
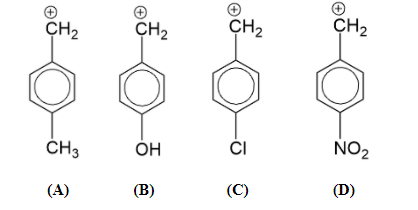
Which carbocation is the most stable?

Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: Carbocations are stabilized by the effect of electron donation tendency of groups. So, in this question we have to find which of the following groups which are attached at para position is most electron donating in nature.
Complete step by step answer:
First, we have to get some basic ideas about carbocation.
A carbocation is a molecule in which a carbon atom has a positive charge on it and three bonds attached to other elements or compounds. We can basically say that they are carbon cations. Carbocation today is defined as any even-electron cation that possesses a positive charge on the carbon atom.
The carbocations are very reactive and unstable due to an incomplete octet. In other words, carbocations do not have eight electrons, therefore they do not satisfy the octet rule so they are unstable in nature and want to fulfil their octet.
In carbocation, the hybridization of carbon will be $s{p^2}$ and its shape will be trigonal planar. There is also a vacant p orbital which indicates that they are electron-deficient in nature. The carbocation has 6 electrons in its valence shell. Due to this, it is an electron-deficient species, also called an electrophile.
Now, to find the answer to the above question, we have to know the electron donating tendency of different groups and also have to get some basic idea about inductive and mesomeric effects. Let's talk about them:
- Inductive effect: In chemistry, the inductive effect is an effect of transmission of unequal sharing of the bonding electron through a chain of atoms in a molecule, leading to a permanent dipole moment in a bond. The electron-withdrawing inductive effect is known as the -I effect and groups which tend to donate electrons is known as the +I effect.
- Mesomeric effect: The mesomeric effect is a property of substituents or functional groups in a chemical compound. It is the polarity produced in the molecule by the interaction of two pi bonds or between a pi bond and lone pair of electrons present on an adjacent atom. The effect is used in a qualitative way and describes the electron withdrawing or releasing properties of substituents and is symbolized by the letter M. The mesomeric effect is negative (–M) when the substituent is an electron-withdrawing group and the effect is positive (+M) when the substituent is an electron donating group.
According to the above discussion we can say that the correct answer is option (B) since the oxygen of OH has lone pair and due to mesomeric effect, it will stabilize the carbocation by a great extent.
Note: In the questions which include the stability of carbocation or carbanion, the mesomeric effect will only work when the groups with +M or -M characteristics are attached to ortho or para position with respect to the position of carbocation or carbanion.
Complete step by step answer:
First, we have to get some basic ideas about carbocation.
A carbocation is a molecule in which a carbon atom has a positive charge on it and three bonds attached to other elements or compounds. We can basically say that they are carbon cations. Carbocation today is defined as any even-electron cation that possesses a positive charge on the carbon atom.
The carbocations are very reactive and unstable due to an incomplete octet. In other words, carbocations do not have eight electrons, therefore they do not satisfy the octet rule so they are unstable in nature and want to fulfil their octet.
In carbocation, the hybridization of carbon will be $s{p^2}$ and its shape will be trigonal planar. There is also a vacant p orbital which indicates that they are electron-deficient in nature. The carbocation has 6 electrons in its valence shell. Due to this, it is an electron-deficient species, also called an electrophile.
Now, to find the answer to the above question, we have to know the electron donating tendency of different groups and also have to get some basic idea about inductive and mesomeric effects. Let's talk about them:
- Inductive effect: In chemistry, the inductive effect is an effect of transmission of unequal sharing of the bonding electron through a chain of atoms in a molecule, leading to a permanent dipole moment in a bond. The electron-withdrawing inductive effect is known as the -I effect and groups which tend to donate electrons is known as the +I effect.
- Mesomeric effect: The mesomeric effect is a property of substituents or functional groups in a chemical compound. It is the polarity produced in the molecule by the interaction of two pi bonds or between a pi bond and lone pair of electrons present on an adjacent atom. The effect is used in a qualitative way and describes the electron withdrawing or releasing properties of substituents and is symbolized by the letter M. The mesomeric effect is negative (–M) when the substituent is an electron-withdrawing group and the effect is positive (+M) when the substituent is an electron donating group.
According to the above discussion we can say that the correct answer is option (B) since the oxygen of OH has lone pair and due to mesomeric effect, it will stabilize the carbocation by a great extent.
Note: In the questions which include the stability of carbocation or carbanion, the mesomeric effect will only work when the groups with +M or -M characteristics are attached to ortho or para position with respect to the position of carbocation or carbanion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




