
Three concentric metallic spherical shells of radii R, 2R 3R are given charges ${{\text{Q}}_{\text{1}}}\text{, }{{\text{Q}}_{\text{2}}}\text{, }{{\text{Q}}_{\text{3}}}$ respectively. It is found that the surface charge densities in the outer surfaces of the shells are equal. Then the ratio of the charges given to the shells, ${{\text{Q}}_{\text{1}}}\text{:}{{\text{Q}}_{\text{2}}}\text{: }{{\text{Q}}_{\text{3}}},$ is
A)1:2:3
B)1:3:5
C)1:4:9
D)1:8:18
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: In the question it is mentioned that the shells are made up of metal. Hence each of the shells will induce a charge on the surface of each other. If the charge is induced on the inner surface of the spherical shell, then the charge basically gets added up on the outer surface charge density. Hence we will determine the net charge on each of the spherical shells and then accordingly take the ratio of i.e. ${{\text{Q}}_{\text{1}}}\text{:}{{\text{Q}}_{\text{2}}}\text{: }{{\text{Q}}_{\text{3}}}$
Complete answer:
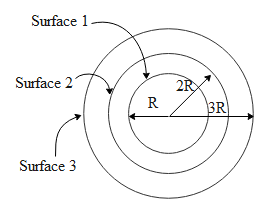
In the above diagram we can see that there are three concentric spherical shells given some charge. Surface 1 has a charge of ${{\text{Q}}_{\text{1}}}$, surface 2 has charge ${{\text{Q}}_{\text{2}}}$and surface 3 has charge ${{\text{Q}}_{\text{3}}}$. Now since the shells are metallic, they will induce charge on each other. Surface 1 will induce a charge $\text{-}{{\text{Q}}_{\text{1}}}$ on the inner side of the surface 2. As a result, surface 2 will have a total charge of ${{\text{Q}}_{\text{1}}}+{{\text{Q}}_{2}}$on its outer surface. Similarly surface 2 will induce a charge $\text{- (}{{\text{Q}}_{\text{1}}}+{{\text{Q}}_{2}})$ on the inner surface of shell 3. Hence The total charge on the outer surface of surface 3 is equal to, ${{\text{Q}}_{1}}+{{\text{Q}}_{2}}+{{\text{Q}}_{3}}$.
The surface charge density of the spherical shell is defined as the ratio of total charge on the shell to its surface area. Surface area of the sphere is equal to $4\pi {{r}^{2}}$ where radius the radius of the sphere. It is given to us that the surface charge density on the outer surface of all the three shells are equal. Hence we can write,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{\text{Q}}_{1}}}{4\pi {{R}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{\text{Q}}_{1}}+{{\text{Q}}_{2}}}{4\pi {{(2R)}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{\text{Q}}_{1}}+{{\text{Q}}_{2}}+{{\text{Q}}_{3}}}{4\pi {{(3R)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Q}}_{1}}}{4\pi {{R}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{\text{Q}}_{1}}+{{\text{Q}}_{2}}}{4(4\pi {{R}^{2}})}=\dfrac{{{\text{Q}}_{1}}+{{\text{Q}}_{2}}+{{\text{Q}}_{3}}}{9(4\pi {{R}^{2}})} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\text{Q}}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{\text{Q}}_{1}}+{{\text{Q}}_{2}}}{4}=\dfrac{{{\text{Q}}_{1}}+{{\text{Q}}_{2}}+ {{\text{Q}}_{\text{3}}}}{9} \\
\end{align}$
Further let us obtain the value of charge on the surface 2 and 3 in terms of 1.
