
The principle behind the working of an atom bomb is:
a.) Nuclear fusion
b.) Nuclear fission
c.) Radioactivity
d.) None of these
Answer
600k+ views
Hint: When a heavier nuclei having high atomic number and mass number disintegrates into lighter nuclei of lower mass number and atomic number, a large amount of energy is produced which can be used as a weapon of mass destruction if implemented in a certain way.
Detailed step by step solution:
An atom bomb is a weapon which can cause a lot of destruction in the area where it is dropped.
The working of an atomic bomb is based on the phenomenon of nuclear fission.
Nuclear fission can be defined as a nuclear phenomenon in which the nucleus of an element having high atomic number and mass number splits into a lighter nuclei of smaller mass number and atomic number.
This phenomena is based on the binding energy per nucleon curve shown below.
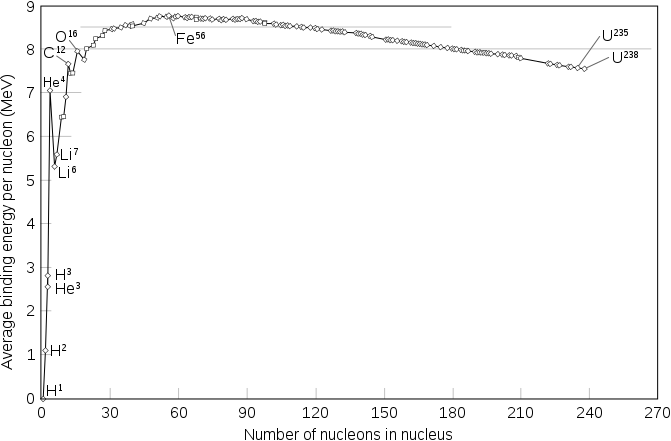
In this plot, the elements beyond iron have big nuclei with large numbers of nucleons and are unstable. They try to achieve stability by undergoing nuclear fission to reduce their number of nucleons.
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note:
1. Radioactivity and nuclear fission are two different phenomena in the sense that in radioactivity, the nucleus of a radioactive isotope undergoes decay to emit certain radiation whereas in case of nuclear fission, a heavier unstable nucleus breaks into nuclei of lighter mass giving off a lot of energy.
2. In nuclear fusion, lighter nuclei combine to form a heavier nuclei. This process requires a lot of energy. It is the process by which the sun’s core gets its energy. On earth, we have not yet discovered a method to produce the required amount of energy required for nuclear fusion to occur.
Detailed step by step solution:
An atom bomb is a weapon which can cause a lot of destruction in the area where it is dropped.
The working of an atomic bomb is based on the phenomenon of nuclear fission.
Nuclear fission can be defined as a nuclear phenomenon in which the nucleus of an element having high atomic number and mass number splits into a lighter nuclei of smaller mass number and atomic number.
This phenomena is based on the binding energy per nucleon curve shown below.

In this plot, the elements beyond iron have big nuclei with large numbers of nucleons and are unstable. They try to achieve stability by undergoing nuclear fission to reduce their number of nucleons.
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note:
1. Radioactivity and nuclear fission are two different phenomena in the sense that in radioactivity, the nucleus of a radioactive isotope undergoes decay to emit certain radiation whereas in case of nuclear fission, a heavier unstable nucleus breaks into nuclei of lighter mass giving off a lot of energy.
2. In nuclear fusion, lighter nuclei combine to form a heavier nuclei. This process requires a lot of energy. It is the process by which the sun’s core gets its energy. On earth, we have not yet discovered a method to produce the required amount of energy required for nuclear fusion to occur.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




