
What is the product of the reaction?
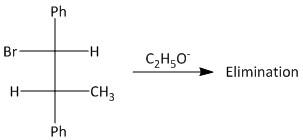

Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint:Elimination reaction is a type of organic chemical reaction in which the two substituents are removed from a compound or molecule via one step or two steps. The ethoxide ion serves as a base for abstracting protons.
Complete step by step answer:
Elimination reaction leads to removal of molecules from a compound. The leaving groups result in dehydration and dehydrohalogenation. The elimination reaction is of three types, \[E1\] , \[E2\] and \[E1cb\].
-The mechanism of elimination reaction depends on the thermodynamics and the kinetics of a reaction. The mechanism involves abstraction of protons and removal of leaving groups with formation of pi bond.
-In the given compound the bromo group attached to the carbon atom is the leaving group. The reaction takes place by abstraction of the proton present on the beta carbon atom adjacent to the bromo substituted carbon.
-The elimination results in formation of a double bond between the alpha and beta carbon atoms. The product of the reaction can be derived using the mechanism of the elimination reaction.
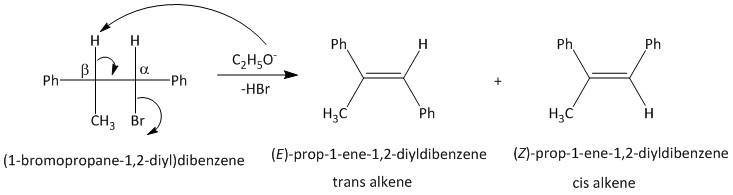
-Theoretically two products (trans and cis) are possible for an elimination reaction from a unsymmetrical alkane. The thermodynamic stability of the products and the mechanism of the reaction will decide the outcome of the product alkene and its configuration.
-In this compound (\[1\] -bromopropane-\[1,2\] -diyl)dibenzene, an \[E2\] type of elimination reaction or an anti elimination will occur to produce a trans alkene.
Note:
\[E1\] elimination is also competitive with the \[E2\] elimination. In \[E1\] elimination a carbanion is formed by abstraction of protons. The relative stability of the carbanion decides the product of the reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
Elimination reaction leads to removal of molecules from a compound. The leaving groups result in dehydration and dehydrohalogenation. The elimination reaction is of three types, \[E1\] , \[E2\] and \[E1cb\].
-The mechanism of elimination reaction depends on the thermodynamics and the kinetics of a reaction. The mechanism involves abstraction of protons and removal of leaving groups with formation of pi bond.
-In the given compound the bromo group attached to the carbon atom is the leaving group. The reaction takes place by abstraction of the proton present on the beta carbon atom adjacent to the bromo substituted carbon.
-The elimination results in formation of a double bond between the alpha and beta carbon atoms. The product of the reaction can be derived using the mechanism of the elimination reaction.

-Theoretically two products (trans and cis) are possible for an elimination reaction from a unsymmetrical alkane. The thermodynamic stability of the products and the mechanism of the reaction will decide the outcome of the product alkene and its configuration.
-In this compound (\[1\] -bromopropane-\[1,2\] -diyl)dibenzene, an \[E2\] type of elimination reaction or an anti elimination will occur to produce a trans alkene.
Note:
\[E1\] elimination is also competitive with the \[E2\] elimination. In \[E1\] elimination a carbanion is formed by abstraction of protons. The relative stability of the carbanion decides the product of the reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




