
What are Alkanes?
Answer
519.3k+ views
Hint: We have to remember that the hydrocarbons are the compounds having carbon and hydrogen atoms in them. They can be of three classes alkane, alkene and alkyne. The bonds in these hydrocarbons can be saturated or unsaturated. Now you can define alkane easily. Ethane is an example of alkane.
Complete answer:
We also need to know that alkanes are hydrocarbons that contain carbon and hydrogen atoms in them. Carbon and hydrogen atoms are bonded in such a way that a bond is formed between them. When two carbon atoms have a single bond between them, then the hydrocarbon is known as alkane. Alkanes are not very reactive since they have carbon atoms having valence electrons four thus forming four covalent bonds between carbon and hydrogen atoms. Suffix used in deining nomenclature of alkane is –ane.
We need to remember that the general formula for alkane is \[{C_n}{H_{2n + 2}}\], Alkanes can be a linear chain, branched chain or in a cyclic chain also. Cycloalkanes are also saturated as it has a cyclic ring containing carbon atoms that has only single bonds in it. The most common name reaction for the synthesis of alkane can be wurtz reaction or corey house reaction.
We will look at the examples for each type of alkane.
1.Linear chain: Alkane chain having straight long chain of carbon atoms.
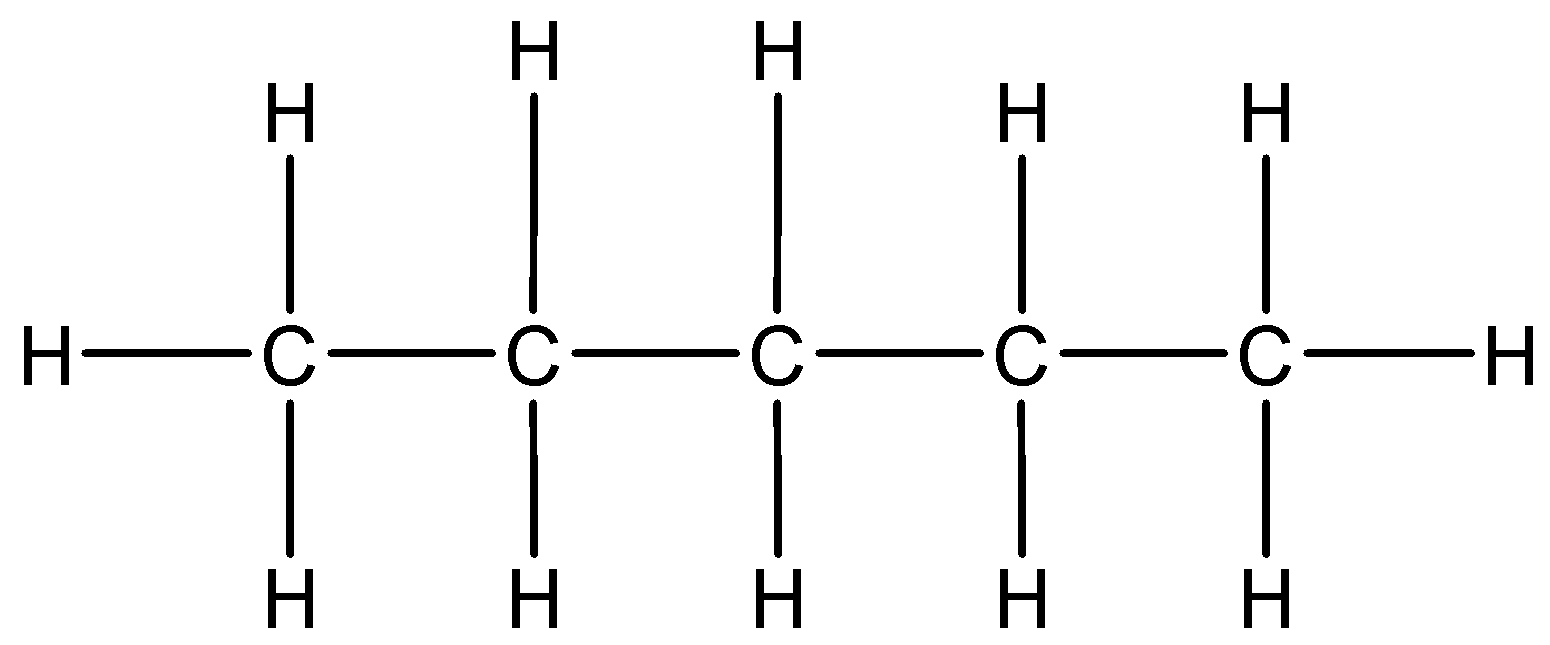
This is a structure of n-pentane having a molecular formula \[{C_5}{H_{12}}\].
