
Bond order of${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$, $\text{O}_{\text{2}}^{\text{+}}$, $O_{2}^{-}$ and \[\text{O}_{\text{2}}^{\text{2-}}\] is in order.
(A) $\text{O}_{\text{2}}^{\text{- }}\langle \text{ O}_{2}^{2-}\text{ }\langle \text{ }{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ }\langle \text{ O}_{2}^{+}$
(B) $\text{O}_{\text{2}}^{\text{2- }}\langle \text{ O}_{2}^{-}\text{ }\langle \text{ }{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ }\langle \text{ O}_{2}^{+}$
(C) $\text{O}_{\text{2}}^{\text{+ }}\langle \text{ O}_{2}^{{}}\text{ }\langle \text{ O}_{2}^{-}\text{ }\langle \text{ O}_{2}^{2-}$
(D) $\text{O}_{\text{2}}^{\text{ }}\langle \text{ O}_{2}^{+}\text{ }\langle \text{ O}_{2}^{-}\text{ }\langle \text{ O}_{2}^{2-}$
Answer
537.3k+ views
Hint: First draw a molecular orbital diagram (MOT) where the atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals. The total electrons associated with the molecules are filled in the MOT diagram.
To solve this question, we need to write the molecular orbital configuration. To find out the bond order from the molecular orbital configuration is:
$\text{Bond order =}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\left[ \text{Bonding - antibonding} \right]$
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s first draw the MOT of the oxygen molecule. The oxygen molecule ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ contains the 16 electrons. The MOT is as shown below:
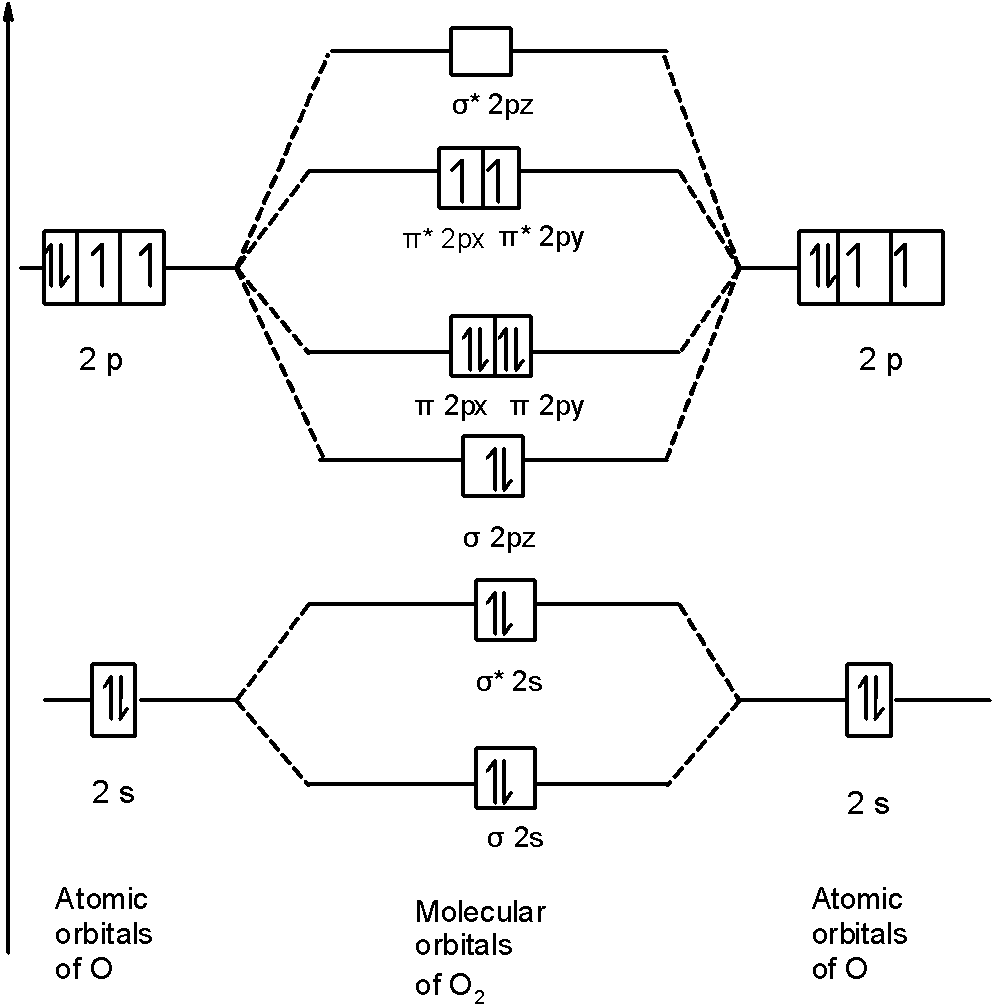
First of all, we can write the molecular orbital configuration of ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ the molecule. In a ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule, there are a total of 16 electrons. The molecular orbital configuration of ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ the molecule is as follows:
\[\]\[\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{,}{{\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }{{\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 2}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}_{z}\text{, 2p}_{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ = 2p}_{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ , 2p}_{\text{x}}^{1}{{\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{=2p}_{\text{y}}^{1}{{\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\]
There are 10 bonding and 6 nonbonding electrons in the orbitals according to the molecular orbital configuration.
