
Three resistances each of $4\Omega $ are connected in the form of an equilateral triangle. The effective resistance between any two corners is
A. $8\Omega $
B. $12\Omega $
C. $\dfrac{8}{3}\Omega $
D. $\dfrac{3}{8}\Omega $
Answer
497.7k+ views
Hint:Equilateral triangle corresponds to those triangles whose all sides and angles are equal. To find the effective resistance between the corners we have to first make a simplified circuit. Two of the resistance will be in series while the other in parallel. Then by calculating the total resistance we will find the answer.
Complete step by step answer:
The figure as per the question suggested is below:
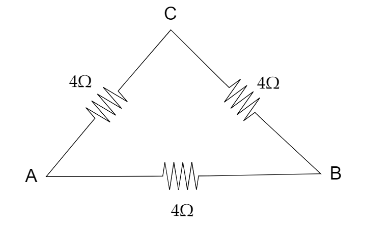
We have to find the effective resistance between A and B. In order to find this, the simplified circuit we get is the place where ACB are in series with parallel combination to AB.The figure is depicted below:
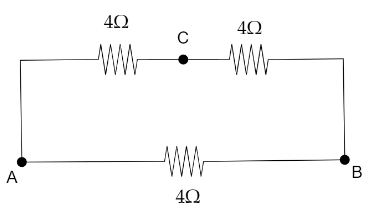
The resistance between ACB is in series condition. Let the total resistance in the circuit ACB be ${R_1}$.Therefore,
${R_1} = \left( {4 + 4} \right)\Omega = 8\Omega $
The resistance ${R_1}$ is in parallel with the resistance in the circuit AB.Let the effective resistance between the corners A and B be $R$.
$R = \dfrac{{8 \times 4}}{{8 + 4}} = \dfrac{8}{3}\Omega $
Thus, the effective resistance across any corner of the equilateral triangle is $\dfrac{8}{3}\Omega $.
Note: It must be noted that in order to find the resistance of any complex circuit we must simplify it with smaller circuits. The series combination of resistance refers to the combination of resistance in which the algebraic sum of all resistance gives the total resistance. Parallel combination of resistance refers to the combination of resistance in which algebraic sum of reciprocal of all the resistances gives the total value.
Complete step by step answer:
The figure as per the question suggested is below:

We have to find the effective resistance between A and B. In order to find this, the simplified circuit we get is the place where ACB are in series with parallel combination to AB.The figure is depicted below:

The resistance between ACB is in series condition. Let the total resistance in the circuit ACB be ${R_1}$.Therefore,
${R_1} = \left( {4 + 4} \right)\Omega = 8\Omega $
The resistance ${R_1}$ is in parallel with the resistance in the circuit AB.Let the effective resistance between the corners A and B be $R$.
$R = \dfrac{{8 \times 4}}{{8 + 4}} = \dfrac{8}{3}\Omega $
Thus, the effective resistance across any corner of the equilateral triangle is $\dfrac{8}{3}\Omega $.
Note: It must be noted that in order to find the resistance of any complex circuit we must simplify it with smaller circuits. The series combination of resistance refers to the combination of resistance in which the algebraic sum of all resistance gives the total resistance. Parallel combination of resistance refers to the combination of resistance in which algebraic sum of reciprocal of all the resistances gives the total value.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




