
Two aliphatic aldehydes P and Q react in the presence of aqueous $\text{ }{{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }$ to give compound R, which upon treatment with $\text{ HCN }$ provides compound S. On acidification and heating gives the product shown below:
The compound R is :

(A)
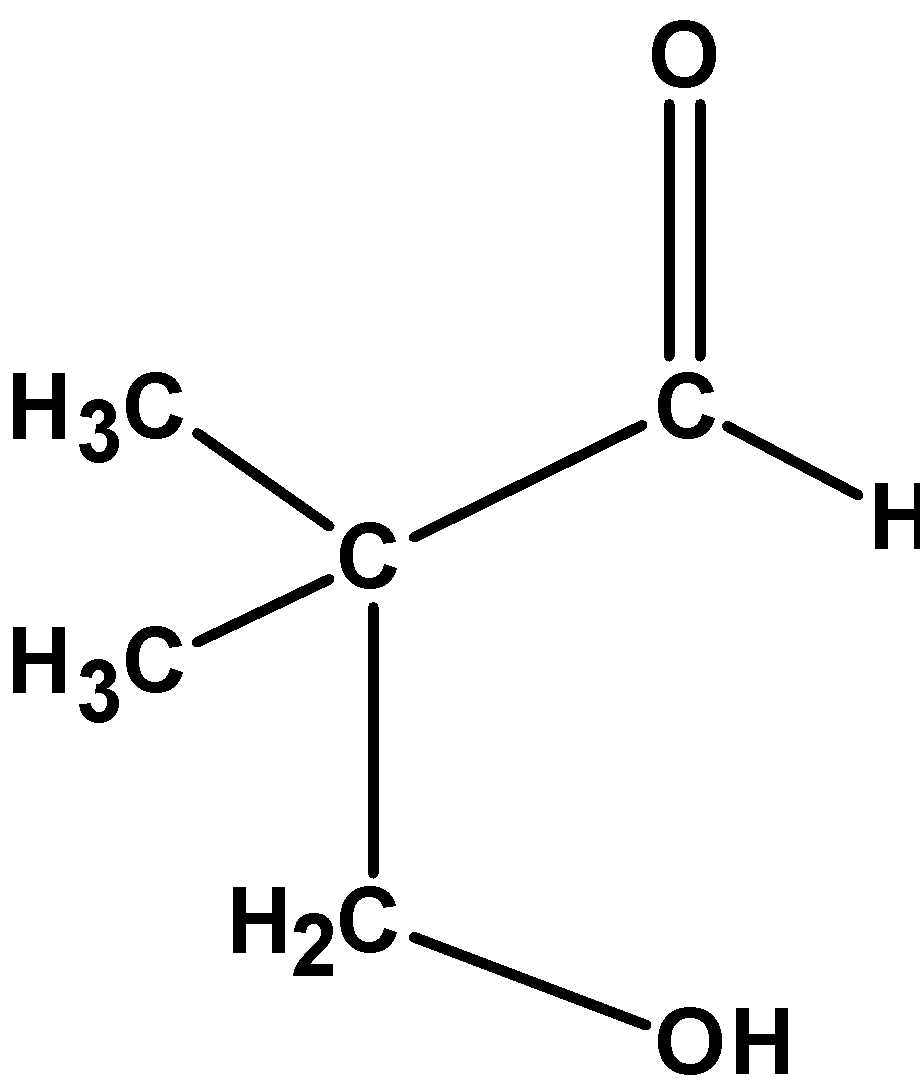
(B)