Therefore, $\text{Bond order =}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\left[ \text{Bonding-antibonding} \right]$
= $\frac{1}{2}\left[ 10-6 \right]=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 4 \right)=2$
Thus, the bond order ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is 2.
Similarly, in $\text{O}_{\text{2}}^{\text{+}}$ a molecule, there are 15 electrons. Therefore, the MOT diagram $\text{O}_{\text{2}}^{\text{+}}$ contains the 15 electrons. We will write down the MOT diagram for the $\text{2p}$ orbital as the bonding between the $\text{1s}$ and $\text{2s}$ is the same as that of the ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ . The MOT diagram is,
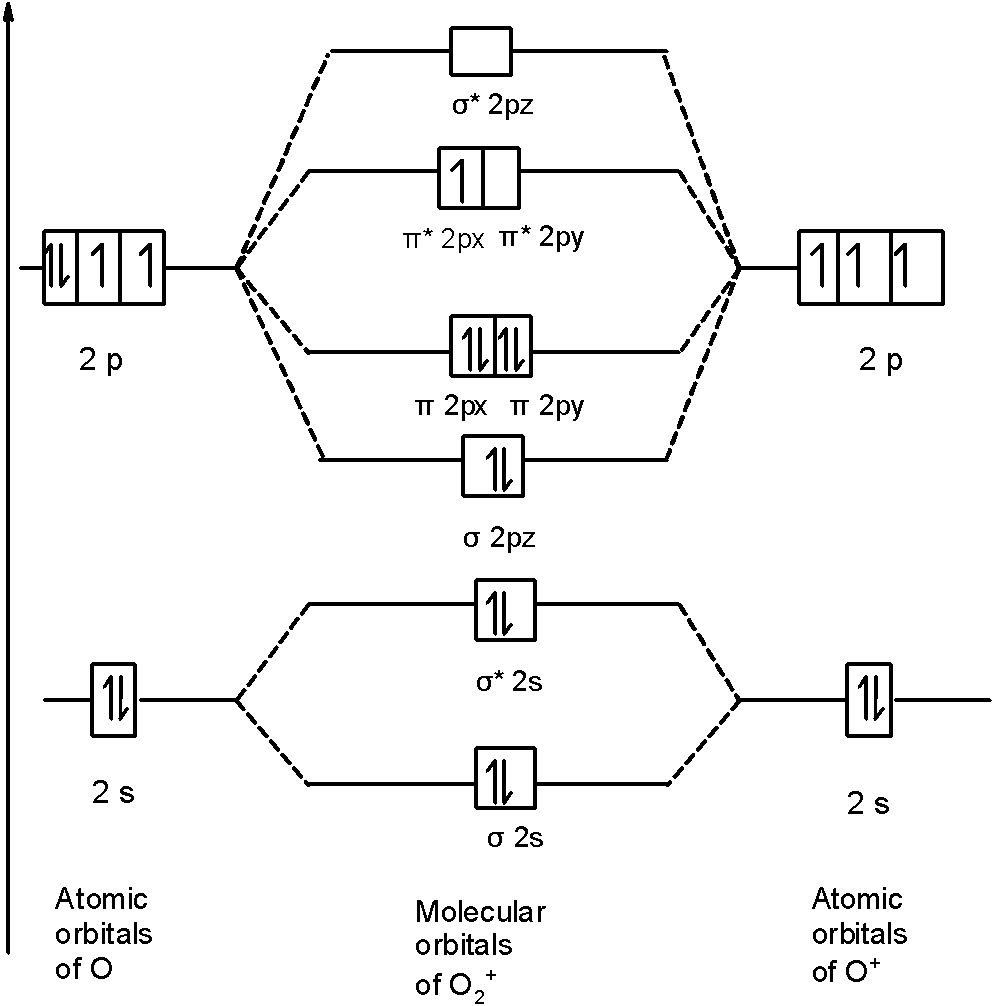
Therefore, the molecular orbital configuration of $\text{O}_{\text{2}}^{\text{+}}$ is as follows:$\text{O}_{\text{2}}^{\text{+}}$
\[\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{,}{{\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }{{\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 2}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}_{z}\text{, 2p}_{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ = 2p}_{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ , 2p}_{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}{{\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{=2p}_{\text{y}}^{0}{{\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\]
There are 10 bonding (including molecular orbitals formed by the $\text{1s}$ orbitals) and 5 nonbonding electrons in the orbitals according to the molecular orbital configuration.