2.Branched chain: Alkane chain having branches is termed as branched alkane chain.
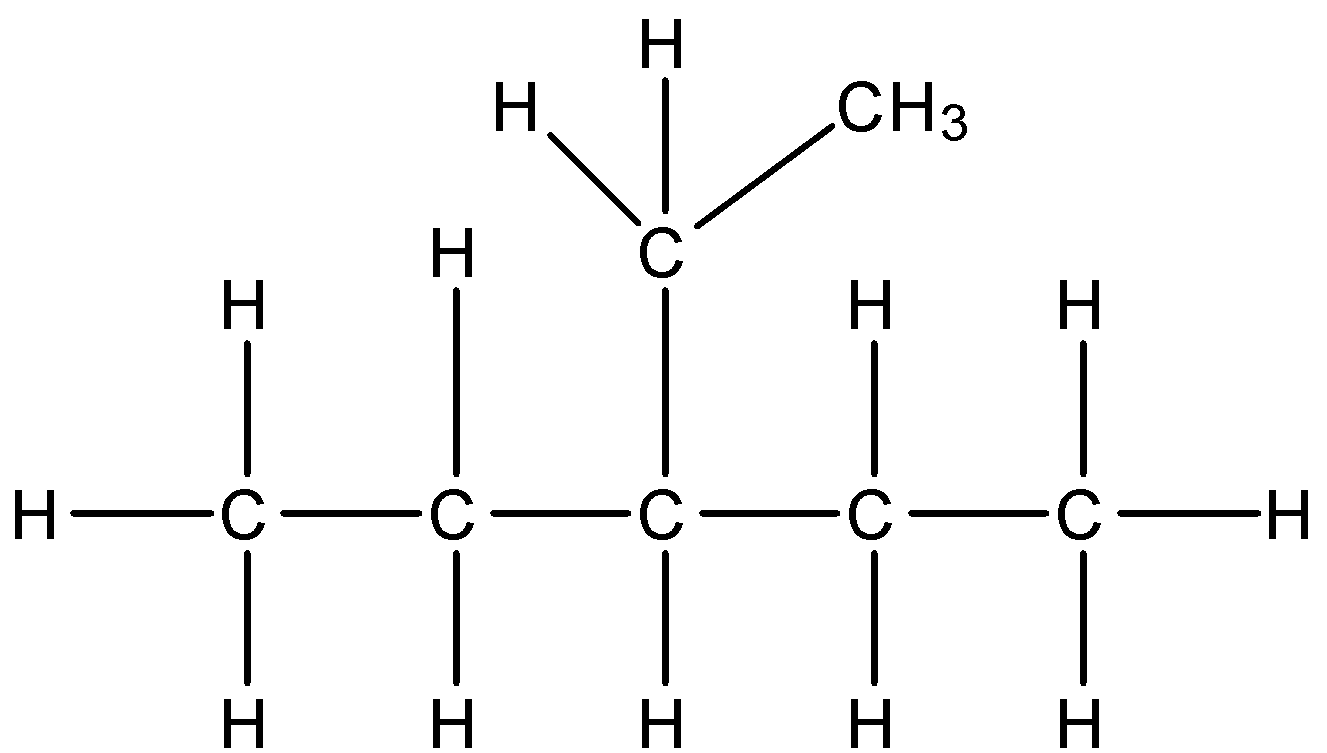
3.Cyclic chain: Alkanes that have cyclic rings in them which are saturated, are known as cycloalkanes.
