
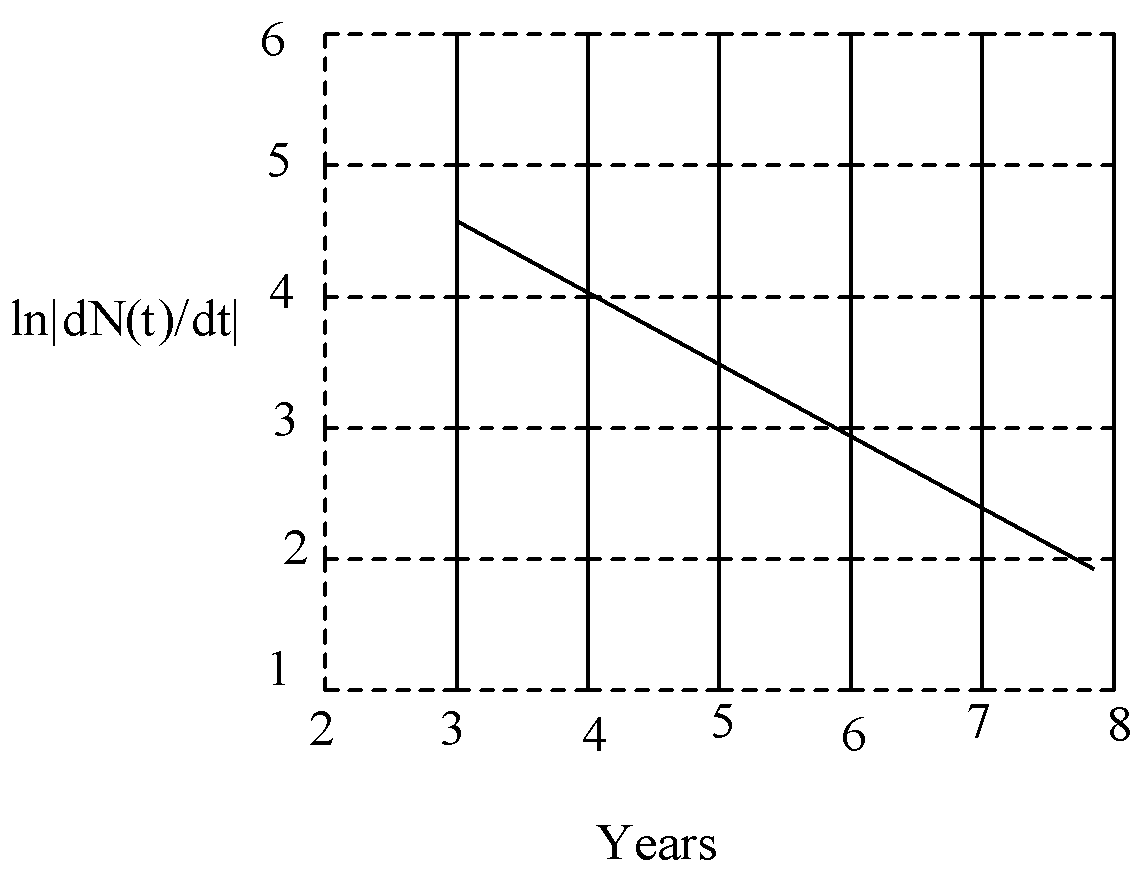
To determine the half-life of a radioactive element, the student plots a graph of ln|dN(t)/dt| versus t. Here dN(t)/dt is the rate of radioactive decay at time t. If the number of radioactive nuclei of this element decreases by a factor of p after 4.16 years, the value of p is:

Answer
592.5k+ views
Hint: To calculate the radioactive decay, the equation used is $N(t)={{N}_{\circ }}{{e}^{-\lambda t}}$ where N is the radioactive nuclei present at time t and ${{N}_{\circ }}$ is the number of radioactive nuclei present initially. The half-life of the first-order reaction is calculated by dividing 0.693 to radioactive decay constant.
Complete answer:
The number of nuclei disintegration per second of a radioactive sample at any instant is directly proportional to the number of undecayed nuclei present in the sample at that instant.
The equation which represents the radioactive decay law is:
$N(t)={{N}_{\circ }}{{e}^{-\lambda t}}$
$\dfrac{dN}{dt}={{N}_{\circ }}\lambda {{e}^{-\lambda t}}$
Where N is the radioactive nuclei present at time t
${{N}_{\circ }}$ is the number of radioactive nuclei present initially.
$dN$ is the number of radioactive nuclei which disintegrate in the small time interval of time dt.