Therefore, $\text{Bond order =}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\left[ \text{Bonding-antibonding} \right]$
$=\frac{1}{2}\left[ 10-5 \right]=2.5$
Therefore, the bond order of $\text{O}_{\text{2}}^{\text{+}}$ is $2.5$.
In $O_{2}^{-}$ a molecule, there are 17 electrons. The MOT diagram holds a total of 17 electrons. The MOT diagram is as shown below,
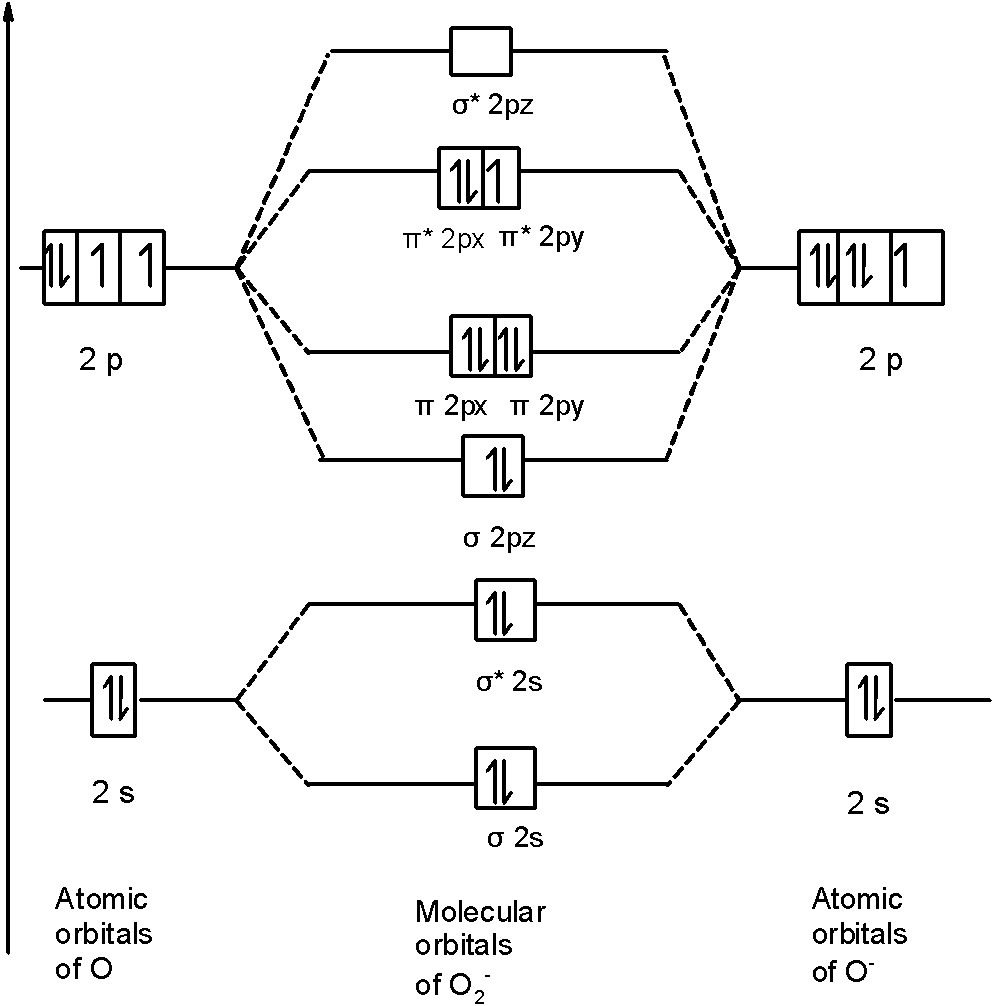
So, the molecular orbital configuration is as follows:
\[\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{,}{{\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }{{\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 2}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}_{z}\text{, 2p}_{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ = 2p}_{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ , 2p}_{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}{{\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{=2p}_{\text{y}}^{1}{{\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\]
There are 10 bonding electrons (including molecular orbitals formed by the $\text{1s}$ orbitals.) and 7 nonbonding electrons.
