
The stability of free radicals in the increasing order of:
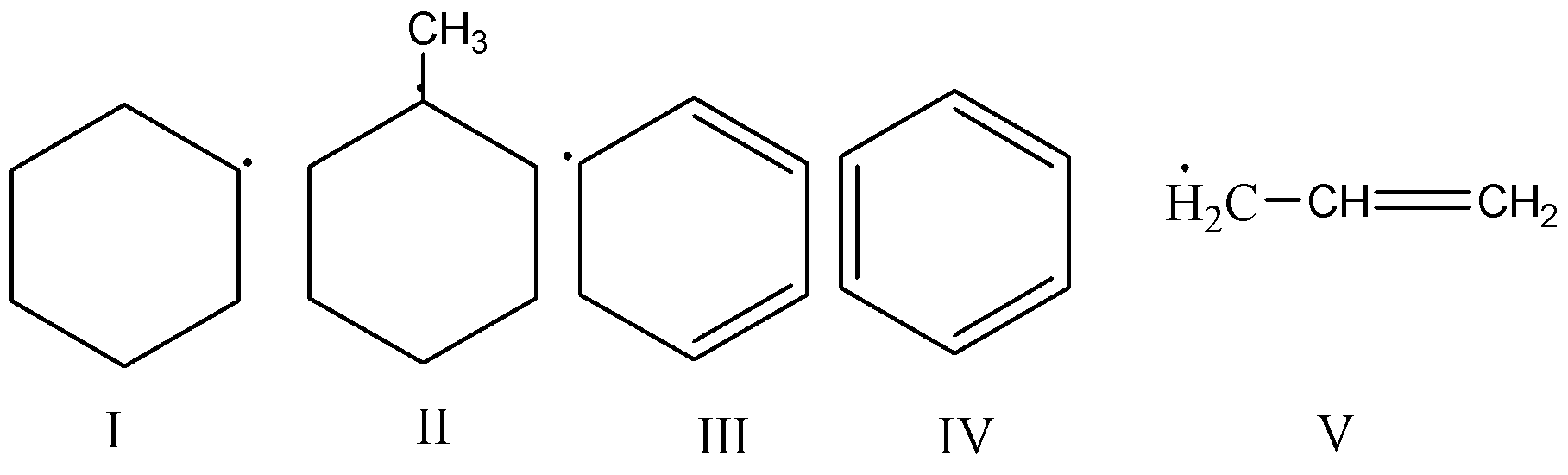
A. IV < I < II < III < V
B. IV < I < V < II < III
C. V < I < III < II < IV
D. III < II < I < V > IV

Answer
523.2k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we need to understand the meaning of free radicals and then understand the stability of free radicals. A free radical is an atom or a group of atoms that belong to the same or different elements that behave as a single unit and possess a negative or positive charge. Any free radical can be a basic radical which has a positive charge or a cation. Else a free radical can also be an acidic radical that has a negative charge or an anion.
Complete step by step answer:
We must know that the free radicals possess their own combination power and based on this combination power their chemical formula is formed. To check out the stability of free radicals in increasing order we need to keep in mind that the order goes in the following way: methyl < primary radicals < secondary radicals < tertiary radicals.
