
Water containing cavities in vascular bundles occurs in
a) Sunflower
b) Maize
c) Pinus
d) Cycas
Answer
592.5k+ views
Hint: It is monocot plant, cambium is not present in the vascular bundles i.e the vascular bundles are closed, collateral or lepto centric and conjoint.
Complete answer:
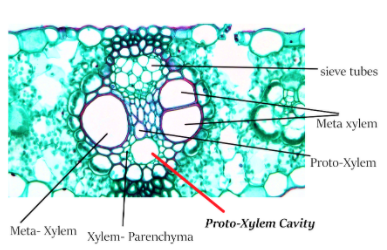
The only monocot in the given options is Maize. Pinus and cycas are gymnosperms and thus out of discussion of monocot and dicot. Sunflower is an angiosperm but it is a dicot. In vascular bundles of maize, xylem parenchyma cells and the lowermost proto-xylem vessels dissolve to form schizo-lysigenous cavity (water containing cavity) known as proto-xylem cavity or lysigenous cavity or lacuna or Proto-xylem cavity. In the smaller vascular bundles in maize the absence of protophloem may be observed.
Additional information:
Both upper and lower epidermises are uniseriate and well cutinized. Within the upper, or adaxial, epidermis, large white bulliform cells shrink, allowing the leaf to roll during drought. Vascular bundles in monocots are of different sizes, the smaller size bundles are present in peripheral areas and larger ones in the center. They seem to be embedded in ground tissue in a cross section. The bundle sheaths made up of sclerenchyma encircles the vascular bundle. The bundle caps are absent. Usually in monocots hollow stems are present. The arrangement of their vascular bundles appeared to be in a ring, due to the rare space. It increases the flexibility of the stem which results to satisfy the great need of required property for the aquatic plants of running water, while at the same time it decreases the strength of the stem, which may affect terrestrial plants.
Note:The presence of hollow stems can be used as one of the identifying features to distinguish Monocots from Dicots and Gymnosperms.
Complete answer:
The only monocot in the given options is Maize. Pinus and cycas are gymnosperms and thus out of discussion of monocot and dicot. Sunflower is an angiosperm but it is a dicot. In vascular bundles of maize, xylem parenchyma cells and the lowermost proto-xylem vessels dissolve to form schizo-lysigenous cavity (water containing cavity) known as proto-xylem cavity or lysigenous cavity or lacuna or Proto-xylem cavity. In the smaller vascular bundles in maize the absence of protophloem may be observed.

Additional information:
Both upper and lower epidermises are uniseriate and well cutinized. Within the upper, or adaxial, epidermis, large white bulliform cells shrink, allowing the leaf to roll during drought. Vascular bundles in monocots are of different sizes, the smaller size bundles are present in peripheral areas and larger ones in the center. They seem to be embedded in ground tissue in a cross section. The bundle sheaths made up of sclerenchyma encircles the vascular bundle. The bundle caps are absent. Usually in monocots hollow stems are present. The arrangement of their vascular bundles appeared to be in a ring, due to the rare space. It increases the flexibility of the stem which results to satisfy the great need of required property for the aquatic plants of running water, while at the same time it decreases the strength of the stem, which may affect terrestrial plants.
Note:The presence of hollow stems can be used as one of the identifying features to distinguish Monocots from Dicots and Gymnosperms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