Therefore, $\text{Bond order =}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\left[ \text{Bonding-antibonding} \right]$
$=\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ 10-7 \right]=1.5$
Therefore, the bond order $O_{2}^{-}$ is $1.5$.
In \[\text{O}_{\text{2}}^{\text{2-}}\] a molecule, there are 18 electrons. The MOT diagram is as shown below,
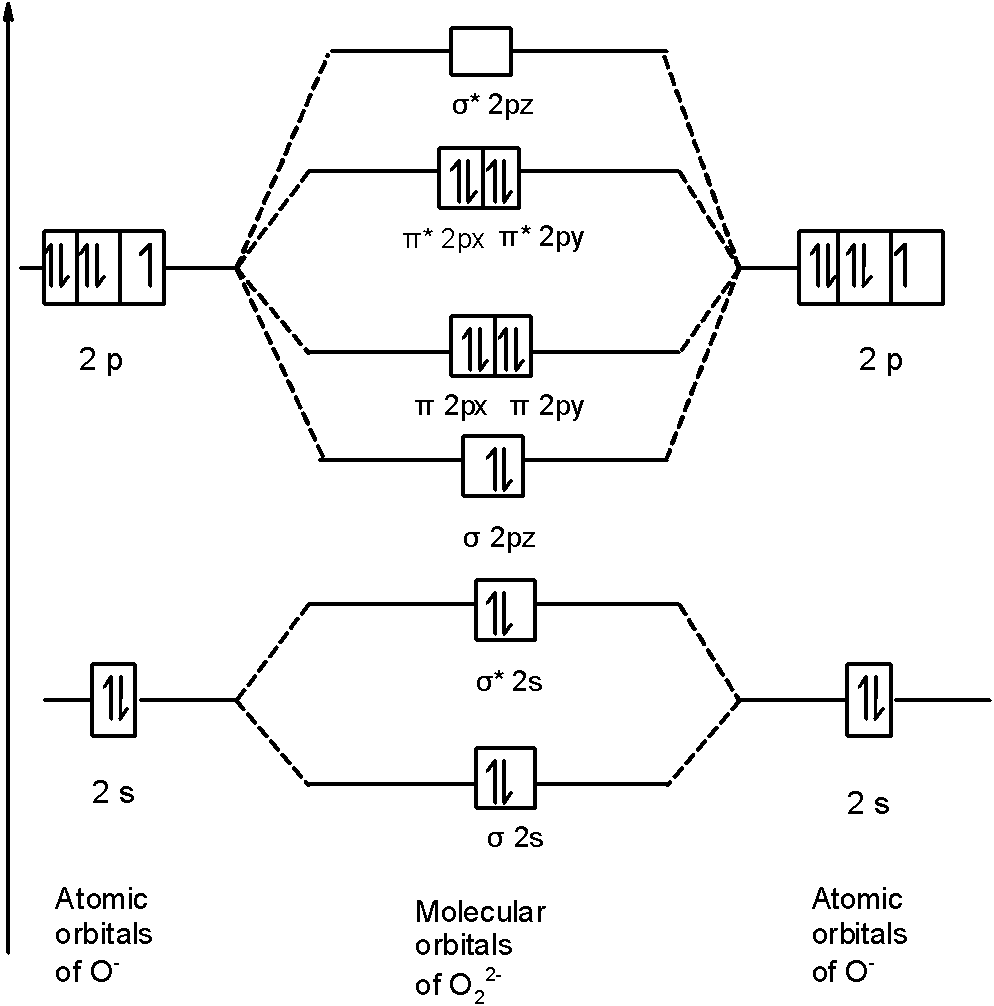
So, the molecular orbital configuration is as follows:
\[\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{,}{{\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }{{\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 2}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}_{z}\text{, 2p}_{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ = 2p}_{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ , 2p}_{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}{{\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{=2p}_{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}{{\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\]
There are 10 bonding electrons and 8 nonbonding electrons.
Therefore, $\text{bond order =}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\left[ \text{Bonding-antibonding} \right]$
$=\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ 10-8 \right]=1$
Therefore, the bond order \[\text{O}_{\text{2}}^{\text{2-}}\] is 1.
