
The oxoacid of sulphur that does not contain the bond between the sulphur atoms is:
A. ${{H}_{2}}{{S}_{4}}{{O}_{6}}$
B. ${{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}$
C. ${{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$
D. ${{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{4}}$
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint:. The linkage between the atoms in any oxyacid depends on the oxidation number of the central atom present in the compound and also on the highest oxidation number that can be attained by the central atom.
Complete step by step answer:
-The oxyacids of sulphur have the central atom as sulfur. Sulphur belongs to the group 16 and so it has 6 valence electrons in its shell. It has vacant d-orbitals and so can show covalency and the maximum valency it can attain is +6. So its maximum oxidation number is +6.
-The given compounds have different numbers of oxygen atoms in them and so they will have different oxidation number values for sulphur also. This decides the bond linkage between the sulphur and the oxygen atom.
-The oxidation states of sulphur in the following given oxyacids are +2.5, +6, +2 and +3 respectively. If the oxidation state of sulphur in an oxyacid is such that it reaches the maximum oxidation state of the central atom, which is sulphur here, then that oxyacid has the linkage as X-O-X where X is the central atom.
-If the oxidation number of the central atom in oxyacid is less than the maximum value of the oxidation number possible for the atom, then the oxyacid has the linkage X-X and if the oxidation number of the central atom in oxyacid is more than the maximum value of the oxidation number possible for the atom, then the oxyacid has the linkage of peroxide which is represented as X-O-O-X.
-Here, only one compound has the oxidation number of +6 which is maximum for sulphur and so it will have the linkage as S-O-S and not the bond between the sulphur atoms. Others will have the bond between the sulphur atoms which will be represented as S-S.
-The structure of all the oxyacids can be shown as
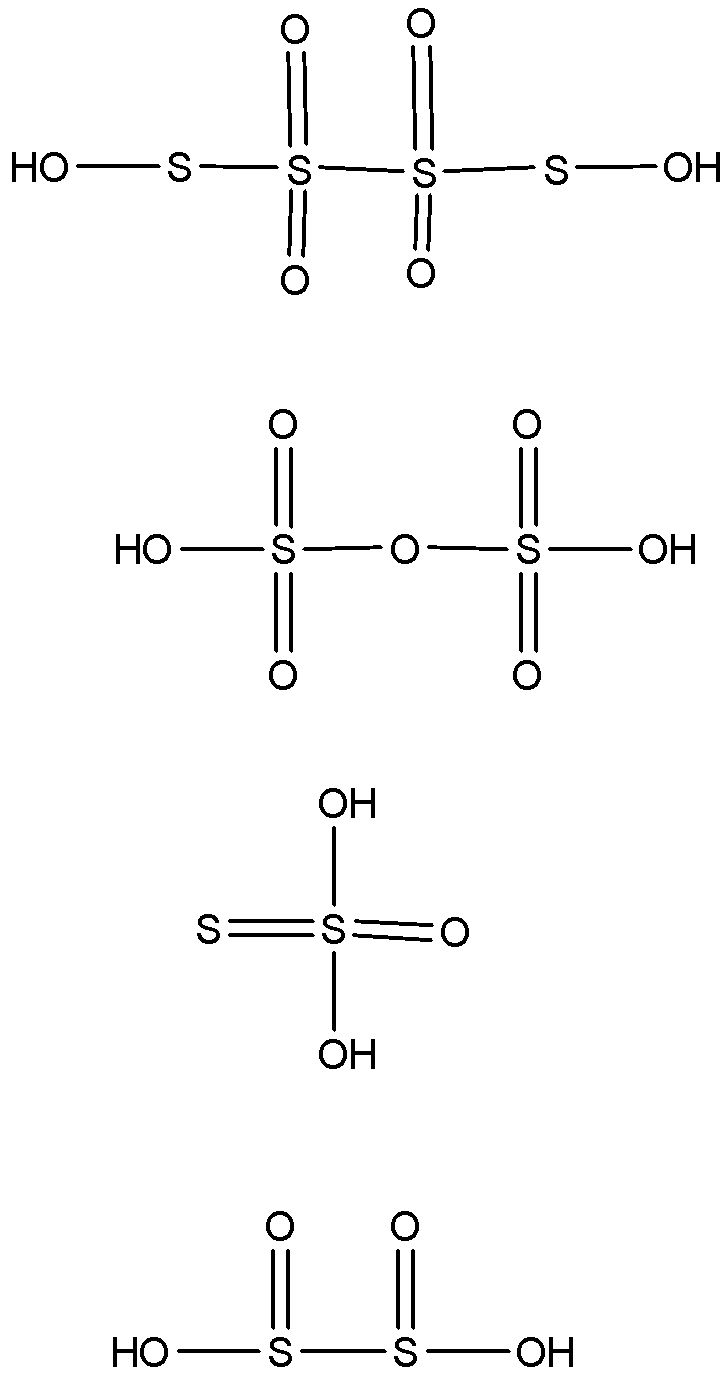
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: There are two oxyacids which do not follow the above mentioned rules. They are ${{I}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}\text{ and }{{\text{H}}_{4}}{{\text{P}}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}$ . There is no X-O-X bond present in the latter oxyacid while this bond is present in the former oxyacid though it does not have the maximum oxidation number of the central atom I.
Complete step by step answer:
-The oxyacids of sulphur have the central atom as sulfur. Sulphur belongs to the group 16 and so it has 6 valence electrons in its shell. It has vacant d-orbitals and so can show covalency and the maximum valency it can attain is +6. So its maximum oxidation number is +6.
-The given compounds have different numbers of oxygen atoms in them and so they will have different oxidation number values for sulphur also. This decides the bond linkage between the sulphur and the oxygen atom.
-The oxidation states of sulphur in the following given oxyacids are +2.5, +6, +2 and +3 respectively. If the oxidation state of sulphur in an oxyacid is such that it reaches the maximum oxidation state of the central atom, which is sulphur here, then that oxyacid has the linkage as X-O-X where X is the central atom.
-If the oxidation number of the central atom in oxyacid is less than the maximum value of the oxidation number possible for the atom, then the oxyacid has the linkage X-X and if the oxidation number of the central atom in oxyacid is more than the maximum value of the oxidation number possible for the atom, then the oxyacid has the linkage of peroxide which is represented as X-O-O-X.
-Here, only one compound has the oxidation number of +6 which is maximum for sulphur and so it will have the linkage as S-O-S and not the bond between the sulphur atoms. Others will have the bond between the sulphur atoms which will be represented as S-S.
-The structure of all the oxyacids can be shown as

So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: There are two oxyacids which do not follow the above mentioned rules. They are ${{I}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}\text{ and }{{\text{H}}_{4}}{{\text{P}}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}$ . There is no X-O-X bond present in the latter oxyacid while this bond is present in the former oxyacid though it does not have the maximum oxidation number of the central atom I.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




