
Two point sources \[{S_1}\] and \[{S_2}\] are \[24cm\] apart. Where should a convex lens of focal length \[9cm\] be placed in between them so that the images of both sources are formed at the same place?
(A) \[6cm\] from \[{S_1}\]
(B) \[15cm\] from \[{S_1}\]
(C) \[10cm\] from \[{S_1}\]
(D) \[12cm\] from \[{S_1}\]
Answer
475.2k+ views
Hint: The given condition will be satisfied only if one source ${S_1}$ is placed on one side such that $u < f$ ( i.e. it lies under the focus). The other source ${S_2}$ is placed on the other side of the lens such that $u > f$ (i.e. it lies beyond the focus).
Complete step by step solution:
According to the question, the diagram will be-
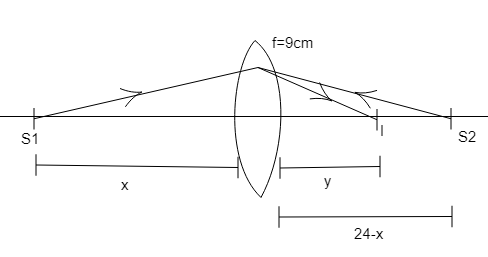
According to the convex lens equation,
\[\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u}\]
Here, \[u\] is the object distance
\[v\] is the image distance, and
\[f\] is the focal length
This formula relates the focal length of a lens with the distance of an object placed in front of it and the image formed of that object. All image or object left to the optical point is negative and all image or object on the right side of the optic centre is positive. Also, all the distances are to be measured from the optical centre.
As given in the above diagram,
When the refraction takes place from the left hand source,
\[\dfrac{1}{{ - v}} - \dfrac{1}{{ - x}} = \dfrac{1}{9}\]
Similarly, when the refraction takes place from the right hand source,
\[\dfrac{1}{{ - v}} - \dfrac{1}{{ - (24 - x)}} = \dfrac{1}{9}\]
On adding the above equations and simplifying them, we get,
\[{x^2} - 24x + 108 = 0\]
On solving the above quadratic equation, we get,
Either \[x = 6cm\] or \[x = 18cm\]
So, the final answer is (A) \[6cm\] from \[{S_1}\]
Note:
It is important to note that when a ray of light passes through a lens, then refraction takes place two times, first when the light ray enters the lens and again when the light ray leaves the lens. But, for convenience and for easily calculations, we assume that refraction takes place only one time.
Complete step by step solution:
According to the question, the diagram will be-

According to the convex lens equation,
\[\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u}\]
Here, \[u\] is the object distance
\[v\] is the image distance, and
\[f\] is the focal length
This formula relates the focal length of a lens with the distance of an object placed in front of it and the image formed of that object. All image or object left to the optical point is negative and all image or object on the right side of the optic centre is positive. Also, all the distances are to be measured from the optical centre.
As given in the above diagram,
When the refraction takes place from the left hand source,
\[\dfrac{1}{{ - v}} - \dfrac{1}{{ - x}} = \dfrac{1}{9}\]
Similarly, when the refraction takes place from the right hand source,
\[\dfrac{1}{{ - v}} - \dfrac{1}{{ - (24 - x)}} = \dfrac{1}{9}\]
On adding the above equations and simplifying them, we get,
\[{x^2} - 24x + 108 = 0\]
On solving the above quadratic equation, we get,
Either \[x = 6cm\] or \[x = 18cm\]
So, the final answer is (A) \[6cm\] from \[{S_1}\]
Note:
It is important to note that when a ray of light passes through a lens, then refraction takes place two times, first when the light ray enters the lens and again when the light ray leaves the lens. But, for convenience and for easily calculations, we assume that refraction takes place only one time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