So, the correct order of bond order is $\text{O}_{\text{2}}^{\text{2- }}\langle \text{ O}_{2}^{-}\text{ }\langle \text{ }{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ }\langle \text{ O}_{2}^{+}$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: You should notice that bond order is indirectly proportional to the length of the bond. The higher the bond order, the shorter and stronger will be the bond. The addition of each electron in the antibonding molecular orbital will decrease the bond order.
To solve this question, we need to write the molecular orbital configuration. To find out the bond order from the molecular orbital configuration is:
$\text{Bond order =}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\left[ \text{Bonding - antibonding} \right]$
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s first draw the MOT of the oxygen molecule. The oxygen molecule ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ contains the 16 electrons. The MOT is as shown below:

First of all, we can write the molecular orbital configuration of ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ the molecule. In a ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule, there are a total of 16 electrons. The molecular orbital configuration of ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ the molecule is as follows:
\[\]\[\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{,}{{\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }{{\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 2}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}_{z}\text{, 2p}_{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ = 2p}_{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ , 2p}_{\text{x}}^{1}{{\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{=2p}_{\text{y}}^{1}{{\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\]
There are 10 bonding and 6 nonbonding electrons in the orbitals according to the molecular orbital configuration.
Therefore, $\text{Bond order =}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\left[ \text{Bonding-antibonding} \right]$
= $\frac{1}{2}\left[ 10-6 \right]=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 4 \right)=2$
Thus, the bond order ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is 2.
Similarly, in $\text{O}_{\text{2}}^{\text{+}}$ a molecule, there are 15 electrons. Therefore, the MOT diagram $\text{O}_{\text{2}}^{\text{+}}$ contains the 15 electrons. We will write down the MOT diagram for the $\text{2p}$ orbital as the bonding between the $\text{1s}$ and $\text{2s}$ is the same as that of the ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ . The MOT diagram is,

Therefore, the molecular orbital configuration of $\text{O}_{\text{2}}^{\text{+}}$ is as follows:$\text{O}_{\text{2}}^{\text{+}}$
\[\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{,}{{\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }{{\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 2}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}_{z}\text{, 2p}_{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ = 2p}_{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ , 2p}_{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}{{\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{=2p}_{\text{y}}^{0}{{\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\]
There are 10 bonding (including molecular orbitals formed by the $\text{1s}$ orbitals) and 5 nonbonding electrons in the orbitals according to the molecular orbital configuration.
Therefore, $\text{Bond order =}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\left[ \text{Bonding-antibonding} \right]$
$=\frac{1}{2}\left[ 10-5 \right]=2.5$
Therefore, the bond order of $\text{O}_{\text{2}}^{\text{+}}$ is $2.5$.
In $O_{2}^{-}$ a molecule, there are 17 electrons. The MOT diagram holds a total of 17 electrons. The MOT diagram is as shown below,

So, the molecular orbital configuration is as follows:
\[\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{,}{{\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }{{\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 2}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}_{z}\text{, 2p}_{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ = 2p}_{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ , 2p}_{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}{{\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{=2p}_{\text{y}}^{1}{{\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\]
There are 10 bonding electrons (including molecular orbitals formed by the $\text{1s}$ orbitals.) and 7 nonbonding electrons.
Therefore, $\text{Bond order =}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\left[ \text{Bonding-antibonding} \right]$
$=\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ 10-7 \right]=1.5$
Therefore, the bond order $O_{2}^{-}$ is $1.5$.
In \[\text{O}_{\text{2}}^{\text{2-}}\] a molecule, there are 18 electrons. The MOT diagram is as shown below,

So, the molecular orbital configuration is as follows:
\[\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{,}{{\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }{{\text{ }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{, }\!\!\sigma\!\!\text{ 2}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}_{z}\text{, 2p}_{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ = 2p}_{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ , 2p}_{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}{{\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\text{=2p}_{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}{{\text{ }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ }}^{\text{*}}}\]
There are 10 bonding electrons and 8 nonbonding electrons.
Therefore, $\text{bond order =}\dfrac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\left[ \text{Bonding-antibonding} \right]$
$=\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ 10-8 \right]=1$
Therefore, the bond order \[\text{O}_{\text{2}}^{\text{2-}}\] is 1.
So, the correct order of bond order is $\text{O}_{\text{2}}^{\text{2- }}\langle \text{ O}_{2}^{-}\text{ }\langle \text{ }{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ }\langle \text{ O}_{2}^{+}$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: You should notice that bond order is indirectly proportional to the length of the bond. The higher the bond order, the shorter and stronger will be the bond. The addition of each electron in the antibonding molecular orbital will decrease the bond order.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




