
True roots are absent in
(a) Bryophytes
(b) Pteridophytes
(c) Gymnosperm
(d)Angiosperm
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: True roots are absent in the primitive plants. Instead, those plants possess root-like structures. These plants are abundant in Western Himalayas. Their name was given by Robert Braun.
Complete answer:
Bryophytes are non- flowering terrestrial plants of damp habitat which lack vessels. A multicellular diploid sporophyte which lives as a parasite on an independent multicellular haploid gametophyte. These include various mosses and liverworts that are found commonly growing in moist shaded areas in the hill. The bryophytes are more differentiated than that of algae. It is thallus like and maybe prostrate or erect. They lack true roots, stems, or leaves but possess root-like, leaf-like, or stem-like structures. The plant body is attached to the substratum by root-like structures called rhizoids. The rhizoids may be unicellular or multicellular.
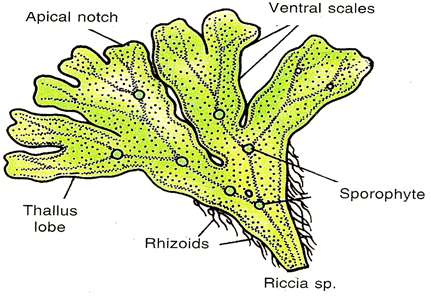
So, the answer is, ‘Bryophytes.’
Additional Information:
- They are found commonly in damp, humid, and shaded localities. - The plants are called amphibians of the plant kingdom because they live in soil but they require water for sexual reproduction. - The main or dominant phase of the plant body is a free-living gametophyte and sporophyte is borne on the gametophyte. - The gametophyte is the haploid stage of a plant that generates gametes by the process of mitosis.
Note:
- Vascular tissues i.e. xylem and phloem are absent. - The gametophyte of bryophyte consists of multicellular sex organs. The male reproductive organ is named antheridium and therefore the female reproductive organ is named archegonium. - They are present as female and male thallus in liverwort. - Bryophytes are homosporous i.e. they produce only one type of spores. - Vegetative reproduction occurs through fragmentation, gemmae, and budding. - Zygotes don’t undergo reduction division rather undergo mitotic division to form an embryo. Thus, they are the first embryophytes. - The sporophyte is a parasite that is attached to photosynthetic gametophyte and derives nourishment from it.
Complete answer:
Bryophytes are non- flowering terrestrial plants of damp habitat which lack vessels. A multicellular diploid sporophyte which lives as a parasite on an independent multicellular haploid gametophyte. These include various mosses and liverworts that are found commonly growing in moist shaded areas in the hill. The bryophytes are more differentiated than that of algae. It is thallus like and maybe prostrate or erect. They lack true roots, stems, or leaves but possess root-like, leaf-like, or stem-like structures. The plant body is attached to the substratum by root-like structures called rhizoids. The rhizoids may be unicellular or multicellular.

So, the answer is, ‘Bryophytes.’
Additional Information:
- They are found commonly in damp, humid, and shaded localities. - The plants are called amphibians of the plant kingdom because they live in soil but they require water for sexual reproduction. - The main or dominant phase of the plant body is a free-living gametophyte and sporophyte is borne on the gametophyte. - The gametophyte is the haploid stage of a plant that generates gametes by the process of mitosis.
Note:
- Vascular tissues i.e. xylem and phloem are absent. - The gametophyte of bryophyte consists of multicellular sex organs. The male reproductive organ is named antheridium and therefore the female reproductive organ is named archegonium. - They are present as female and male thallus in liverwort. - Bryophytes are homosporous i.e. they produce only one type of spores. - Vegetative reproduction occurs through fragmentation, gemmae, and budding. - Zygotes don’t undergo reduction division rather undergo mitotic division to form an embryo. Thus, they are the first embryophytes. - The sporophyte is a parasite that is attached to photosynthetic gametophyte and derives nourishment from it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




