
The strongest acid among the following aromatic compounds is:
A. Ortho-nitrophenol
B. Para-chlorophenol
C. Para-nitrophenol
D. Meta-nitrophenol
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: To find the strongest acid among the following aromatic compounds first we will study about their structures, substituents and most important the position of substituents. We will also try to figure out the factors which affect the acidic strength of aromatic compounds. After considering all these points we will be able to find the strongest acid among the following aromatic compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
First we will draw the structures of all the given aromatic compounds one by one. Then we will figure out the substituent and its position in the aromatic compound. So the given aromatic compounds are as follows.
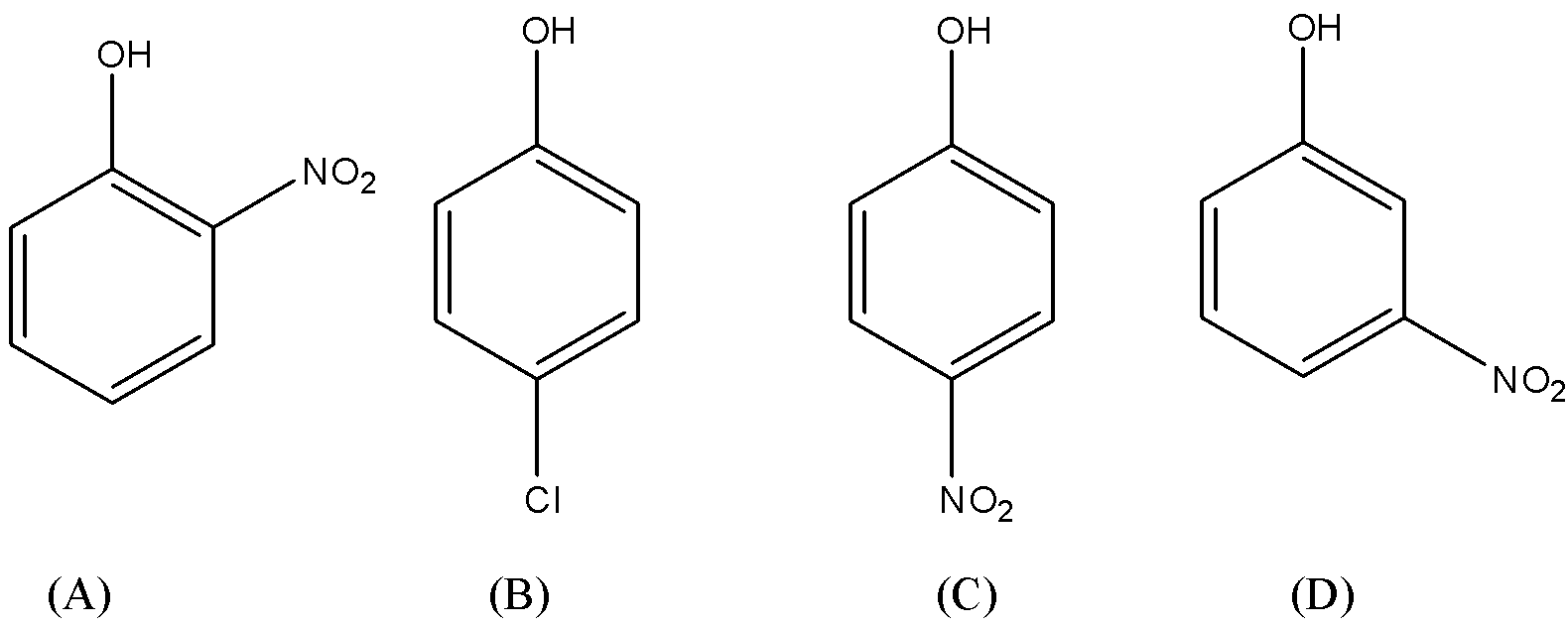
In (A), (B) and (C) the substituent is nitro-group $\left( { - N{O_2}} \right)$ and is present at ortho, Meta and para positions. In option (B) substituent $\left( { - Cl} \right)$ is present at para position.
The nitro group $\left( { - N{O_2}} \right)$ and $\left( { - Cl} \right)$ both are the electron withdrawing groups which means it withdraws electrons from the electro centre. There is one relation you should keep in mind that the electron withdrawing group increases the acidic strength.
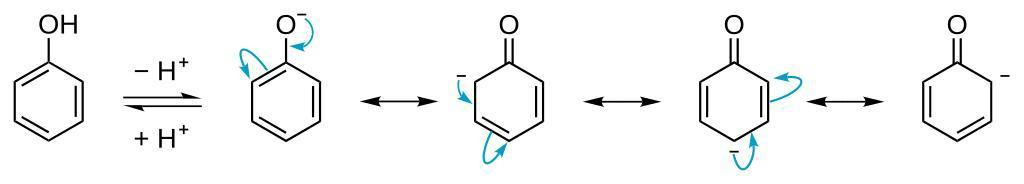
Both substituents are electron withdrawing groups but nitrophenol is more acidic than chlorophenol due to resonance. According to above resonance structure delocalisation is possible only at ortho and para position. Meta position is not delocalized.
Now out of ortho and para nitrophenol. ortho-nitrophenol takes part in hydrogen bonding which makes it less acidic than the para-nitrophenol. So para-nitrophenol is the strongest acid among the following aromatic compounds.
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: Electron withdrawing effect is represented as $\left( { - I} \right)$ inductive effect. When all the substituents are electron withdrawing groups we can use a priority order.
The priority order is as follows: ${R_3}N > N{O_2} > CN > COOH > F > Cl > Br > I > OH > {C_6}{H_5} > CH = C{H_2} > H$
Complete step by step answer:
First we will draw the structures of all the given aromatic compounds one by one. Then we will figure out the substituent and its position in the aromatic compound. So the given aromatic compounds are as follows.

In (A), (B) and (C) the substituent is nitro-group $\left( { - N{O_2}} \right)$ and is present at ortho, Meta and para positions. In option (B) substituent $\left( { - Cl} \right)$ is present at para position.
The nitro group $\left( { - N{O_2}} \right)$ and $\left( { - Cl} \right)$ both are the electron withdrawing groups which means it withdraws electrons from the electro centre. There is one relation you should keep in mind that the electron withdrawing group increases the acidic strength.

Both substituents are electron withdrawing groups but nitrophenol is more acidic than chlorophenol due to resonance. According to above resonance structure delocalisation is possible only at ortho and para position. Meta position is not delocalized.
Now out of ortho and para nitrophenol. ortho-nitrophenol takes part in hydrogen bonding which makes it less acidic than the para-nitrophenol. So para-nitrophenol is the strongest acid among the following aromatic compounds.
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: Electron withdrawing effect is represented as $\left( { - I} \right)$ inductive effect. When all the substituents are electron withdrawing groups we can use a priority order.
The priority order is as follows: ${R_3}N > N{O_2} > CN > COOH > F > Cl > Br > I > OH > {C_6}{H_5} > CH = C{H_2} > H$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




