
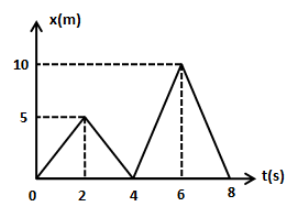
The position-time (x-t) graph for a particle moving along x-axis is as shown. Average speed of the particle between \[t = 0\] and \[t = 8\,{\text{s}}\] is
A. Zero
B. 8 m/s
C. 3.75 m/s
D. 4.25 m/s

Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint:The average speed of the particle is the ratio of total distance travelled to the total time taken. The total distance travelled by the particle is the area under the curve of the above figure. The area under the curve consists of two triangles as shown in the above figure.
Formula used:
Average speed, \[{v_{avg}} = \dfrac{D}{t}\]
Here, D is the total distance and t is the total elapsed time.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the average speed of the particle is the ratio of total distance travelled to the total time taken.
\[{v_{avg}} = \dfrac{D}{t}\]
Here, D is the total distance and t is the total elapsed time.
In the above figure, the total distance travelled by the particle can be calculated by determining the area under the curve. We can see the area under the curve has two triangles of the same base length and different height.
The area under the curve is,
\[D = A = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {4 \times 5} \right) + \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {4 \times 10} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow D = 10 + 20\]
\[ \Rightarrow D = 30\,{\text{m}}\]
Now, the average speed of the particle is,
\[{v_{avg}} = \dfrac{D}{t}\]
Substituting \[D = 30\,{\text{m}}\] and \[t = 8\,{\text{s}}\] in the above equation, we get,
\[{v_{avg}} = \dfrac{{30}}{8}\]
\[ \therefore {v_{avg}} = 3.75\,{\text{m/s}}\]
Therefore, the average speed of the particle between \[t = 0\] and \[t = 8\,{\text{s}}\] is 3.75 m/s.
So, the correct answer is option C.
Note: If you are asked to determine the average velocity of the particle from the given distance-time graph, then the average velocity is zero because the initial and final position of the particle is the same. The average velocity deals with displacement of the particle while the average speed deals with total distance travelled by the particle. Note that the area under the curve is not the average speed of the particle.
Formula used:
Average speed, \[{v_{avg}} = \dfrac{D}{t}\]
Here, D is the total distance and t is the total elapsed time.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the average speed of the particle is the ratio of total distance travelled to the total time taken.
\[{v_{avg}} = \dfrac{D}{t}\]
Here, D is the total distance and t is the total elapsed time.
In the above figure, the total distance travelled by the particle can be calculated by determining the area under the curve. We can see the area under the curve has two triangles of the same base length and different height.
The area under the curve is,
\[D = A = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {4 \times 5} \right) + \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {4 \times 10} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow D = 10 + 20\]
\[ \Rightarrow D = 30\,{\text{m}}\]
Now, the average speed of the particle is,
\[{v_{avg}} = \dfrac{D}{t}\]
Substituting \[D = 30\,{\text{m}}\] and \[t = 8\,{\text{s}}\] in the above equation, we get,
\[{v_{avg}} = \dfrac{{30}}{8}\]
\[ \therefore {v_{avg}} = 3.75\,{\text{m/s}}\]
Therefore, the average speed of the particle between \[t = 0\] and \[t = 8\,{\text{s}}\] is 3.75 m/s.
So, the correct answer is option C.
Note: If you are asked to determine the average velocity of the particle from the given distance-time graph, then the average velocity is zero because the initial and final position of the particle is the same. The average velocity deals with displacement of the particle while the average speed deals with total distance travelled by the particle. Note that the area under the curve is not the average speed of the particle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




