
The taxi fare in a city is as follows: For the first kilometer, the fare is 8 and for the subsequent distance it is 5 per km. Taking the distance covered as \[x\] km and total fare as \[Rs.y\], write a linear equation for this information and draw its graph.
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint:
Here, we have to find the linear equation using the given information. First, we have to frame a linear equation for the information. We will arrive at a linear equation in one variable. We have to draw a graph for the linear equation. We have to plot the graph by finding the coordinates with the help of the linear equation.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us consider the distance covered as \[x\] km and total fare as \[Rs.y\].
Taxi fare for first kilometer \[ = {\rm{Rs}}.8\]
Taxi fare for subsequent distance \[ = {\rm{Rs}}.5\]
Total distance covered \[ = x\]
Total fare \[ = y\]
From the given Problem, we have
Fare for \[\left( {x-1} \right)\] kilometer \[ = 5\left( {x - 1} \right)\]
Since the fare for the first kilometer is equal to 8 rupees.
So, the total fare \[y = 5\left( {x - 1} \right) + 8\]
Multiplying the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow y = 5x-5 + 8\]
Simplifying the equation, we have
\[ \Rightarrow y = 5x + 3\] …………………………………..\[\left( 1 \right)\]
Therefore, \[y = 5x + 3\] is the required linear equation.
Now, Substituting the value of in Equation \[\left( 1 \right)\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow y = 5 \times 0 + 3\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = 0 + 3 = 3\]
So the solution is \[\left( {0,3} \right)\]
Substituting the value of \[x = 1\] in Equation \[\left( 1 \right)\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow y = 5 \times 1 + 3\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = 5 + 3 = 8\].
So the solution is \[\left( {1,8} \right)\]
Substituting the value of \[x=2\] in Equation \[\left( 1 \right)\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow y = 5 \times 2 + 3\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = 10 + 3 = 13\].
So the solution is \[\left( {2,13} \right)\].
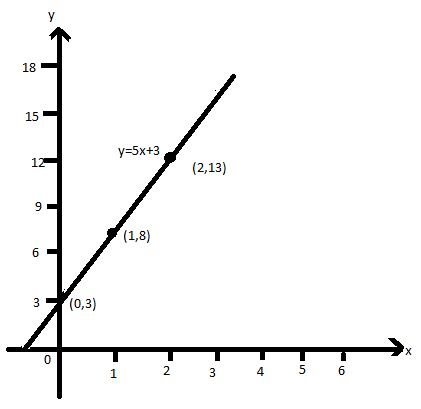
Therefore, the coordinates of a Point are \[\left( {0,3} \right)\], \[\left( {1,8} \right)\],\[\left( {2,13} \right)\].
Now we will draw the graph using these points.
Note:
We have to be very careful in framing a linear equation. First of all, we have to read the given problem carefully and note down the given and required quantities separately. We denote the unknown quantities as ‘\[x\]’, ‘\[y\]’, ‘\[z\]’, etc. Then translate the problem into mathematical language or statement. Form the linear equation in one variable using the given conditions in the problem. Solve the equation for the unknown quantity. This procedure is applicable for linear equations in one variable.
Here, we have to find the linear equation using the given information. First, we have to frame a linear equation for the information. We will arrive at a linear equation in one variable. We have to draw a graph for the linear equation. We have to plot the graph by finding the coordinates with the help of the linear equation.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us consider the distance covered as \[x\] km and total fare as \[Rs.y\].
Taxi fare for first kilometer \[ = {\rm{Rs}}.8\]
Taxi fare for subsequent distance \[ = {\rm{Rs}}.5\]
Total distance covered \[ = x\]
Total fare \[ = y\]
From the given Problem, we have
Fare for \[\left( {x-1} \right)\] kilometer \[ = 5\left( {x - 1} \right)\]
Since the fare for the first kilometer is equal to 8 rupees.
So, the total fare \[y = 5\left( {x - 1} \right) + 8\]
Multiplying the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow y = 5x-5 + 8\]
Simplifying the equation, we have
\[ \Rightarrow y = 5x + 3\] …………………………………..\[\left( 1 \right)\]
Therefore, \[y = 5x + 3\] is the required linear equation.
Now, Substituting the value of in Equation \[\left( 1 \right)\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow y = 5 \times 0 + 3\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = 0 + 3 = 3\]
So the solution is \[\left( {0,3} \right)\]
Substituting the value of \[x = 1\] in Equation \[\left( 1 \right)\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow y = 5 \times 1 + 3\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = 5 + 3 = 8\].
So the solution is \[\left( {1,8} \right)\]
Substituting the value of \[x=2\] in Equation \[\left( 1 \right)\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow y = 5 \times 2 + 3\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = 10 + 3 = 13\].
So the solution is \[\left( {2,13} \right)\].
Therefore, the coordinates of a Point are \[\left( {0,3} \right)\], \[\left( {1,8} \right)\],\[\left( {2,13} \right)\].
Now we will draw the graph using these points.

Note:
We have to be very careful in framing a linear equation. First of all, we have to read the given problem carefully and note down the given and required quantities separately. We denote the unknown quantities as ‘\[x\]’, ‘\[y\]’, ‘\[z\]’, etc. Then translate the problem into mathematical language or statement. Form the linear equation in one variable using the given conditions in the problem. Solve the equation for the unknown quantity. This procedure is applicable for linear equations in one variable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




