
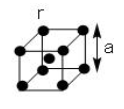
The unit cell in a body centred cubic lattice is given in the figure. Each sphere has radius $r$ and the cube side $a$. What fraction of the total cube volume is empty?
A) $1 - \dfrac{8}{3}\pi \dfrac{{{r^3}}}{{{a^3}}}$
B) $\dfrac{4}{3}\pi \dfrac{{{r^3}}}{{{a^3}}}$
C) $\dfrac{r}{a}$
D) $2 - \dfrac{4}{3}\pi \dfrac{{{r^3}}}{{{a^3}}}$

Answer
548.4k+ views
Hint:
To answer this question, you must find the relation between the edge length of the unit cell and radius of the constituent particles. In a body centered cubic unit cell, each corner touches the body centre atom. So, closest contact is along the body diagonal of the cube.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 a}}{4} = r$
Where $a$ is the side of the cube and $r$ is the radius of the constituent atoms.
Complete step by step solution:
In a body centred cubic lattice, the effective number of atoms in the unit cell is $n = 2$ .
Firstly, we must find the volume of the unit cell. We have with us a cubic unit cell.
The volume of a cube is given by
$V = {a^3}$ ..….
The next step is to find the volume occupied by the atoms.
The volume of a sphere is given by
$v = \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {r^3}$
Where $r$ is the radius of the sphere.
Hence, we can say that the volume occupied by one atom is $v = \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {r^3}$
So, the volume occupied by two atoms will be${v_n} = 2 \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {r^3} = \dfrac{8}{3}\pi {r^3}$ .….
To solve the question further we need to find the relation between the radius of constituent particles and edge length of the unit cell.
The body diagonal of the cube is given by $d = \sqrt 3 a$
The body diagonal of the unit cell is equal to 4 times the radius of constituent atoms.
Hence,
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt 3 a = 4r$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 a}}{4} = r$ ……
Substituting the value of $r$ in terms of $a$ into equation (2), we get
${v_n} = \dfrac{8}{3}\pi {\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 a}}{4}} \right)^3}$
${v_n} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{8}\pi {a^3}$ …..
Volume of cube that is empty is given by,
${v_e} = V - {v_n} = \left( {1 - \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{8}\pi {a^3}} \right) \approx 0.3{a^3}$
Fraction of the total cube volume empty:
$\dfrac{{{v_e}}}{{V - {v_n}}} = \dfrac{{0.3{a^3}}}{{{a^3}}} = 0.3$
Note:
To find the number of atoms in a unit cell we use the formula
$n = \dfrac{{{n_c}}}{8} + \dfrac{{{n_f}}}{2} + \dfrac{{{n_i}}}{1} + \dfrac{{{n_e}}}{4}$
where,$n$ is effective number of atoms in unit cell
${n_c}$ is number of atoms at the corners of the unit cell
${n_f}$ is number of atoms at the six faces of the unit cell
${n_i}$ is number of atoms completely inside the unit cell
${n_e}$ is number of atoms at the edge centres of the unit cell
Firstly, we start by finding the effective number of atoms in the unit cell
In a body centred cubic unit cell, atoms are present at the corners and the body centre of the cube. So, we can write that,
${n_c} = $ number of atoms at the corners of the unit cell $ = 8$
${n_f} = $number of atoms at the six faces of the unit cell $ = 0$
${n_i} = $ number of atoms completely inside the unit cell $ = 1$
${n_e} = $number of atoms at the edge centres of the unit cell $ = 0$
Thus, the total number of atoms in a body centred unit cell is
$n = \dfrac{{{n_c}}}{8} + \dfrac{{{n_f}}}{2} + \dfrac{{{n_i}}}{1} + \dfrac{{{n_e}}}{4}$
Substituting the values, we get
$n = \dfrac{8}{8} + \dfrac{0}{2} + \dfrac{1}{1} + \dfrac{0}{4}$
$n = 1 + 0 + 1 + 0$
Thus, $n = 2$
To answer this question, you must find the relation between the edge length of the unit cell and radius of the constituent particles. In a body centered cubic unit cell, each corner touches the body centre atom. So, closest contact is along the body diagonal of the cube.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 a}}{4} = r$
Where $a$ is the side of the cube and $r$ is the radius of the constituent atoms.
Complete step by step solution:
In a body centred cubic lattice, the effective number of atoms in the unit cell is $n = 2$ .
Firstly, we must find the volume of the unit cell. We have with us a cubic unit cell.
The volume of a cube is given by
$V = {a^3}$ ..….
The next step is to find the volume occupied by the atoms.
The volume of a sphere is given by
$v = \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {r^3}$
Where $r$ is the radius of the sphere.
Hence, we can say that the volume occupied by one atom is $v = \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {r^3}$
So, the volume occupied by two atoms will be${v_n} = 2 \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {r^3} = \dfrac{8}{3}\pi {r^3}$ .….
To solve the question further we need to find the relation between the radius of constituent particles and edge length of the unit cell.
The body diagonal of the cube is given by $d = \sqrt 3 a$
The body diagonal of the unit cell is equal to 4 times the radius of constituent atoms.
Hence,
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt 3 a = 4r$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 a}}{4} = r$ ……
Substituting the value of $r$ in terms of $a$ into equation (2), we get
${v_n} = \dfrac{8}{3}\pi {\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 a}}{4}} \right)^3}$
${v_n} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{8}\pi {a^3}$ …..
Volume of cube that is empty is given by,
${v_e} = V - {v_n} = \left( {1 - \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{8}\pi {a^3}} \right) \approx 0.3{a^3}$
Fraction of the total cube volume empty:
$\dfrac{{{v_e}}}{{V - {v_n}}} = \dfrac{{0.3{a^3}}}{{{a^3}}} = 0.3$
Note:
To find the number of atoms in a unit cell we use the formula
$n = \dfrac{{{n_c}}}{8} + \dfrac{{{n_f}}}{2} + \dfrac{{{n_i}}}{1} + \dfrac{{{n_e}}}{4}$
where,$n$ is effective number of atoms in unit cell
${n_c}$ is number of atoms at the corners of the unit cell
${n_f}$ is number of atoms at the six faces of the unit cell
${n_i}$ is number of atoms completely inside the unit cell
${n_e}$ is number of atoms at the edge centres of the unit cell
Firstly, we start by finding the effective number of atoms in the unit cell
In a body centred cubic unit cell, atoms are present at the corners and the body centre of the cube. So, we can write that,
${n_c} = $ number of atoms at the corners of the unit cell $ = 8$
${n_f} = $number of atoms at the six faces of the unit cell $ = 0$
${n_i} = $ number of atoms completely inside the unit cell $ = 1$
${n_e} = $number of atoms at the edge centres of the unit cell $ = 0$
Thus, the total number of atoms in a body centred unit cell is
$n = \dfrac{{{n_c}}}{8} + \dfrac{{{n_f}}}{2} + \dfrac{{{n_i}}}{1} + \dfrac{{{n_e}}}{4}$
Substituting the values, we get
$n = \dfrac{8}{8} + \dfrac{0}{2} + \dfrac{1}{1} + \dfrac{0}{4}$
$n = 1 + 0 + 1 + 0$
Thus, $n = 2$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




