
What are apoplast and symplast?
Answer
393.3k+ views
Hint: Apoplasts are the non-living components of the cell. Water moves bulk through the cell wall and intercellular spaces because cortical cells are loosely packed, and there is no barrier to water transport. When water enters the endodermis, which contains the Casparian strip, it uses the symplast channel rather than the apoplast pathway to reach the xylem vessels. The apoplast route is faster than the symplast process because it does not require water to reach the cell membrane.
Complete step by step answer:
The apoplast is the region outside the plasma membrane where material can freely spread. The Casparian strip in roots, air gaps between plant cells, and the plant cuticle break it apart. The apoplast pathway allows water and solutes to be transported across a tissue or organ. This is known as an apoplastic transfer.
There are two transport pathways for moving water from one location to another. Water can take either a symplast or an apoplast route. The symplast is the channel by which water molecules migrate in cells' plasmodesmata area. The symplast is a live area between two cells that links one to the other. The apoplast route is the channel that water takes between intercellular gaps. The nonliving regions between cells and cell membranes are included in the apoplast.
Additional Information Water and low-molecular-weight solutes may readily pass through the symplast, the inner side of the plasma membrane. Symplast cells contain several nuclei. Water penetrates the cell's cytoplasm through the plasma membrane; hence, the symplastic route must cross cell membranes. The symplastic route is also known as the transmembrane pathway since it penetrates the cell membrane. Cytoplasmic streaming aids in the transport of water through the symplastic pathway.
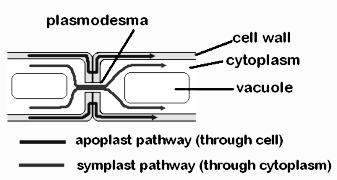
Image: Diagram showing apoplast and symplast.
Note: The apoplast pathway is a permeable path via which water moves via passive diffusion. On the other hand, the symplast is a selectively permeable pathway through which water moves by osmosis. Water and any solutes dissolved in water are prevented from flowing through this layer via the apoplast route by the endodermis. Water can also travel through the endodermis by crossing the endodermal cell membrane twice. Water going in and out of the apoplast's xylem, which is part of the apoplast, may be controlled since it must enter the endodermis's symplast.
Complete step by step answer:
The apoplast is the region outside the plasma membrane where material can freely spread. The Casparian strip in roots, air gaps between plant cells, and the plant cuticle break it apart. The apoplast pathway allows water and solutes to be transported across a tissue or organ. This is known as an apoplastic transfer.
There are two transport pathways for moving water from one location to another. Water can take either a symplast or an apoplast route. The symplast is the channel by which water molecules migrate in cells' plasmodesmata area. The symplast is a live area between two cells that links one to the other. The apoplast route is the channel that water takes between intercellular gaps. The nonliving regions between cells and cell membranes are included in the apoplast.
Additional Information Water and low-molecular-weight solutes may readily pass through the symplast, the inner side of the plasma membrane. Symplast cells contain several nuclei. Water penetrates the cell's cytoplasm through the plasma membrane; hence, the symplastic route must cross cell membranes. The symplastic route is also known as the transmembrane pathway since it penetrates the cell membrane. Cytoplasmic streaming aids in the transport of water through the symplastic pathway.

Image: Diagram showing apoplast and symplast.
Note: The apoplast pathway is a permeable path via which water moves via passive diffusion. On the other hand, the symplast is a selectively permeable pathway through which water moves by osmosis. Water and any solutes dissolved in water are prevented from flowing through this layer via the apoplast route by the endodermis. Water can also travel through the endodermis by crossing the endodermal cell membrane twice. Water going in and out of the apoplast's xylem, which is part of the apoplast, may be controlled since it must enter the endodermis's symplast.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell




