
Which behaves both as a nucleophile and electrophile?
A.\[C{H_3}N{H_2}\]
B.\[C{H_3}OH\]
C.\[C{H_3}CN\]
D.\[C{H_3}Cl\]
Answer
517.5k+ views
Hint: When any atom in the molecule is electron deficient and has a tendency to accept electrons, then it is termed as an electrophile. In simple words, these are electron loving molecules. When any atom in the molecule is electron rich and has a tendency to donate electrons, then it is termed as a nucleophile. In simple words, these are nucleus loving molecules.
Complete answer:
A molecule can behave as both nucleophile as well as electrophile when there are both possibilities i.e., donating electrons and accepting electrons. It can be possible only in two ways which are explained as follows:
Case-1: If an electronegative element with lone pairs is bonded to the molecule via double or triple bond, then the molecule can behave as both electrophile as well as nucleophile. As, the atom with lone pair can donate its electrons and will behave as a nucleophile whereas the element connected via double bond can accept electrons and will behave as an electrophile.
For example, the structure of carbonyl compound is shown below:
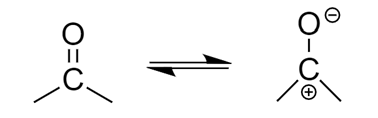
Hence, due to electronegativity difference, bonds become polar and therefore the molecule can act as both, a nucleophile as well as an electrophile.
Case-2: If the molecule is present in the form of zwitterion, then the positively charged group will act as an electrophile whereas the negatively charged group will behave as a nucleophile.
For example:
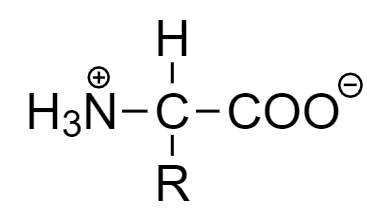
In the given compound, nitrogen atom will act as an electrophile and oxygen atom will act as nucleophile.
Now among the given options, the only compound which satisfies case-1 is \[C{H_3}CN\] because due to presence of lone pairs on nitrogen atom, it can act as a nucleophile and as it is connected to carbon atom via triple bond, so the carbon atom acts as an electrophile. Hence, \[C{H_3}CN\] behaves both as a nucleophile and electrophile.
Thus, option (C) is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to note that the compounds which are nucleophiles are also referred to as Lewis bases and the compounds which are electrophiles are referred to as Lewis acids. Also, the strength of nucleophilicity and electrophilicity changes according to the electronegativity of the atoms.
Complete answer:
A molecule can behave as both nucleophile as well as electrophile when there are both possibilities i.e., donating electrons and accepting electrons. It can be possible only in two ways which are explained as follows:
Case-1: If an electronegative element with lone pairs is bonded to the molecule via double or triple bond, then the molecule can behave as both electrophile as well as nucleophile. As, the atom with lone pair can donate its electrons and will behave as a nucleophile whereas the element connected via double bond can accept electrons and will behave as an electrophile.
For example, the structure of carbonyl compound is shown below:

Hence, due to electronegativity difference, bonds become polar and therefore the molecule can act as both, a nucleophile as well as an electrophile.
Case-2: If the molecule is present in the form of zwitterion, then the positively charged group will act as an electrophile whereas the negatively charged group will behave as a nucleophile.
For example:

In the given compound, nitrogen atom will act as an electrophile and oxygen atom will act as nucleophile.
Now among the given options, the only compound which satisfies case-1 is \[C{H_3}CN\] because due to presence of lone pairs on nitrogen atom, it can act as a nucleophile and as it is connected to carbon atom via triple bond, so the carbon atom acts as an electrophile. Hence, \[C{H_3}CN\] behaves both as a nucleophile and electrophile.
Thus, option (C) is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to note that the compounds which are nucleophiles are also referred to as Lewis bases and the compounds which are electrophiles are referred to as Lewis acids. Also, the strength of nucleophilicity and electrophilicity changes according to the electronegativity of the atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




