
Wall of the heart is covered externally by
(a)Epicardium
(b)Epithelium
(c)endothelium
(d)Glisson’s capsule
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: The inner layer of the pericardium, a conical sac of fibrous tissue that surrounds the heart and therefore the roots of the blood vessels. The pericardium has outer and inner coats.
Complete answer:
(a)Epicardium is the outer layer of the wall of the heart. It forms the innermost membrane of the pericardium that covers the heart externally.
(b)Epithelium layer lines the outer surfaces of blood vessels and organs of the body.
(c)The endothelium is the inner layer of blood vessels.
(d)Glisson's capsule is a layer of connective tissue which surrounds the liver.
The epicardium is a thin layer of elastic connective tissue and fat that forms an extra layer of protection from trauma or friction for the heart under the pericardium. This layer contains the coronary blood vessels, which oxygenate the tissues of the heart with a blood supply from the coronary arteries.
Thus the wall of the heart is covered externally by Epicardium.
Additional Information: Structure of the Heart:
The human heart muscular organ which has 4 chambers, shaped and just has the size of a man's fist with two-thirds of the mass to the left of midline. The heart is present in a pericardial sac which is lined with the parietal layers of a serosa. The inner layer of the serous membrane forms the epicardium.
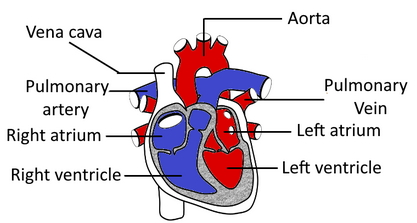
Chambers of the Heart:
The internal cavity of the heart is split into four chambers:
Right atrium
Right ventricle
Left atrium
Left ventricle
The two atria are thin-walled chambers which receive blood from the veins. The two ventricles are thick-walled chambers that forcefully pump blood out of the centre.
The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from systemic veins; the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins.
So, the correct answer is, “Epicardium.”
Note: -The four main functions of the Heart are:
-To transport the nutrients, gases and waste products all over the body.
-To protect the body from infection and blood loss.
-To help the body maintain constant body temperature ('thermoregulation').
-To help maintain fluid balance within the body.
Complete answer:
(a)Epicardium is the outer layer of the wall of the heart. It forms the innermost membrane of the pericardium that covers the heart externally.
(b)Epithelium layer lines the outer surfaces of blood vessels and organs of the body.
(c)The endothelium is the inner layer of blood vessels.
(d)Glisson's capsule is a layer of connective tissue which surrounds the liver.
The epicardium is a thin layer of elastic connective tissue and fat that forms an extra layer of protection from trauma or friction for the heart under the pericardium. This layer contains the coronary blood vessels, which oxygenate the tissues of the heart with a blood supply from the coronary arteries.
Thus the wall of the heart is covered externally by Epicardium.
Additional Information: Structure of the Heart:
The human heart muscular organ which has 4 chambers, shaped and just has the size of a man's fist with two-thirds of the mass to the left of midline. The heart is present in a pericardial sac which is lined with the parietal layers of a serosa. The inner layer of the serous membrane forms the epicardium.
Chambers of the Heart:
The internal cavity of the heart is split into four chambers:
Right atrium
Right ventricle
Left atrium
Left ventricle
The two atria are thin-walled chambers which receive blood from the veins. The two ventricles are thick-walled chambers that forcefully pump blood out of the centre.
The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from systemic veins; the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins.

So, the correct answer is, “Epicardium.”
Note: -The four main functions of the Heart are:
-To transport the nutrients, gases and waste products all over the body.
-To protect the body from infection and blood loss.
-To help the body maintain constant body temperature ('thermoregulation').
-To help maintain fluid balance within the body.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




