
The point of attachment of funicle with the chalazal end is called as
(a)Placenta
(b)Integument
(c)Nucellus
(d)Hilum
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: Ovules is that structure off the plants which gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells. They are attached to the ovaries by a stalk called funicle in angiosperms. This point of attachment is seen as a scar, later in the angiosperm seeds.
Complete answer:
Ovules are present inside the ovaries. The ovules are attached to the ovaries through the funicle which is a part of the ovary wall. The chalazal end represents the base of the ovule. The ovarian wall or Funicle is attached to the chalaza by the hilum.
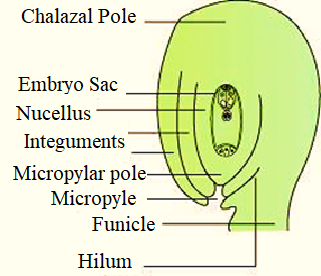
Additional Information: Based on this attachment and the orientation of hilum, chalaza, and micropyle (Opening of the ovule through which pollen tube penetrates) ovules are classified into six types.
-Orthotropous or atropous
The body of the ovule is straight with the hilum, chalaza, and micropyle in a straight line
Example - Polygonum.
-Anatropous
The body of the ovule is completely inverted during development due to which the micropyle lies very close to the hilum
Example - Gamopetalae members
-Hemi-anatropous or hemitropous
The body of the ovule is transversely placed at right angles to the funicle. Micropyle and chalaza lie in a straight line
Example - Ranunculus
-Campylotropous
The ovule is curved or bent round so the micropyle and chalaza do not lie in the same straight line. Example - Leguminosae
-Amphitropous
The curvature of the ovule is pronounced and the embryo sac also becomes curved
Example - Alismataceae
-Circinotropous
The nucellus and axis lie in the same line in the beginning. Due to rapid growth on one side however, the ovule becomes anatropous. The curvature increases further and the micropyle points upwards
Example - Opuntia.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Hilum.’
Note: In the seeds, the hilum is seen as a small scar in the seeds which represent this point of attachment.
These structures are seen only in Angiosperms.
In the development stage, gymnosperms are unitegmic and angiosperms are bitegmic which gives rise to the Ovary.
Since gymnosperms lack ovaries, ovules are present directly on the cones and hence lack funicle and hilum.
Complete answer:
Ovules are present inside the ovaries. The ovules are attached to the ovaries through the funicle which is a part of the ovary wall. The chalazal end represents the base of the ovule. The ovarian wall or Funicle is attached to the chalaza by the hilum.

Additional Information: Based on this attachment and the orientation of hilum, chalaza, and micropyle (Opening of the ovule through which pollen tube penetrates) ovules are classified into six types.
-Orthotropous or atropous
The body of the ovule is straight with the hilum, chalaza, and micropyle in a straight line
Example - Polygonum.
-Anatropous
The body of the ovule is completely inverted during development due to which the micropyle lies very close to the hilum
Example - Gamopetalae members
-Hemi-anatropous or hemitropous
The body of the ovule is transversely placed at right angles to the funicle. Micropyle and chalaza lie in a straight line
Example - Ranunculus
-Campylotropous
The ovule is curved or bent round so the micropyle and chalaza do not lie in the same straight line. Example - Leguminosae
-Amphitropous
The curvature of the ovule is pronounced and the embryo sac also becomes curved
Example - Alismataceae
-Circinotropous
The nucellus and axis lie in the same line in the beginning. Due to rapid growth on one side however, the ovule becomes anatropous. The curvature increases further and the micropyle points upwards
Example - Opuntia.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Hilum.’
Note: In the seeds, the hilum is seen as a small scar in the seeds which represent this point of attachment.
These structures are seen only in Angiosperms.
In the development stage, gymnosperms are unitegmic and angiosperms are bitegmic which gives rise to the Ovary.
Since gymnosperms lack ovaries, ovules are present directly on the cones and hence lack funicle and hilum.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




