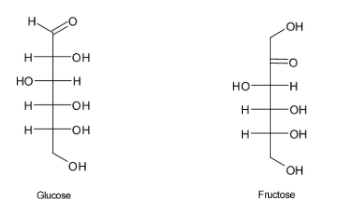
In glucose aldehyde group is the main functional group and in fructose the functional group present is ketone.
Oligosaccharides are carbohydrates , which is made up of two or more monosaccharides units joined together by condensation reaction. 2 to 10 molecules of the same or different monosaccharides can be joined together to form oligosaccharides. A glycosidic bond is formed between two monosaccharides. On hydrolysis oligosaccharides yields two to ten molecules of the same or different monosaccharides. Based on the number of monosaccharides , which oligosaccharides yield on hydrolysis it is further classified into disaccharides , trisaccharide and tetra saccharides etc..
Examples for oligosaccharides are
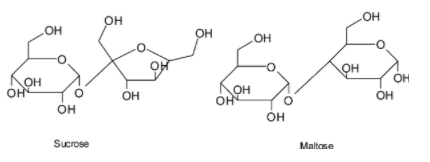
Sucrose is formed by linking of two monosaccharides glucose and fructose , whereas maltose is formed when two glucose are linked together. Linkage is called glycosidic linkage.
Polysaccharides are those which contain 10 or more monosaccharides units.
Example is starch. Starch consists of a large number of glucose units by glycosidic linkage .
Now we look at the main reaction which is given by carbohydrates.
An important reaction which is undergone by monosaccharides is the oxidation of the aldehyde group, monosaccharides which contain aldehyde as a functional group is glucose. Aldehyde is most easily oxidized with any mild oxidizing agent such as tollens reagent. It is called the Tollens test.
Tollens test is also known as silver mirror test, which is used to distinguish between aldehyde and ketone because it is already known that aldehydes readily oxidize with mild oxidizing agents where ketones are not. Only aldehydes gives tollens test.
Tollens test we are using tollens reagent which is basic aqueous solution containing silver ions that are coordinated with ammonia $\left[ {{\text{Ag}}{{\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)}^{2 + }}} \right]$
This tollens reagent oxidizes aldehyde to corresponding carboxylic acid
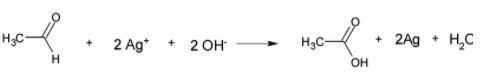
So here the aldehyde is oxidised by silver(I) to carboxylic acid and silver (I) is reduced by the aldehyde forming atomic silver which forms a mirror in the atomic flask.
So hence the monosaccharide which contains aldehyde group is glucose so glucose being the reducing sugar undergo tollens test giving silver mirror.
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Note:
A glycosidic bond is formed between two monosaccharides. If carbon 1 of the one monosaccharide joins carbon 4 on the other monosaccharide then it is called a 1,4- glycosidic bond. Glucose exists in both straight chain and ring form. In carbohydrates hydrogen and oxygen being present in a 2:1 ratio.
Carbohydrates have general formula given by
${{\text{C}}_{\text{x}}}{\left( {{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}} \right)_{\text{y}}}$
Complete answer:
Carbohydrates are mainly classified into three types Monosaccharides, Oligosaccharides and Polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are simple sugars possessing a free aldehyde (-CHO) or ketone (C=O) group and two or more hydroxyl (-OH) groups. Simplest sugars which cannot be hydrolysed further into smaller units. Basically monosaccharides are reducing sugars.
Examples for monosaccharides:

In glucose aldehyde group is the main functional group and in fructose the functional group present is ketone.
Oligosaccharides are carbohydrates , which is made up of two or more monosaccharides units joined together by condensation reaction. 2 to 10 molecules of the same or different monosaccharides can be joined together to form oligosaccharides. A glycosidic bond is formed between two monosaccharides. On hydrolysis oligosaccharides yields two to ten molecules of the same or different monosaccharides. Based on the number of monosaccharides , which oligosaccharides yield on hydrolysis it is further classified into disaccharides , trisaccharide and tetra saccharides etc..
Examples for oligosaccharides are

Sucrose is formed by linking of two monosaccharides glucose and fructose , whereas maltose is formed when two glucose are linked together. Linkage is called glycosidic linkage.
Polysaccharides are those which contain 10 or more monosaccharides units.
Example is starch. Starch consists of a large number of glucose units by glycosidic linkage .
Now we look at the main reaction which is given by carbohydrates.
An important reaction which is undergone by monosaccharides is the oxidation of the aldehyde group, monosaccharides which contain aldehyde as a functional group is glucose. Aldehyde is most easily oxidized with any mild oxidizing agent such as tollens reagent. It is called the Tollens test.
Tollens test is also known as silver mirror test, which is used to distinguish between aldehyde and ketone because it is already known that aldehydes readily oxidize with mild oxidizing agents where ketones are not. Only aldehydes gives tollens test.
Tollens test we are using tollens reagent which is basic aqueous solution containing silver ions that are coordinated with ammonia $\left[ {{\text{Ag}}{{\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)}^{2 + }}} \right]$
This tollens reagent oxidizes aldehyde to corresponding carboxylic acid

So here the aldehyde is oxidised by silver(I) to carboxylic acid and silver (I) is reduced by the aldehyde forming atomic silver which forms a mirror in the atomic flask.
So hence the monosaccharide which contains aldehyde group is glucose so glucose being the reducing sugar undergo tollens test giving silver mirror.
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Note:
A glycosidic bond is formed between two monosaccharides. If carbon 1 of the one monosaccharide joins carbon 4 on the other monosaccharide then it is called a 1,4- glycosidic bond. Glucose exists in both straight chain and ring form. In carbohydrates hydrogen and oxygen being present in a 2:1 ratio.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