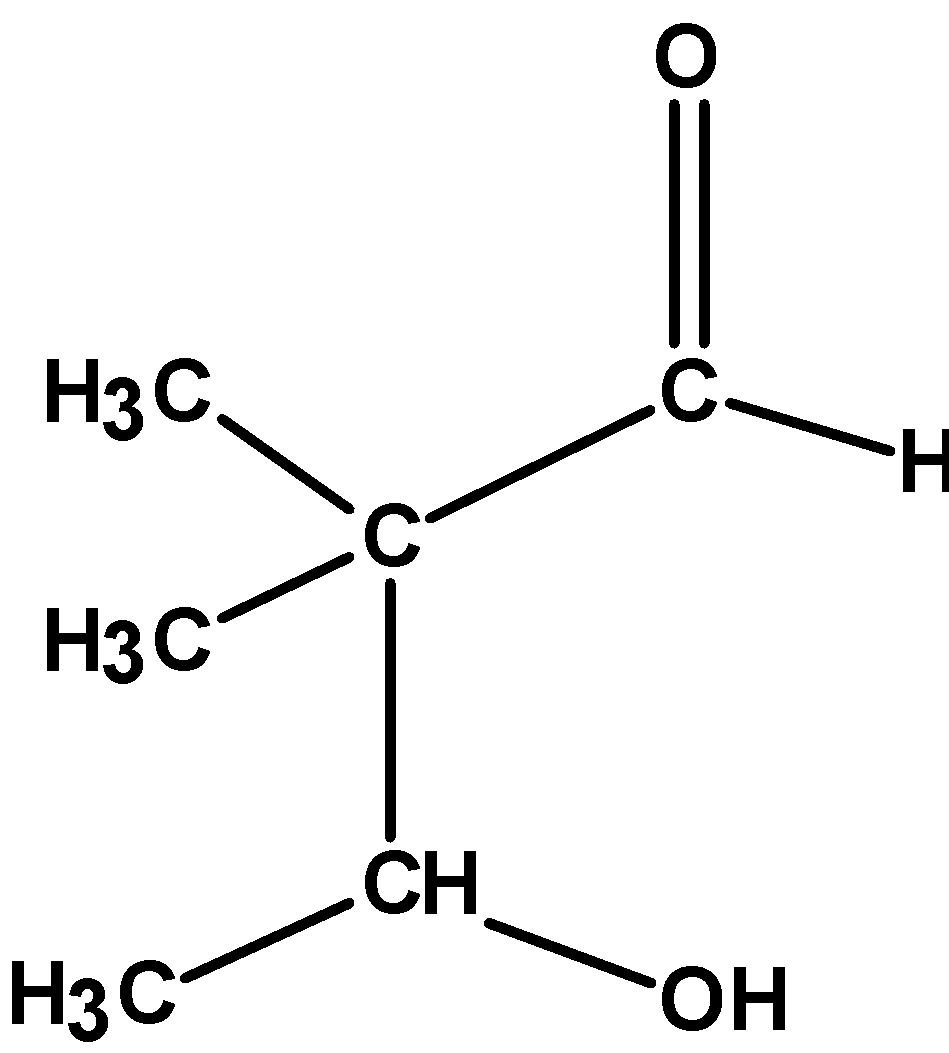
(C)
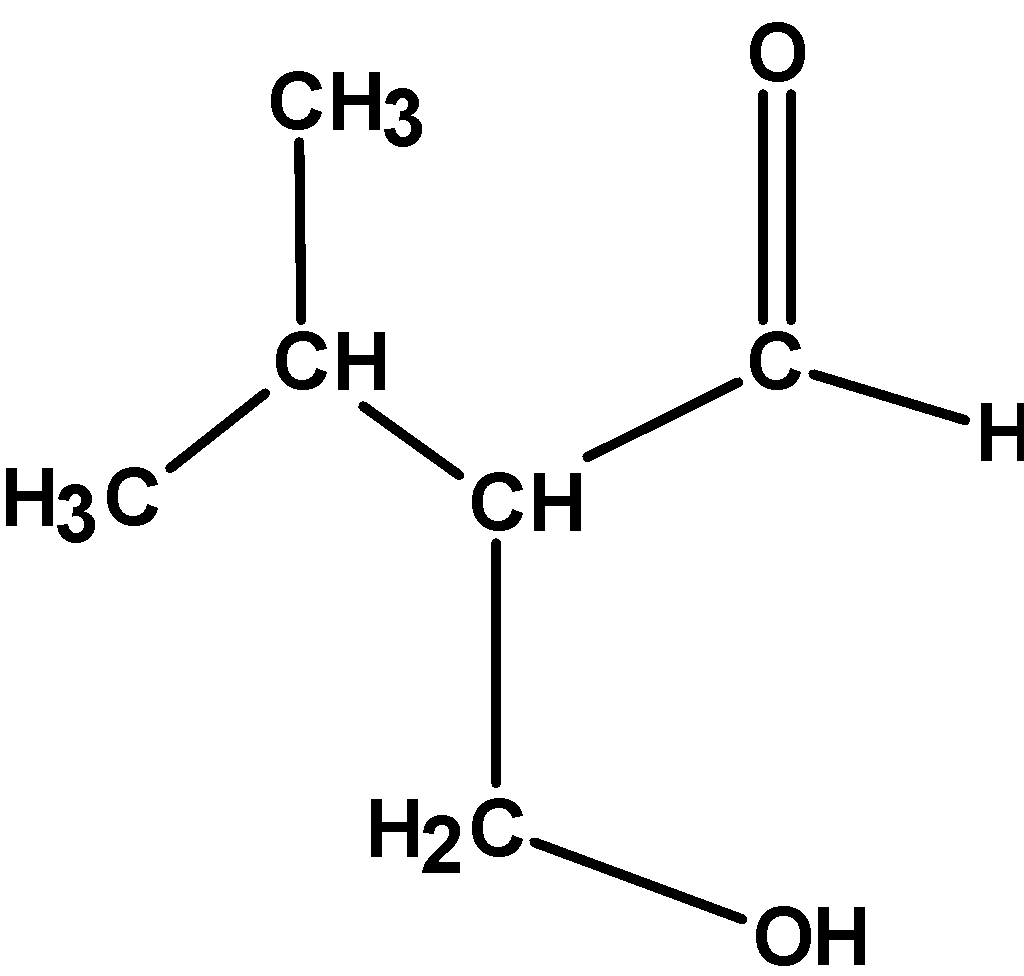
(D)
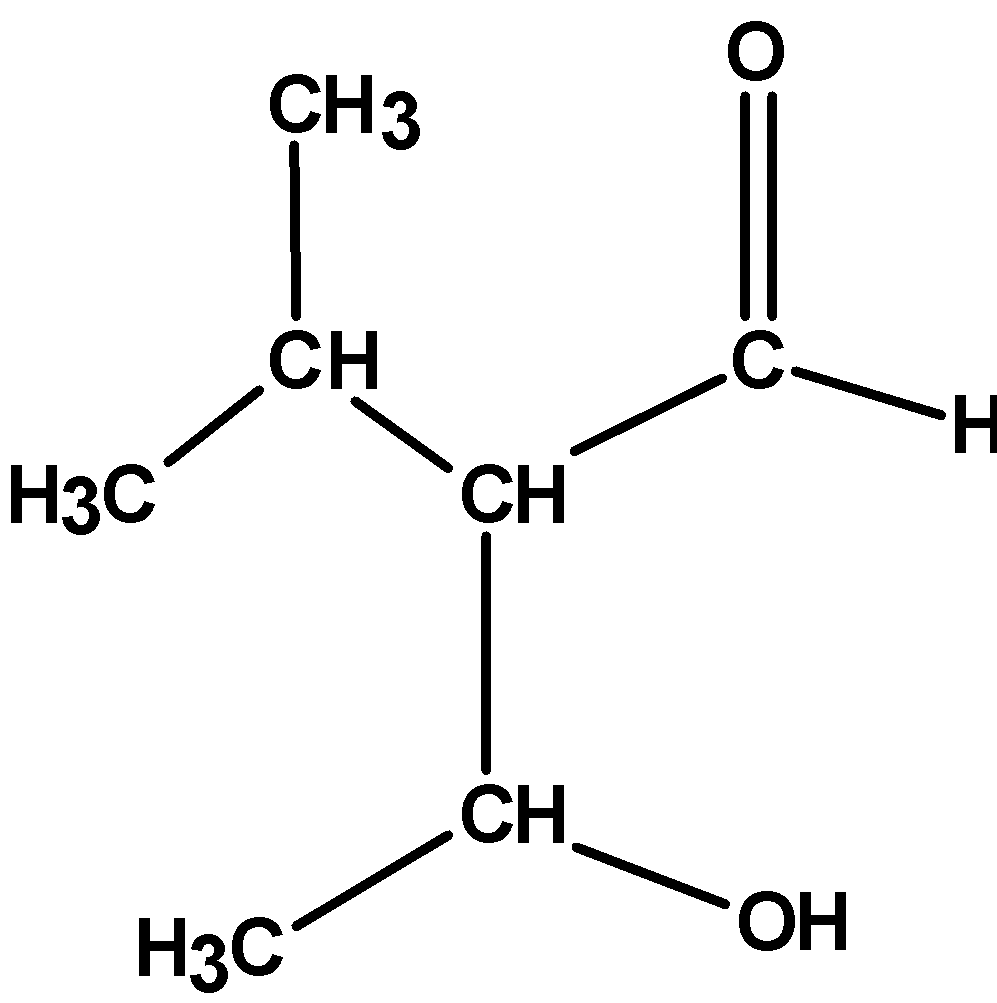

| (A) | 
|
| (B) | 
|
| (C) | 
|
| (D) | 
|
Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: The aldehydes and ketone which do not contain the$\text{ }\alpha \text{-}$ hydrogen atom undergoes cross aldol condensation. The condensation results in the hydroxyl aldehyde compound. This method is useful over the self-condensation as we can use two different carbonyl compounds which may or may not have $\text{ }\alpha \text{-}$ hydrogen atom. The reaction of carbonyl compounds with the hydrogen cyanide results in cyanohydrins, which have very wide application in the preparation of carboxylic acid.
