
What is the bond order of $C{{O}_{2}}$?
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: First you should know about the total number of bonds present in the $C{{O}_{2}}$ molecule and then, using the formula of bond order as;- $B.O.=\dfrac{Total\text{ no}\text{. }of\text{ }bonds}{no.\text{ }of\text{ }sigma\text{ }bonds}$, you can easily find the bond order of the given molecule. Now solve it.
Complete step by step answer:
First let's discuss carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is a gas which is formed by the reaction between the two non-metals i.e. carbon and oxygen. The chemical is supposed to take place as;-
$C+{{O}_{2}}\to C{{O}_{2}}$
Now coming next to the bond order. It is defined as the number of covalent bonds present between the two bonded atoms in a molecule. It is denoted as B.O. and can be found by dividing the total number present in the carbon dioxide molecule with the number of the sigma bonds present in the molecule.
Mathematically:-
$B.O.=\dfrac{Total\text{ no}\text{. }of\text{ }bonds}{no.\text{ }of\text{ }sigma\text{ }bonds}$
Now considering the statement as;-
The structure of the carbon dioxide molecule is as;-
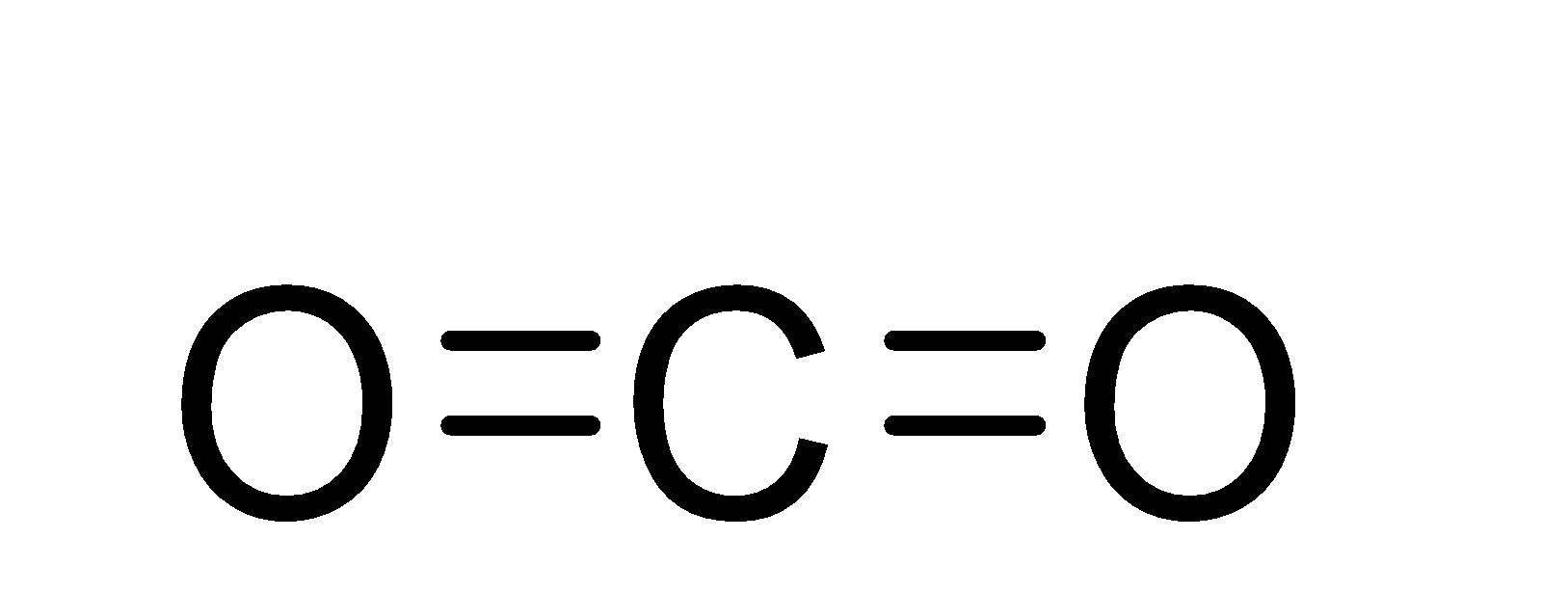
So, from the structure, we can see that there are a total number of four bonds in the carbon dioxide molecule and out of these 4 bonds, 2 are sigma bonds and two are pi-bonds.
So, the bond order of carbon dioxide molecule is as;-
$\begin{align}
& B.O = \dfrac{4}{2} \\
& \text{ =2} \\
\end{align}$
So, thus the bond order of carbon dioxide molecules is 2.