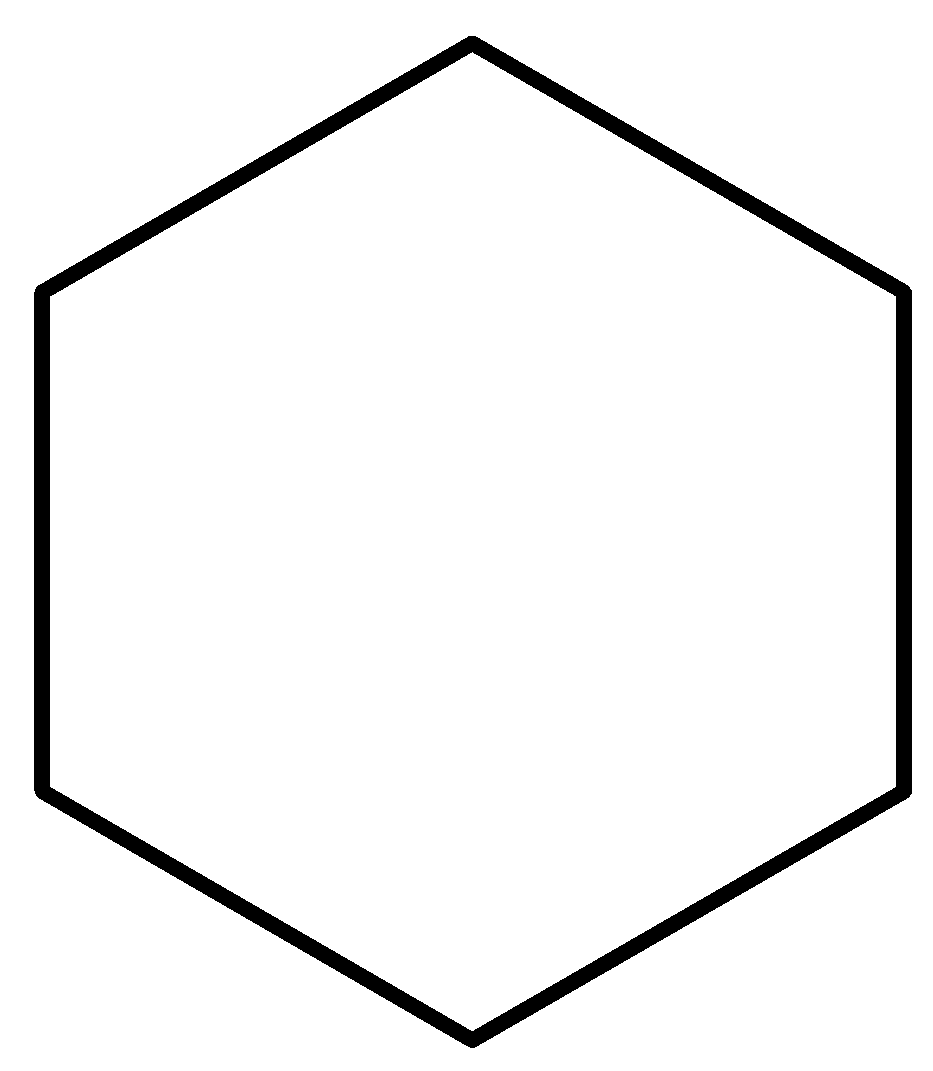
This is an example of cycloalkane which is cyclohexane.
Note:
We need to remember that alkenes and alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbons since they have double and triple bonds in them respectively while alkane has a single bond between carbon atoms thus it is a saturated hydrocarbon.
Complete answer:
We also need to know that alkanes are hydrocarbons that contain carbon and hydrogen atoms in them. Carbon and hydrogen atoms are bonded in such a way that a bond is formed between them. When two carbon atoms have a single bond between them, then the hydrocarbon is known as alkane. Alkanes are not very reactive since they have carbon atoms having valence electrons four thus forming four covalent bonds between carbon and hydrogen atoms. Suffix used in deining nomenclature of alkane is –ane.
We need to remember that the general formula for alkane is \[{C_n}{H_{2n + 2}}\], Alkanes can be a linear chain, branched chain or in a cyclic chain also. Cycloalkanes are also saturated as it has a cyclic ring containing carbon atoms that has only single bonds in it. The most common name reaction for the synthesis of alkane can be wurtz reaction or corey house reaction.
We will look at the examples for each type of alkane.
1.Linear chain: Alkane chain having straight long chain of carbon atoms.

This is a structure of n-pentane having a molecular formula \[{C_5}{H_{12}}\].
2.Branched chain: Alkane chain having branches is termed as branched alkane chain.

3.Cyclic chain: Alkanes that have cyclic rings in them which are saturated, are known as cycloalkanes.

This is an example of cycloalkane which is cyclohexane.
Note:
We need to remember that alkenes and alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbons since they have double and triple bonds in them respectively while alkane has a single bond between carbon atoms thus it is a saturated hydrocarbon.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




