
The word ‘Newton’ is printed on a paper and is placed on a horizontal surface below a cubical glass. The minimum value of refractive index of cubical glass, for which letters are not visible from any vertical faces of the glass, is:
(A) $ \sqrt 3 $
(B) $ 0.5 $
(C) $ 1 $
(D) $ \sqrt 2 $
Answer
582k+ views
Hint
For letters being not visible from any vertical faces, the primary condition is that there should be total internal reflection. The light that enters from the cubical glass should not refract through the vertical faces. Considering these conditions, we can calculate the refractive index using the condition for total internal reflection
Snell’s law: $ \dfrac{{sin{\theta _i}}}{{sin{\theta _r}}} = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}} $
where $ {\theta _i} $ is the angle of incidence, $ {\theta _r} $ is the angle of refraction, and $ {n_1} $ and $ {n_2} $ are the indices of refraction for the glass and air respectively.
Complete step by step answer
Let us consider the angle of incidence of the light rays on the top inner layer of the cubic glass be $ {\theta _i} $ and the angle of refraction be $ {\theta _r} $ . Let us also assume that $ {n_1} $ and $ {n_2} $ are the refractive indices of the glass and air respectively.
The figure below shows the cross-section of the cubical glass and let us consider that all the sides of the cubical glass is of length $ a $ .
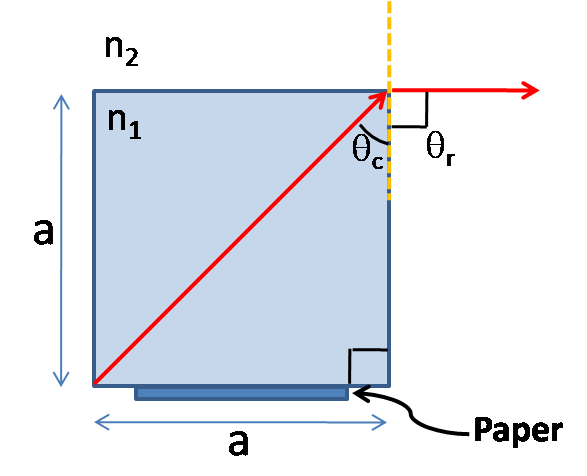
For the total internal reflection to happen so that the light will not refract out through the vertical faces, the boundary condition is that the refracted angle $ {\theta _r} = 90^\circ $ . Since, all the sides of a cube are equal in dimensions from the figure it is clear that the critical angle $ {\theta _c} = 45^\circ $ .
Now, from Snell’s law, we know that:
$ \dfrac{{sin{\theta _c}}}{{sin{\theta _r}}} = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}} $
But, for air, the index of refraction, $ {n_2} = 1 $ .
Therefore, we can rewrite the above equation as:
$ \dfrac{{sin45^\circ }}{{sin90^\circ }} = \dfrac{1}{{{n_1}}} $
Solving this, we get the minimum value of refractive index of the cubical glass as:
$ {n_1} = \dfrac{1}{{sin45^\circ }} = \sqrt 2 $ .
Hence, the correct answer is option (D).
Note
In this problem, the boundary condition to get the letters invisible from the vertical faces is the total internal reflection when the light reaches the vertical faces from inside. When the incident angle is equal to the critical angle, then the entire light rays incident are completely reflected. Thus, no light enters the air medium from the glass and the condition is achieved.
For letters being not visible from any vertical faces, the primary condition is that there should be total internal reflection. The light that enters from the cubical glass should not refract through the vertical faces. Considering these conditions, we can calculate the refractive index using the condition for total internal reflection
Snell’s law: $ \dfrac{{sin{\theta _i}}}{{sin{\theta _r}}} = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}} $
where $ {\theta _i} $ is the angle of incidence, $ {\theta _r} $ is the angle of refraction, and $ {n_1} $ and $ {n_2} $ are the indices of refraction for the glass and air respectively.
Complete step by step answer
Let us consider the angle of incidence of the light rays on the top inner layer of the cubic glass be $ {\theta _i} $ and the angle of refraction be $ {\theta _r} $ . Let us also assume that $ {n_1} $ and $ {n_2} $ are the refractive indices of the glass and air respectively.
The figure below shows the cross-section of the cubical glass and let us consider that all the sides of the cubical glass is of length $ a $ .

For the total internal reflection to happen so that the light will not refract out through the vertical faces, the boundary condition is that the refracted angle $ {\theta _r} = 90^\circ $ . Since, all the sides of a cube are equal in dimensions from the figure it is clear that the critical angle $ {\theta _c} = 45^\circ $ .
Now, from Snell’s law, we know that:
$ \dfrac{{sin{\theta _c}}}{{sin{\theta _r}}} = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}} $
But, for air, the index of refraction, $ {n_2} = 1 $ .
Therefore, we can rewrite the above equation as:
$ \dfrac{{sin45^\circ }}{{sin90^\circ }} = \dfrac{1}{{{n_1}}} $
Solving this, we get the minimum value of refractive index of the cubical glass as:
$ {n_1} = \dfrac{1}{{sin45^\circ }} = \sqrt 2 $ .
Hence, the correct answer is option (D).
Note
In this problem, the boundary condition to get the letters invisible from the vertical faces is the total internal reflection when the light reaches the vertical faces from inside. When the incident angle is equal to the critical angle, then the entire light rays incident are completely reflected. Thus, no light enters the air medium from the glass and the condition is achieved.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