Note: The bond orders of 1,2 and 3 correspond to single, double and triple bonds but bond order can be fractional as well. The positive value of bond order indicates that the molecule is stable whereas the negative value indicates, the molecule is unstable.
Complete step by step answer:
First let's discuss carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is a gas which is formed by the reaction between the two non-metals i.e. carbon and oxygen. The chemical is supposed to take place as;-
$C+{{O}_{2}}\to C{{O}_{2}}$
Now coming next to the bond order. It is defined as the number of covalent bonds present between the two bonded atoms in a molecule. It is denoted as B.O. and can be found by dividing the total number present in the carbon dioxide molecule with the number of the sigma bonds present in the molecule.
Mathematically:-
$B.O.=\dfrac{Total\text{ no}\text{. }of\text{ }bonds}{no.\text{ }of\text{ }sigma\text{ }bonds}$
Now considering the statement as;-
The structure of the carbon dioxide molecule is as;-
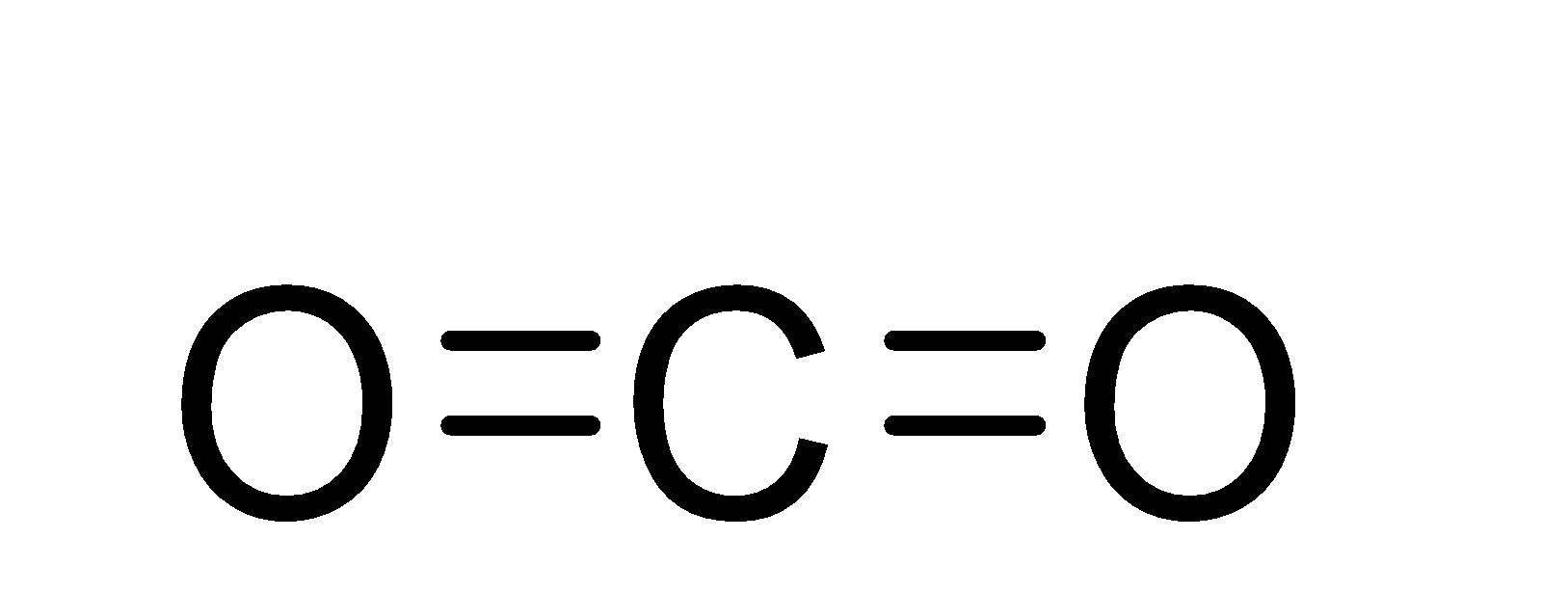
So, from the structure, we can see that there are a total number of four bonds in the carbon dioxide molecule and out of these 4 bonds, 2 are sigma bonds and two are pi-bonds.
So, the bond order of carbon dioxide molecule is as;-
$\begin{align}
& B.O = \dfrac{4}{2} \\
& \text{ =2} \\
\end{align}$
So, thus the bond order of carbon dioxide molecules is 2.
Note: The bond orders of 1,2 and 3 correspond to single, double and triple bonds but bond order can be fractional as well. The positive value of bond order indicates that the molecule is stable whereas the negative value indicates, the molecule is unstable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