Taking log on both side of the equation, we get
$\ln \dfrac{dN}{dt}=\ln ({{N}_{\circ }}\lambda -\lambda t)$
So, from this equation the slope of the curve, $m=-\lambda $
So, from the graph,
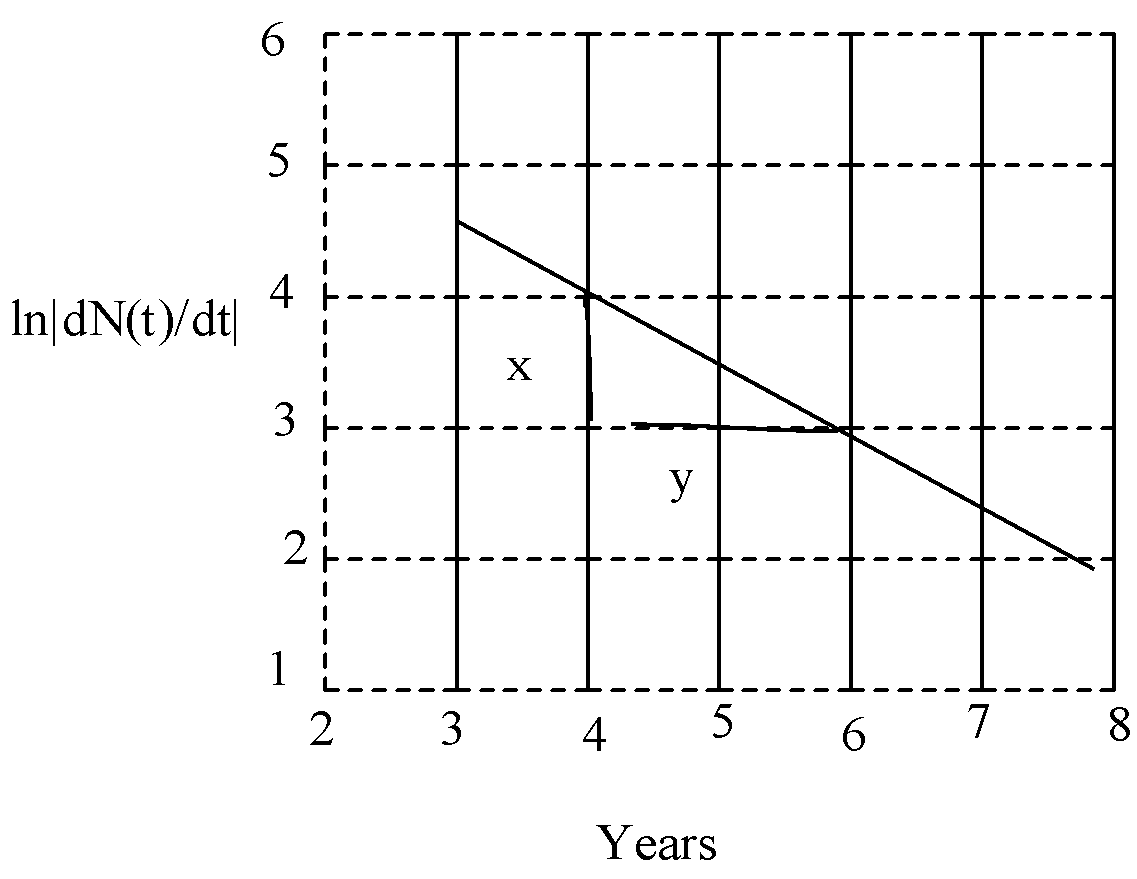
$m=\dfrac{\Delta y}{\Delta x}=\dfrac{1}{2}=0.5$
So, the radioactive decay constant is 0.5.
The half life of first order reaction is calculated by dividing 0.693 to radioactive decay constant.
${{t}_{1/2}}=\dfrac{0.693}{\lambda }$
So, putting the values, we get
${{t}_{1/2}}=\dfrac{0.693}{\lambda }=\dfrac{0.693}{0.5}=0.3465years$
Hence, the half life of the radioactive sample is 0.3465 years.
According to the question,
$N(t)={{N}_{\circ }}{{e}^{-\lambda t}}$
$\dfrac{1}{p}={{e}^{-\lambda t}}$
The time given is 4.16 years.
So, $\dfrac{1}{p}={{e}^{-0.5\text{ x 4}\text{.16}}}$
$p=8$
So, the value of p is 8.
Note: All the formulas must be taken correctly. When converting the equation to log form the negative sign must also be taken. In half-life, the value of log 2 is directly taken 0.693.
Complete answer:
The number of nuclei disintegration per second of a radioactive sample at any instant is directly proportional to the number of undecayed nuclei present in the sample at that instant.
The equation which represents the radioactive decay law is:
$N(t)={{N}_{\circ }}{{e}^{-\lambda t}}$
$\dfrac{dN}{dt}={{N}_{\circ }}\lambda {{e}^{-\lambda t}}$
Where N is the radioactive nuclei present at time t
${{N}_{\circ }}$ is the number of radioactive nuclei present initially.
$dN$ is the number of radioactive nuclei which disintegrate in the small time interval of time dt.
Taking log on both side of the equation, we get
$\ln \dfrac{dN}{dt}=\ln ({{N}_{\circ }}\lambda -\lambda t)$
So, from this equation the slope of the curve, $m=-\lambda $
So, from the graph,

$m=\dfrac{\Delta y}{\Delta x}=\dfrac{1}{2}=0.5$
So, the radioactive decay constant is 0.5.
The half life of first order reaction is calculated by dividing 0.693 to radioactive decay constant.
${{t}_{1/2}}=\dfrac{0.693}{\lambda }$
So, putting the values, we get
${{t}_{1/2}}=\dfrac{0.693}{\lambda }=\dfrac{0.693}{0.5}=0.3465years$
Hence, the half life of the radioactive sample is 0.3465 years.
According to the question,
$N(t)={{N}_{\circ }}{{e}^{-\lambda t}}$
$\dfrac{1}{p}={{e}^{-\lambda t}}$
The time given is 4.16 years.
So, $\dfrac{1}{p}={{e}^{-0.5\text{ x 4}\text{.16}}}$
$p=8$
So, the value of p is 8.
Note: All the formulas must be taken correctly. When converting the equation to log form the negative sign must also be taken. In half-life, the value of log 2 is directly taken 0.693.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