Complete answer:
Aldehydes and ketones undergo the condensation in presence of dilute alkali to form hydroxyl aldehyde. The condensation of two different carbonyl compounds (two aldehydes, two ketones or one aldehyde one ketone) in presence of base is called the cross aldol condensation or mixed aldol condensation reaction.
Cross aldol condensation is very useful when the carbonyl compounds do not contain the $\text{ }\alpha \text{-}$ hydrogen atom.
Let’s consider two aldehydes which are 2, methyl propionaldehyde $\text{ C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{CH(C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{)CHO }$ and formaldehyde $\text{ HCHO }$ .These aldehydes are different and instead of self-condensation they condense via cross aldol condensation.
Step 1) The base ($\text{ }{{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }$ or $\text{ LDA }$ ) abstracts a proton from the 2, methyl propionaldehyde and generates a kinetic enolate .The formation of enolate is as shown below,
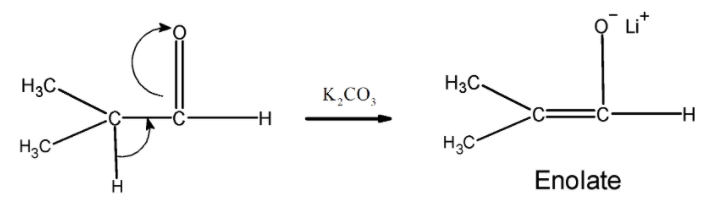
Step 2) this enolate ion formed now attacks on the carbon atom of the carbonyl of the formaldehyde .The attack is as shown below followed by the hydrolysis. This step results in the formation of 3-hydroxy -2, 2 dimethyl propanal.

The 3 –hydroxy -2,2 –dimethylpropanal is a condensed product of 2,methylpropanal and formaldehyde.
Hence, (A) is the correct option.
Note:
It may be noted that in cross aldol condensation one of the reactants forms an enolate ion and other is more likely to react with it. The reaction is not an aldol condensation as the two same aldehydes are not used .Moreover, the molecules do not have the alpha-hydrogen atom.
Complete answer:
Aldehydes and ketones undergo the condensation in presence of dilute alkali to form hydroxyl aldehyde. The condensation of two different carbonyl compounds (two aldehydes, two ketones or one aldehyde one ketone) in presence of base is called the cross aldol condensation or mixed aldol condensation reaction.
Cross aldol condensation is very useful when the carbonyl compounds do not contain the $\text{ }\alpha \text{-}$ hydrogen atom.
Let’s consider two aldehydes which are 2, methyl propionaldehyde $\text{ C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{CH(C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{)CHO }$ and formaldehyde $\text{ HCHO }$ .These aldehydes are different and instead of self-condensation they condense via cross aldol condensation.
Step 1) The base ($\text{ }{{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{ }$ or $\text{ LDA }$ ) abstracts a proton from the 2, methyl propionaldehyde and generates a kinetic enolate .The formation of enolate is as shown below,

Step 2) this enolate ion formed now attacks on the carbon atom of the carbonyl of the formaldehyde .The attack is as shown below followed by the hydrolysis. This step results in the formation of 3-hydroxy -2, 2 dimethyl propanal.

The 3 –hydroxy -2,2 –dimethylpropanal is a condensed product of 2,methylpropanal and formaldehyde.
Hence, (A) is the correct option.
Note:
It may be noted that in cross aldol condensation one of the reactants forms an enolate ion and other is more likely to react with it. The reaction is not an aldol condensation as the two same aldehydes are not used .Moreover, the molecules do not have the alpha-hydrogen atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