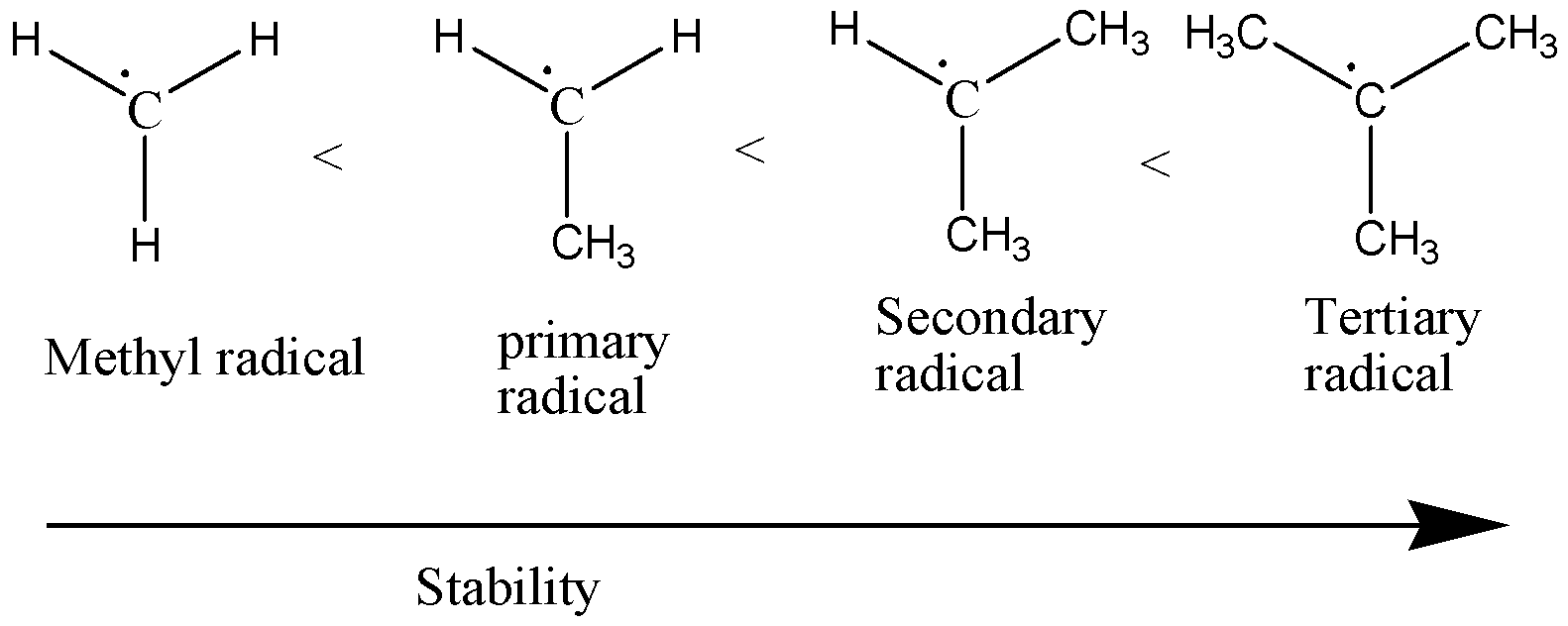
Also, the free radicals get stabilized by resonance or delocalization.
Here, in this question based on the stability order of the stability of free radicals, the correct order will be V>III>II>I>IV .
As in the V free radical, it gets stabilized by hyperconjugation as from hyperconjugation the most dominant factor for stability is derived.
In III free radical, we can see that the stabilization occurs by extended conjugation or resonance.
In II free radical, stabilization occurs by resonance and electron donating effect of \[ - C{H_3}\]
In the free radical, the stabilization occurs by simple ${2^ \circ }$ Carbon.
And in the IV free radical present in Benzene is the least and most difficult one to get stabilized.
$\therefore $The option A is correct answer.
Note:
We must know that the free radicals are destabilized by removal of electron density, stability decreases with the increment in s-character of the orbital, stability decreases with increasing electronegativity of the atom and decreases with a decrease in polarity.
Complete step by step answer:
We must know that the free radicals possess their own combination power and based on this combination power their chemical formula is formed. To check out the stability of free radicals in increasing order we need to keep in mind that the order goes in the following way: methyl < primary radicals < secondary radicals < tertiary radicals.

Also, the free radicals get stabilized by resonance or delocalization.
Here, in this question based on the stability order of the stability of free radicals, the correct order will be V>III>II>I>IV .
As in the V free radical, it gets stabilized by hyperconjugation as from hyperconjugation the most dominant factor for stability is derived.
In III free radical, we can see that the stabilization occurs by extended conjugation or resonance.
In II free radical, stabilization occurs by resonance and electron donating effect of \[ - C{H_3}\]
In the free radical, the stabilization occurs by simple ${2^ \circ }$ Carbon.
And in the IV free radical present in Benzene is the least and most difficult one to get stabilized.
$\therefore $The option A is correct answer.
Note:
We must know that the free radicals are destabilized by removal of electron density, stability decreases with the increment in s-character of the orbital, stability decreases with increasing electronegativity of the atom and decreases with a decrease in polarity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