$\begin{align}
& {{\text{Q}}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{\text{Q}}_{1}}+{{\text{Q}}_{2}}}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\text{Q}}_{2}}=3{{\text{Q}}_{1}} \\
\end{align}$
$\begin{align}
& {{\text{Q}}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{\text{Q}}_{1}}+{{\text{Q}}_{2}}+{{\text{Q}}_{3}}}{9} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\text{Q}}_{3}}=5{{\text{Q}}_{1}} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the ratio of ${{\text{Q}}_{\text{1}}}:{{\text{Q}}_{2}}:{{\text{Q}}_{3}}$ in terms of ${{\text{Q}}_{\text{1}}}$ is 1:3:5.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
Whenever a charge is induced on the inner surface of the sphere, the same amount appears on the outer surface of the metallic sphere. This is because the charge gets moved on the opposite side of the metal due to repulsion of the same charge or the like charge. Hence we have taken the same amount of charge to appear on the outer surface of the spherical shells.
Complete answer:

In the above diagram we can see that there are three concentric spherical shells given some charge. Surface 1 has a charge of ${{\text{Q}}_{\text{1}}}$, surface 2 has charge ${{\text{Q}}_{\text{2}}}$and surface 3 has charge ${{\text{Q}}_{\text{3}}}$. Now since the shells are metallic, they will induce charge on each other. Surface 1 will induce a charge $\text{-}{{\text{Q}}_{\text{1}}}$ on the inner side of the surface 2. As a result, surface 2 will have a total charge of ${{\text{Q}}_{\text{1}}}+{{\text{Q}}_{2}}$on its outer surface. Similarly surface 2 will induce a charge $\text{- (}{{\text{Q}}_{\text{1}}}+{{\text{Q}}_{2}})$ on the inner surface of shell 3. Hence The total charge on the outer surface of surface 3 is equal to, ${{\text{Q}}_{1}}+{{\text{Q}}_{2}}+{{\text{Q}}_{3}}$.
The surface charge density of the spherical shell is defined as the ratio of total charge on the shell to its surface area. Surface area of the sphere is equal to $4\pi {{r}^{2}}$ where radius the radius of the sphere. It is given to us that the surface charge density on the outer surface of all the three shells are equal. Hence we can write,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{\text{Q}}_{1}}}{4\pi {{R}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{\text{Q}}_{1}}+{{\text{Q}}_{2}}}{4\pi {{(2R)}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{\text{Q}}_{1}}+{{\text{Q}}_{2}}+{{\text{Q}}_{3}}}{4\pi {{(3R)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Q}}_{1}}}{4\pi {{R}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{\text{Q}}_{1}}+{{\text{Q}}_{2}}}{4(4\pi {{R}^{2}})}=\dfrac{{{\text{Q}}_{1}}+{{\text{Q}}_{2}}+{{\text{Q}}_{3}}}{9(4\pi {{R}^{2}})} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\text{Q}}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{\text{Q}}_{1}}+{{\text{Q}}_{2}}}{4}=\dfrac{{{\text{Q}}_{1}}+{{\text{Q}}_{2}}+ {{\text{Q}}_{\text{3}}}}{9} \\
\end{align}$
Further let us obtain the value of charge on the surface 2 and 3 in terms of 1.
$\begin{align}
& {{\text{Q}}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{\text{Q}}_{1}}+{{\text{Q}}_{2}}}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\text{Q}}_{2}}=3{{\text{Q}}_{1}} \\
\end{align}$
$\begin{align}
& {{\text{Q}}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{\text{Q}}_{1}}+{{\text{Q}}_{2}}+{{\text{Q}}_{3}}}{9} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\text{Q}}_{3}}=5{{\text{Q}}_{1}} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the ratio of ${{\text{Q}}_{\text{1}}}:{{\text{Q}}_{2}}:{{\text{Q}}_{3}}$ in terms of ${{\text{Q}}_{\text{1}}}$ is 1:3:5.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
Whenever a charge is induced on the inner surface of the sphere, the same amount appears on the outer surface of the metallic sphere. This is because the charge gets moved on the opposite side of the metal due to repulsion of the same charge or the like charge. Hence we have taken the same amount of charge to appear on the outer surface of the spherical shells.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




