
The reaction,
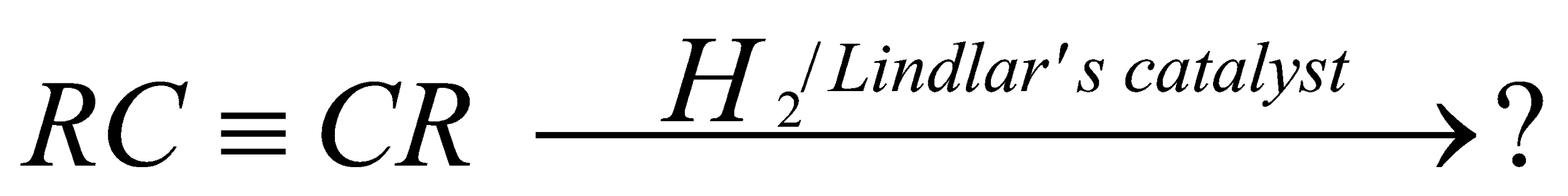 gives the main product as:
gives the main product as:
A. cis-alkene
B. trans-alkene
C. alkane
D. None of these.
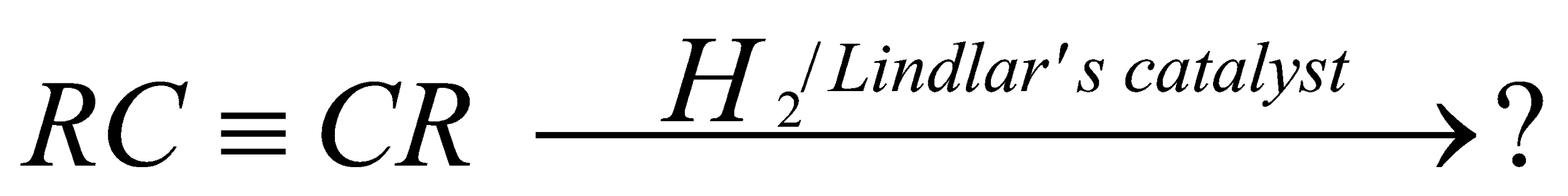
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: The Lindlar's catalyst is used to reduce alkynes to alkenes. Alkyne hydrogenation is always stereoselective and by using Lindlar's catalyst, it occur via syn addition to give the cis-alkene.
Complete step by step answer:
In this question we have been given a reaction, in which the reactant is alkyne and the catalyst is Lindlar's catalyst and we have been asked what will be the product of this reaction.
So, for solving this question we have to know, what does Lindlar's catalyst do?
A Lindlar catalyst is a heterogeneous catalyst and is used for the hydrogenation of alkynes to alkenes (i.e. without further reduction into alkanes).
It can only reduce alkynes and not alkenes. It always gives the cis-alkene, in contrast to $Na$/$NH_3$, which gives the trans alkenes. So, it will change the alkyne into alkene. Now the question arise which type of alkane will form cis or trans.
Alkyne hydrogenation by Lindlar's catalyst is always stereoselective. By using Lindlar's catalyst the reaction occurs via syn addition to give the cis-alkene. It means that both the hydrogen atoms attack from the same side of the plane and the dipole moment will be in the same direction.
So, the correct option will be A. cis alkene.
Note:
A Lindlar’s catalyst is a heterogeneous catalyst and it is also called a poisoned catalyst. It only breaks one bond of the corresponding unsaturated system if the provided moles of catalyst is whatsoever high. This poisoned catalyst consists of palladium, calcium carbonate, lead (II) acetate, and quinoline.
Complete step by step answer:
In this question we have been given a reaction, in which the reactant is alkyne and the catalyst is Lindlar's catalyst and we have been asked what will be the product of this reaction.
So, for solving this question we have to know, what does Lindlar's catalyst do?
A Lindlar catalyst is a heterogeneous catalyst and is used for the hydrogenation of alkynes to alkenes (i.e. without further reduction into alkanes).
It can only reduce alkynes and not alkenes. It always gives the cis-alkene, in contrast to $Na$/$NH_3$, which gives the trans alkenes. So, it will change the alkyne into alkene. Now the question arise which type of alkane will form cis or trans.
Alkyne hydrogenation by Lindlar's catalyst is always stereoselective. By using Lindlar's catalyst the reaction occurs via syn addition to give the cis-alkene. It means that both the hydrogen atoms attack from the same side of the plane and the dipole moment will be in the same direction.
So, the correct option will be A. cis alkene.
Note:
A Lindlar’s catalyst is a heterogeneous catalyst and it is also called a poisoned catalyst. It only breaks one bond of the corresponding unsaturated system if the provided moles of catalyst is whatsoever high. This poisoned catalyst consists of palladium, calcium carbonate, lead (II) acetate, and quinoline.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




