
What will be the reading of ammeter in the circuit below is:
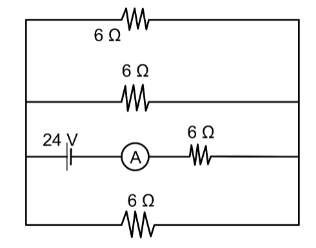
A. $16{\text{ }}A\:$
B. $3{\text{ }}A\:$
C. $4{\text{ }}A\:$
D. $12{\text{ }}A\:$

Answer
508.5k+ views
Hint: We will firstly evaluate the equivalent resistance of the circuit. Then, we will use this value in the ohm’s law formula. We will substitute the given potential difference value and the equivalent resistance and finally evaluate the current out of the cell and this will be the value of current through the ammeter.
Formulae used:
Equivalent resistance of parallel combination of resistances:
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}...{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_n}}}$
Equivalent resistance of series combination of resistances:
${R_{eq}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{R_1}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{R_2}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}...{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{R_n}$
The ohm’s law formula:
$I = {\text{ }}\dfrac{V}{R}$
Complete step by step answer:
The net resistance of the part above the cell arm can be calculated using the formula of parallel combination as the two resistances are connected in parallel. Thus, the net resistance of the upper part can be evaluated as:
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{up}}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}$
Here, the values are
${R_1}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}6{\text{ }}\Omega $
And,
${R_2}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}6{\text{ }}\Omega $
Substituting these values, we get
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{up}}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{6}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{6}{\text{ }} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R_{up}}}}{\text{ }}= {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{3}$
Hence, the value is
${R_{up}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}3{\text{ }}\Omega $
Similarly, the net resistance of the lower part is:
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{low}}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{6}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{6}{\text{ }} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R_{low}}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{3}$
Then, we get
${R_{low}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}3{\text{ }}\Omega $
Now, the equivalent resistance of the circuit can be evaluated using the series formula as the upper and the lower net resistance are in series.
Hence,
${R_{eq}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{R_{up}}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{R_{low}}$
Substituting the values, we get
${R_{eq}}\; = {\text{ }}3{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}3{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}6{\text{ }}\Omega $
Now, the value of potential of the cell is
$V{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}24{\text{ }}V$
Thus, the current through the cell is
$\therefore I{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{24}}{6}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}4{\text{ }}A$
Thus, this current will flow through the ammeter.
Hence the correct option is C.
Note: Students should be very cautious while judging the type of combination of the resistors. For some cases the answer by chance turns out to be correct but in general this mistake can lead to a blunder. Students commit error while noting down the net resistance mainly in a parallel combination as the formula is of a reciprocated form.
Formulae used:
Equivalent resistance of parallel combination of resistances:
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}...{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_n}}}$
Equivalent resistance of series combination of resistances:
${R_{eq}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{R_1}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{R_2}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}...{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{R_n}$
The ohm’s law formula:
$I = {\text{ }}\dfrac{V}{R}$
Complete step by step answer:
The net resistance of the part above the cell arm can be calculated using the formula of parallel combination as the two resistances are connected in parallel. Thus, the net resistance of the upper part can be evaluated as:
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{up}}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}$
Here, the values are
${R_1}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}6{\text{ }}\Omega $
And,
${R_2}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}6{\text{ }}\Omega $
Substituting these values, we get
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{up}}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{6}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{6}{\text{ }} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R_{up}}}}{\text{ }}= {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{3}$
Hence, the value is
${R_{up}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}3{\text{ }}\Omega $
Similarly, the net resistance of the lower part is:
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{low}}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{6}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{6}{\text{ }} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R_{low}}}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{1}{3}$
Then, we get
${R_{low}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}3{\text{ }}\Omega $
Now, the equivalent resistance of the circuit can be evaluated using the series formula as the upper and the lower net resistance are in series.
Hence,
${R_{eq}}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{R_{up}}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{R_{low}}$
Substituting the values, we get
${R_{eq}}\; = {\text{ }}3{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}3{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}6{\text{ }}\Omega $
Now, the value of potential of the cell is
$V{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}24{\text{ }}V$
Thus, the current through the cell is
$\therefore I{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{24}}{6}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}4{\text{ }}A$
Thus, this current will flow through the ammeter.
Hence the correct option is C.
Note: Students should be very cautious while judging the type of combination of the resistors. For some cases the answer by chance turns out to be correct but in general this mistake can lead to a blunder. Students commit error while noting down the net resistance mainly in a parallel combination as the formula is of a reciprocated form.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




